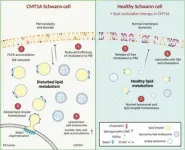
(Press-News.org) Leuven, 4 June 2024 - Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT), a group of heritable disorders that affect the peripheral nerves, is marked by specific genetic changes. Research by the team of Prof. Ludo Van Den Bosch (VIB-KU Leuven) now reveals the effects of one such genetic cause. They found that the duplication of the gene PMP22 causes problems in the cell membrane of Schwann cells that provide the insulating cover for nerves. The results appeared in the journal Brain.
Gene duplication in CMT1A
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a group of inherited disorders that affect the peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness and sensory loss in the extremities. Among the various subtypes of CMT, CMT1A is the most common form, characterized by a duplication of the PMP22 gene. Despite being a well-known genetic abnormality associated with CMT1A, the precise mechanisms by which PMP22 duplication contributes to the disease have remained elusive until now.
The PMP22 gene codes for ‘peripheral myelin protein 22’, a protein that is part of the myelin sheath – the protective cover – of peripheral nerves. That myelin sheath degrades in CMT1A. Because the PMP22 protein is produced by Schwann cells, that's where the lab of Prof. Ludo Van Den Bosch (VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain & Disease Research) focused their attention. By investigating human cell cultures and animal models of CMT with the PMP22 duplication, the researchers could assess the impact of PMP22 duplication on developing Schwann cells.
Lipids and membranes
Starting from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) differentiated into human Schwann cells and using advanced imaging techniques and molecular analyses, the researchers were able to elucidate the intricate pathways through which PMP22 duplication dysregulates lipid metabolism and disrupts the normal functioning of Schwann cells.
Dr. Robert Prior, co-first author of the study (previously VIB-KU Leuven, now UKB Bonn, Germany): "One of our key findings was the identification of dysregulated lipids in the plasma membrane of developing human Schwann cells carrying the PMP22 duplication. This impairs the structural integrity and bending properties of the plasma membrane, compromising the ability of the Schwann cells to ‘wrap’ around the peripheral nerves, producing a lipid-rich cover called myelin. This myelin sheath electrically insulates the nerves and Schwann cells also provide metabolic support. The dysregulation of lipids in the plasma membrane finally allows us to understand why the communication between CMT1A patient Schwann cells and peripheral nerves breaks down, even before the onset of myelination."
Moreover, the researchers discovered that targeting the dysregulated lipid pathways in Schwann cells could potentially reverse some of the detrimental effects of the PMP22 duplication. By modulating lipid metabolism and restoring plasma membrane organization, novel therapeutic strategies could be developed to alleviate the symptoms of CMT1A and to improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Prof. Ludo Van Den Bosch: "Using patient-derived cells, our work provides a foundation for the development of targeted therapies that address the underlying molecular defects in CMT1A. By understanding how PMP22 duplication disrupts lipid homeostasis, we can now explore innovative approaches to restore cellular function and potentially halt the progression of this devastating disease."
As researchers continue to explore the complexities of genetic disorders like CMT1A, new opportunities emerge for the development of therapies that target the root causes of disease. In this case, the effect of a gene duplication on developing Schwann cells points the way ahead to future therapeutic interventions.
Publication
PMP22 duplication dysregulates lipid homeostasis and plasma membrane organization in developing human Schwann cells. Prior, Silva, Vangansewinkel, et al. Brain, 2024. DOI: 10.1093/brain/awae158
Funding
The research (team) was supported by VIB, KU Leuven, VLIR (iBOF23), ABMM, the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA), the Association Française les Myopathies (AFM), the ALS Liga Belgium, the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), the Generet Award for Rare Diseases, and the Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds.
Collaborations
Progress in research is only possible through collaborations both at the national and international level. This research was a close collaboration between the laboratories of Prof. Ludo Van Den Bosch and Prof. Esther Wolfs (UHasselt). For the lipidomic analysis, the expertise of the laboratory of Prof. Johan Swinnen (KU Leuven) was pivotal. In addition, there was an international collaboration with the laboratory of Prof. Kees Fluiter and Prof. Frank Baas (Leiden University Medical Center, The Netherlands). Researchers working in Belgium, The Netherlands, Germany, the Czech Republic, and Australia were involved in this project.
END
The importance of a disturbed lipid metabolism in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
2024-06-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
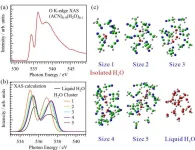
Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy analysis of isolated water molecules within aqueous acetonitrile solutions
2024-06-04
Herein, the O K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) profile of an aqueous acetonitrile solution presented a distinct sharp peak not commonly observed in the corresponding profile of liquid water. Inner-shell calculations coupled with molecular dynamics simulations revealed that this sharp peak originated from isolated water molecules surrounded by acetonitrile molecules, rather than from water clusters. Hence, O K-edge XAS could facilitate the electronic-structural analysis of isolated water molecules, differentiating their contributions ...
US pre-teens discover rare juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex; Science expedition chronicled in extraordinary documentary
2024-06-04
Marmarth, ND – Three keen-eyed young fossil hunters made the discovery of a lifetime when they found the remains of a rare teenage Tyrannosaurus rex that could rewrite history, scientists and filmmakers announce today.
The boys -- brothers Liam and Jessin Fisher, 7 and 10 years old at the time, and their 9-year-old cousin, Kaiden Madsen -- spotted a large fossilized leg bone on a walk in the Hell Creek badlands area of North Dakota on July 31, 2022.
Believing they had found a relatively common duckbill dinosaur, they sent a photo to family friend and Marmarth native Dr. Tyler Lyson, Associate Curator of Vertebrate Palaeontology at the Denver ...
DNA methylation clocks for estimating biological age in Chinese cohorts
2024-06-04
The ovary is an essential organ for female fertility, and its age-dependent decline in function is a major cause of infertility. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying ovarian aging are still not well understood, particularly in higher vertebrates like primates. In this study, researchers used spatiotemporal transcriptomics to analyze the gene expression patterns in young and aged primate ovaries.
Key findings from the study include:
The study identified significant changes in DNA methylation associated with aging. Principal component analysis revealed a reduction in global ...
New 3D-printed microscale photonic lantern open opportunities for spatial mode multiplexing
2024-06-04
Optical waves propagating through air or multi-mode fiber can be patterned or decomposed using orthogonal spatial modes, with far-ranging applications in imaging, communication, and directed energy. Yet the systems that perform these wavefront manipulations are cumbersome and large, restricting their utilization to high-end applications. The development of a Free-Standing Microscale Photonic Lantern Spatial Mode (De-)Multiplexer using 3D Nanoprinting, as revealed by a recent study, marks a significant advancement in photonic technology. This spatial multiplexer, characterized by its compactness, minimal footprint, and ability to directly print ...
Study reveals billion-dollar toll of domestic violence in California
2024-06-04
A comprehensive new study by Tulane University’s Newcomb Institute and the University of California San Diego School of Global Policy and Strategy has quantified the staggering economic impact of intimate partner violence in California, revealing billions in costs that deeply affect survivors, communities and taxpayers across the state.
The report, “The Costs of Intimate Partner Violence in California,” reveals a cost of $73.7 billion to the state in health care, lost productivity and income and criminal justice ...
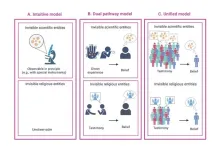
Others’ words, not firsthand experience, shape scientific and religious belief formation, HKUST study finds
2024-06-04
An international research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has uncovered in a recent research project that people’s beliefs in science and religion are primarily shaped by the words of others, rather than their personal experiences. The study could help enhance public understanding of people’s belief formation in important scientific issues, such as climate change and vaccination.
Conventionally, people are generally more confident about the existence of scientific phenomena, like oxygen, than religious phenomena, like God, as it is thought that people can experience oxygen, for instance, while it is harder to observe ...
Human activity contributed to woolly rhinoceros’ extinction
2024-06-04
Researchers have discovered sustained hunting by humans prevented the woolly rhinoceros from accessing favourable habitats as Earth warmed following the Last Ice Age.
An international team of researchers, led by scientists from the University of Adelaide and University of Copenhagen, used computer modelling to make the discovery, shedding light on an aeons-old mystery.
“Using computer models, fossils and ancient DNA, we traced 52,000 years of population history of the woolly rhinoceros across Eurasia at a resolution not previously considered possible,” said lead author Associate ...
Hot weather increases risk of emergency hospitalisations for patients with multimorbidity
2024-06-04
Australians are no strangers to long, hot summers, but new Griffith University research has looked at the impact of hot weather on patients with pre-existing chronic diseases and how it increases their risk of being hospitalised.
The research, recently published in eBioMedicine, found the risk of hospitalisation increased with the number of pre-existing chronic diseases during hot weather.
Individuals over the age of 65 with multimorbidity, defined as having two or more chronic diseases, were most at risk during hot weather.
Dr Zhiwei Xu from Griffith’s School ...
Sunshine spurs spending: Investors bet big on sunny days
2024-06-04
It’s often said we can’t control the weather. But what if the weather controls how and when we invest our money? More specifically, what if the skies control how much we’re willing to gamble in the stock market?
New research by the University of South Australia has found a connection between pleasant weather conditions and higher investment in lottery-like stocks.
Lottery-like stocks are cheap compared to other stocks and, like lottery tickets, they can be seen as an opportunity to make a substantial gain. However, the chance of a higher return is minimal, and it’s therefore considered a high-risk investment. A study by UniSA finance researchers ...
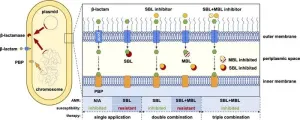
Novel triple antibiotic combination offers breakthrough in combatting antibiotic resistance
2024-06-04
In the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance, a new study published in Engineering by Zhuoren Ling’s research team unveils a promising triple combination of antibiotics that significantly expands our arsenal against drug-resistant bacteria. Titled “The Triple Combination of Meropenem, Avibactam, and a Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitor Optimizes Antibacterial Coverage Against Different β-Lactamase Producers,” the research sheds light on a novel approach to tackle one of the most pressing global ...