Videoconferencing gets older adults moving as health lessons put to practical use
Online group discussions, active learning help sustain healthy habits among countryside residents
2024-06-04
(Press-News.org)
The COVID-19 pandemic made videoconferencing software commonplace in businesses and even schools, but this communication tool has the potential to offer benefits beyond the office or classroom. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led research team has been exploring how videoconferencing can improve the health of older adults living in the countryside.
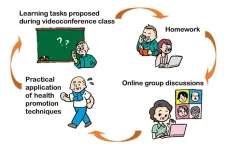
OMU Associate Professor Kazuki Uemura of the Graduate School of Rehabilitation Science and colleagues devised a 12-week health education program conducted using the videoconferencing software Zoom, with the aim of having participants engage in active learning. A control group was provided a similar 12-week program by email, with attached pdf files giving health instructions in a passive learning format.
The researchers assessed the participants before and after the 12 weeks, then performed a follow-up at 36 weeks. Their results showed that compared to the control group the videoconferencing group tended to follow the health advice and showed some improvement in the amount of time spent doing physical activities as opposed to sedentary behavior.
“This study proposes a new health education program that is not dependent on location or distance and takes sustainable behavioral changes into consideration,” Professor Uemura suggested. “In the future, by expanding the implementation scale and conducting further verification, we aim to popularize such health programs that everyone, everywhere can participate in.”
The findings were published in the Journal of Aging and Physical Activity.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-04
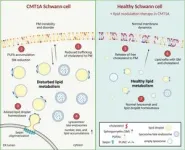
Leuven, 4 June 2024 - Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT), a group of heritable disorders that affect the peripheral nerves, is marked by specific genetic changes. Research by the team of Prof. Ludo Van Den Bosch (VIB-KU Leuven) now reveals the effects of one such genetic cause. They found that the duplication of the gene PMP22 causes problems in the cell membrane of Schwann cells that provide the insulating cover for nerves. The results appeared in the journal Brain.
Gene duplication in CMT1A
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a group of inherited disorders ...
2024-06-04
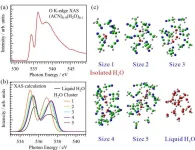
Herein, the O K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) profile of an aqueous acetonitrile solution presented a distinct sharp peak not commonly observed in the corresponding profile of liquid water. Inner-shell calculations coupled with molecular dynamics simulations revealed that this sharp peak originated from isolated water molecules surrounded by acetonitrile molecules, rather than from water clusters. Hence, O K-edge XAS could facilitate the electronic-structural analysis of isolated water molecules, differentiating their contributions ...
2024-06-04
Marmarth, ND – Three keen-eyed young fossil hunters made the discovery of a lifetime when they found the remains of a rare teenage Tyrannosaurus rex that could rewrite history, scientists and filmmakers announce today.
The boys -- brothers Liam and Jessin Fisher, 7 and 10 years old at the time, and their 9-year-old cousin, Kaiden Madsen -- spotted a large fossilized leg bone on a walk in the Hell Creek badlands area of North Dakota on July 31, 2022.
Believing they had found a relatively common duckbill dinosaur, they sent a photo to family friend and Marmarth native Dr. Tyler Lyson, Associate Curator of Vertebrate Palaeontology at the Denver ...
2024-06-04
The ovary is an essential organ for female fertility, and its age-dependent decline in function is a major cause of infertility. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying ovarian aging are still not well understood, particularly in higher vertebrates like primates. In this study, researchers used spatiotemporal transcriptomics to analyze the gene expression patterns in young and aged primate ovaries.
Key findings from the study include:
The study identified significant changes in DNA methylation associated with aging. Principal component analysis revealed a reduction in global ...
2024-06-04
Optical waves propagating through air or multi-mode fiber can be patterned or decomposed using orthogonal spatial modes, with far-ranging applications in imaging, communication, and directed energy. Yet the systems that perform these wavefront manipulations are cumbersome and large, restricting their utilization to high-end applications. The development of a Free-Standing Microscale Photonic Lantern Spatial Mode (De-)Multiplexer using 3D Nanoprinting, as revealed by a recent study, marks a significant advancement in photonic technology. This spatial multiplexer, characterized by its compactness, minimal footprint, and ability to directly print ...
2024-06-04
A comprehensive new study by Tulane University’s Newcomb Institute and the University of California San Diego School of Global Policy and Strategy has quantified the staggering economic impact of intimate partner violence in California, revealing billions in costs that deeply affect survivors, communities and taxpayers across the state.
The report, “The Costs of Intimate Partner Violence in California,” reveals a cost of $73.7 billion to the state in health care, lost productivity and income and criminal justice ...
2024-06-04
An international research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has uncovered in a recent research project that people’s beliefs in science and religion are primarily shaped by the words of others, rather than their personal experiences. The study could help enhance public understanding of people’s belief formation in important scientific issues, such as climate change and vaccination.
Conventionally, people are generally more confident about the existence of scientific phenomena, like oxygen, than religious phenomena, like God, as it is thought that people can experience oxygen, for instance, while it is harder to observe ...
2024-06-04
Researchers have discovered sustained hunting by humans prevented the woolly rhinoceros from accessing favourable habitats as Earth warmed following the Last Ice Age.
An international team of researchers, led by scientists from the University of Adelaide and University of Copenhagen, used computer modelling to make the discovery, shedding light on an aeons-old mystery.
“Using computer models, fossils and ancient DNA, we traced 52,000 years of population history of the woolly rhinoceros across Eurasia at a resolution not previously considered possible,” said lead author Associate ...
2024-06-04
Australians are no strangers to long, hot summers, but new Griffith University research has looked at the impact of hot weather on patients with pre-existing chronic diseases and how it increases their risk of being hospitalised.
The research, recently published in eBioMedicine, found the risk of hospitalisation increased with the number of pre-existing chronic diseases during hot weather.
Individuals over the age of 65 with multimorbidity, defined as having two or more chronic diseases, were most at risk during hot weather.
Dr Zhiwei Xu from Griffith’s School ...
2024-06-04
It’s often said we can’t control the weather. But what if the weather controls how and when we invest our money? More specifically, what if the skies control how much we’re willing to gamble in the stock market?
New research by the University of South Australia has found a connection between pleasant weather conditions and higher investment in lottery-like stocks.
Lottery-like stocks are cheap compared to other stocks and, like lottery tickets, they can be seen as an opportunity to make a substantial gain. However, the chance of a higher return is minimal, and it’s therefore considered a high-risk investment. A study by UniSA finance researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Videoconferencing gets older adults moving as health lessons put to practical use
Online group discussions, active learning help sustain healthy habits among countryside residents