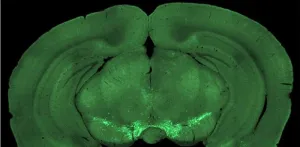
(Press-News.org) Ever wondered how your brain decides when to act? Initiating actions with a specific goal in mind is a complex process. Previous research has identified certain parts of the brain and chemical signals involved. However, it remains unclear what information these signals convey and how they spark initiative.
Recent research reported in Neurophotonics dives into this mystery by investigating how mice time their actions in pursuit of rewards, exploring the role of a specific brain pathway called the mesocortical pathway, in the context of self-initiated movement.
They created a task for mice where they could press a lever at will and receive a reward. The mice would receive a better reward if they waited longer before pressing. The research team found that a certain type of brain signal, mediated by dopamine and its “D2” receptors, plays a crucial role in these self-timed actions. That brain signal kicks into gear just before the mice decide to press a lever but, surprisingly, doesn't fire up when the mice respond to cues.
To understand better why that might be, the team used a novel imaging technique to observe the activity of these brain signals — just before the mice initiated their actions. They discovered a gradual increase in activity in certain parts of the brain about half a second before the self-timed presses. Remarkably, this increase in activity occurred regardless of whether the mice pressed the lever quickly for a small reward or waited for a larger one.
According to senior author Takashi Sato, principal investigator in the Sato Brain Lab at the Medical University of South Carolina, “These findings offer tantalizing clues into the brain's inner workings and contribute to a deeper understanding of how brains control goal-directed behavior.”
The research results raise some interesting questions: How might disruptions in the dopamine-mediated signaling pathway affect an individual's ability to time their actions effectively? Are there parallels between the mechanisms observed in mice and those at play in human decision-making processes? Could manipulating dopamine receptors lead to novel interventions for conditions characterized by impaired impulse control, such as addiction or ADHD?
For details about the research advance, see the original Gold Open Access article by M. Ohtake, K. Abe, M. Hasegawa, T. Itokazu, et al., “Encoding of self-initiated actions in axon terminals of the mesocortical pathway,” Neurophotonics 11(3), 033408 (2024) doi, 10.1117/1.NPh.11.3.033408.
The article appears in the Special Section on Understanding of Neural Circuits with Neurophotonics, edited by Hiroshi Makino, Jennifer Li, Drew Robson, and Spencer LaVere Smith, (in progress) in Neurophotonics Volume 11 Issue 3.
END
Decoding self-initiative: How the brain governs goal-directed actions
Researchers demonstrate how dopamine pathways contribute to complex neural circuits that control goal-directed behavior
2024-06-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Teen Rex’ discovery highlighted in experience and film at the Denver Museum of Nature & Science
2024-06-04
PRESS RELEASE UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL JUNE 4, 2024 at 5 a.m. US EASTERN TIME
CONTACT: Julio Poletti, Public Relations Manager, Julio.poletti@dmns.org, 917.783.6760
DENVER (May 28, 2024) — The Denver Museum of Nature & Science announces the discovery and display of a teenage Tyrannosaurus rex fossil— affectionately named “Teen Rex” — in its temporary experience, "Discovering Teen Rex" opening to the public on June 21, at 1:30 p.m. The fossil was discovered in the badlands of North Dakota by ...
Bloody insights: Organs-on-chip ready to help snake venom research
2024-06-04
May 30, 2024, Leiden, The Netherlands - A 3D model of imitation blood vessels will make it possible to see exactly how snake venom attacks blood vessels, without having to use laboratory animals. This new research model, called an organ-on-a-chip, was developed by a research team from Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, MIMETAS and Naturalis Biodiversity Center.
Roughly one hundred thousand people die annually from the effects of a snake bite and four times as many sustain chronic injuries. Research into how snake venom ...
Some countries could meet their total electricity needs from floating solar panels, research shows
2024-06-04
Floating solar photovoltaic panels could supply all the electricity needs of some countries, new research has shown.
The study, by researchers from Bangor and Lancaster Universities and the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology, aimed to calculate the global potential for deploying low-carbon floating solar arrays. The researchers calculated the daily electrical output for floating photovoltaics (FPV) on nearly 68,000 lakes and reservoirs around the world, using available climate data for each location.
The researchers’ ...
Population shifts, risk factors may triple U.S. cardiovascular disease costs by 2050
2024-06-04
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, June 4, 2024
DALLAS, June 4, 2024 — Driven by an older, more diverse population, along with a significant increase in risk factors including high blood pressure and obesity, total costs related to cardiovascular disease (CVD) conditions are likely to triple by 2050, according to projections from the American Heart Association, observing 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain ...
5-minute test leads to better care for people with dementia in the primary care setting
2024-06-04
June 4, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—The underdiagnosis of dementia, especially among Black and Hispanic patients, is a long-standing challenge in medicine. A new study, published today in Nature Medicine, finds that an easy, five-minute assessment paired with recommendations built into the electronic medical record system led to a three-fold improvement in diagnosis and treatment for patients in a primary care setting compared to a control group. The “5-Cog paradigm,” which was developed by researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System, dramatically enhances ...
Wearable brain imaging gives clearest ever picture of children’s developing brain
2024-06-04
New research has given the clearest ever picture of young children’s developing brains, using a wearable brain scanner to map electrical brain activity. The work opens up new possibilities for tracking how critical developmental milestones, like walking and talking, are underpinned by changing brain function, and how neurodevelopmental conditions like autism emerge.
The research team, led by scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Physics and Astronomy, used a novel design of magnetoencephalography ...
Taking care of caregivers of children with ADHD
2024-06-04
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by elevated levels of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity that can impair academic and social functioning. ADHD is also associated with increased levels of parenting stress, less effective parenting practices, and can disrupt the parent-child relationship. The importance of support for parents of children with ADHD is widely acknowledged in Japan, but specialized parent training programs targeting ADHD have not been available.
However, a new program developed at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) aims to reduce the strain on families ...
Florida infection preventionist successfully advocates for staff growth, keeping pace with hospital’s expanding service lines
2024-06-04
San Antonio, Texas, June 4, 2024 – In an era of hospital budget cuts and staffing freezes, a Florida hospital more than doubled staff positions for infection prevention and control (IPC) over a four-year period, reducing infections and creating opportunities for non-clinical team members to enter the field and excel.
By presenting a business case showing costs of excess healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), infection preventionist (IP) Luz Caicedo, MPH, CPH, CIC, CRCST, VA-BC at AdventHealth in Celebration, Florida was able to increase IPC staff from 2 to 4.8 ...
Surgical site infection rates and other secondary outcomes decrease dramatically at multi-state hospital system through standardized, preoperative, surgical, antibiotic practices
2024-06-04
San Antonio, Texas, June 4, 2024 – Mortality, length of stay, readmissions, and surgical site infections (SSI) all declined after a six-state hospital system implemented a comprehensive surgical site infection (SSI) prevention bundle, according to a report presented today at the 2024 APIC Annual Conference.
Banner Health, which operates facilities in Arizona, California, Colorado, Nebraska, Nevada, and Wyoming, reported on the impact of a surgical antimicrobial prophylaxis (SAP) bundle on more than 57,000 surgical cases from January 2019 to December 2023. Four publicly reportable procedures ...
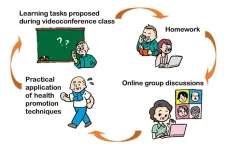
Videoconferencing gets older adults moving as health lessons put to practical use
2024-06-04
The COVID-19 pandemic made videoconferencing software commonplace in businesses and even schools, but this communication tool has the potential to offer benefits beyond the office or classroom. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led research team has been exploring how videoconferencing can improve the health of older adults living in the countryside.
OMU Associate Professor Kazuki Uemura of the Graduate School of Rehabilitation Science and colleagues devised a 12-week health education program conducted using the videoconferencing software Zoom, with the aim of having participants engage in active learning. A control group was provided a similar 12-week ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
Ancient mind-body practice proven to lower blood pressure in clinical trial
SwRI to create advanced Product Lifecycle Management system for the Air Force
Natural selection operates on multiple levels, comprehensive review of scientific studies shows
Developing a national research program on liquid metals for fusion
AI-powered ECG could help guide lifelong heart monitoring for patients with repaired tetralogy of fallot
Global shark bites return to average in 2025, with a smaller proportion in the United States
Millions are unaware of heart risks that don’t start in the heart
What freezing plants in blocks of ice can tell us about the future of Svalbard’s plant communities
[Press-News.org] Decoding self-initiative: How the brain governs goal-directed actionsResearchers demonstrate how dopamine pathways contribute to complex neural circuits that control goal-directed behavior