(Press-News.org) A new study offers first-time insights into three emerging climate innovations to safeguard or increase the carbon naturally captured by ocean and coastal ecosystems: rapid interventions to save the Great Barrier Reef, satellite-tracked kelp beds in the deep ocean, and seagrass nurseries in the United Kingdom. The research, published in Environmental Science & Policy and co-authored by leading climate scholars at Boston University, Aarhus University, and the University of Sussex Business School, advances knowledge of understudied interventions in marine habitat protection to manage greenhouse gas emissions.
These climate change interventions, known as blue carbon, preserve or enhance marine and coastal ecosystems as valuable sources of carbon removal and storage. Currently, more than half of the world’s biological carbon is captured and stored by marine living organisms, which are threatened by acidification, temperature change, severe storms, and pollution. Previous studies have shown that improved management of these habitats could potentially arrest up to 10% of global emissions reductions needed to meet Paris Agreement targets.
Expanding knowledge of potential solutions
While blue carbon solutions could reduce emissions, generate revenue, and advance conservation policy, questions remain around their efficacy and potential effects on sociopolitical systems.
“Compared to the robust history of studying soil and forest systems for carbon management, harnessing marine ecosystems in the fight against climate change is relatively new and remains unproven,” said Benjamin Sovacool, the study’s lead author and director of the Boston University Institute for Global Sustainability, who is also affiliated with Aarhus University and the University of Sussex Business School. “As these emerging technologies are more widely deployed, it is essential that we develop a comprehensive understanding of their ties to cultural, political, and economic systems.”
Understanding each innovation
Drawing on 46 expert interviews, 38 site visits, and extensive document analysis, Sovacool and co-authors Chad M. Baum, Sean Low, and Livia Fritz of Aarhus University evaluated the social narratives, technology, and co-impacts of coral reef preservation in Australia, seagrass restoration in the United Kingdom, and seaweed cultivation and deep ocean storage in the United States.
Coral reef preservation in Australia supports blue carbon as coral tissues consume and capture carbon dioxide and bicarbonate. Through interviews with 23 local experts, the research team identified a narrative of crisis and collapse around saving the Great Barrier Reef as a national treasure. The narrative is also steeped in hope and moral urgency, motivating a willingness to explore a diversity of experimental and controversial new technologies — from genetic editing to cloud brightening. Positive co-impacts of reef preservation include more eco-tourism and better fisheries, while negative co-impacts include the potential for invasive species outbreaks.
Seagrass restoration captures carbon by directly growing biomass and trapping organic particles in the roots and sediments of seagrass meadows. The research team visited restoration efforts in the United Kingdom and conducted 12 interviews with seagrass experts from several universities, organizations, and the charity Project Seagrass. They discovered that narratives around restoration emphasize how unique, fragile, and distinct seagrass is, as well as its potential as an efficient and durable carbon store. Innovation in seagrass restoration requires broad, incremental advancements in knowledge around foundational marine science, botany, and data collection, which may make it relatively costlier and slower to implement. Potential benefits include improving water quality and cleanliness, promoting biodiversity and healthy fisheries, reversing acidification, and preventing coastal erosion.
Seaweed cultivation reduces carbon by increasing biomass through growing massive kelp beds in the deep ocean. Following 11 interviews, most of them with employees at a United States-based startup, the researchers identified a narrative of advancing technological innovation and generating profit grounded in a duty to save the world’s oceans. Innovation is deliberatively non-participatory, driven by a small group seeking to rapidly and massively scale operations. Seaweed cultivation could increase food production, water quality, and waste treatment, but faces a lack of social acceptance and may lead to uncontrolled growth.
Narratives, innovation styles, and co-impacts, plus contextual factors such as place, time, and cultural values, contribute to a given blue technology’s likelihood for success, the researchers conclude. The results of this study offer a glimpse into the future of blue carbon innovations, which the authors anticipate will be an increasingly relevant and popular area of scientific policy and discovery.
END
Exploring three frontiers in marine biomass and blue carbon capture
2024-06-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Microscope system sharpens scientists’ view of neural circuit connections
2024-06-04
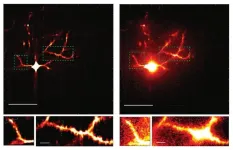
The brain’s ability to learn comes from “plasticity,” in which neurons constantly edit and remodel the tiny connections called synapses that they make with other neurons to form circuits. To study plasticity, neuroscientists seek to track it at high resolution across whole cells, but plasticity doesn’t wait for slow microscopes to keep pace and brain tissue is notorious for scattering light and making images fuzzy. In a paper in Scientific Reports, a collaboration of MIT engineers and neuroscientists describes a new microscopy system designed for fast, clear, and frequent imaging of the living brain.
The system, ...
VHIO researchers demonstrate the utility of high-sensitivity liquid biopsy to predict and monitor response to immunotherapy
2024-06-04
The liquid biopsy technique applied in this work is based on the sequencing of the entire tumor genome from 138 patients and the monitoring of mutations in the blood. This approach achieves high sensitivity in detecting the tumor signal in the blood (1/1,000,000 DNA molecules), and the patterns found reflect how patients respond to immunotherapy.
This study is part of the Comprehensive Program of Cancer Immunotherapy and Immunology (CAIMI) at VHIO, funded by the BBVA Foundation, and is co-led by Dr Rodrigo Toledo, head of the Biomarkers and Clonal Dynamics Group at the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO), ...
Muscle disorder caused by key protein mutations uncovered in new study
2024-06-04
A recent study has found that the SMCHD1 protein plays a key role in controlling how genes are processed, which affects the progression of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD). This discovery about SMCHD1's function in gene regulation is important because it opens new possibilities for developing targeted therapeutic strategies to combat the disease. By understanding more about how SMCHD1 works, scientists can explore new ways to fight the disease.
A recent study by MD-PhD student Eden Engal under the guidance of Dr. Yotam Drier and ...
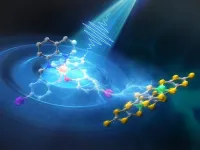
Observing ultrafast photoinduced dynamics in a halogen-bonded supramolecular system
2024-06-04
Researchers uncover how the halogen bond can be exploited to direct sequential dynamics in the multi-functional crystals, offering crucial insights for developing ultrafast-response times for multilevel optical storage.
Halogen bonds are intermolecular interactions that arise from the attraction between a halogen atom (group 17 elements in the periodic table) and another atom with lone pairs, more generally a molecular entity with high electron density. Understanding the distinctive and highly directional nature of halogen bonds is crucial for crystal engineering and studying ...
USPSTF recommendation statement on interventions to prevent falls in community-dwelling older adults
2024-06-04
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends exercise interventions to prevent falls in community-dwelling adults 65 years or older who are at increased risk for falls. The USPSTF recommends that clinicians individualize the decision to offer multifactorial interventions to prevent falls to community-dwelling adults 65 years or older who are at increased risk for falls. Existing evidence indicates that the overall net benefit of routinely offering multifactorial interventions to prevent falls is small. When determining ...
ASCO: Proton therapy demonstrates advantages in Phase III head and neck cancer trial
2024-06-04
ABSTRACT 6006
CHICAGO ― According to preliminary data from a multi-institution Phase III trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, intensity modulated proton therapy (IMPT) achieved similar clinical outcomes and offered significant patient benefits when compared to traditional intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) as part of chemoradiation treatment for patients with oropharyngeal (head and neck) cancer.
The results were presented today at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting by Steven Frank, M.D., professor of Radiation Oncology and executive director of the Particle ...
Mapping lava flows with groundbreaking field instrument
2024-06-04
WASHINGTON, June 4, 2024 – Millions of people live near active volcanoes that are constantly monitored for signs of an impending eruption. When one occurs, scientists and governments rely on data to estimate the extent of the possible damage, informing evacuation plans and disaster response efforts. The nature of eruptions, unfortunately, means collecting data about them can sometimes be as challenging as organizing a response.
In Review of Scientific Instruments, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University at Buffalo developed a tool for measuring the viscosity of lava that could increase our understanding of molten rock as well as better improve ...
Access to prostate-specific antigen testing and mortality among men with prostate cancer
2024-06-04
About The Study: This population-based cohort study of men with prostate cancer suggests that higher county-level prevalence of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening was associated with lower odds of advanced disease, all-cause mortality, and prostate cancer–specific mortality. Associations varied by age, race and ethnicity, and U.S. Census region.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hari S. Iyer, Sc.D., M.P.H., email hari.iyer@rutgers.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Service dogs for veterans and military members with posttraumatic stress disorder
2024-06-04
About The Study: This nonrandomized controlled trial found that compared with usual care alone, partnership with a trained psychiatric service dog was associated with lower posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptom severity and higher psychosocial functioning in veterans. Psychiatric service dogs may be an effective complementary intervention for military service–related PTSD.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Marguerite E. O’Haire, Ph.D., email maggieohaire@arizona.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14686)
Editor’s ...
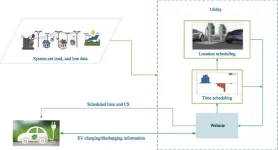
Revolutionizing urban energy: how advanced EV charging schedules enhance grid efficiency
2024-06-04
In response to the escalating demand for sustainable transportation solutions, researchers from the National Institute of Technology Silchar have developed a groundbreaking scheduling system for electric vehicles (EVs) that enhances power grid efficiency and accommodates the growing influx of solar energy. This advanced system, outlined in a recent study by Pritam Das and Partha Kayal, focuses on optimizing the charging and discharging times of EVs to better integrate with photovoltaic (PV) energy ...