People underestimate the probability of including at least one minority member in a group
2024-06-05
(Press-News.org)
Niigata, Japan - Human society includes various minority groups. However, it is often difficult to know whether someone is a minority member simply by looking at the person, as minority traits may not be visually apparent (e.g., sexual orientation, color vision deficiency). In addition, minorities may hide their minority traits or identities. Consequently, we may have been unaware of the presence of minorities in daily life. Probabilistic thinking is critical in such uncertain situations. The people with whom we interact in our daily lives are typically a group of several dozen individuals (e.g., a school class). How do we judge the probability of including at least one minority member in such groups? For example, how does a school teacher estimate the probability of having a minority in the class? Cognitive psychology states that humans often make unrealistic judgments about probabilities, such as risk. So, do we also misperceive the probability of minority inclusion in a group or can we accurately assess the probability through heuristics or knowledge?
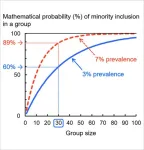
Associate Professor Niimi of Niigata University demonstrated that people unrealistically underestimate such probabilities. First, we examine how the probabilities are computed mathematically. If the prevalence of the minority in question is 0.03 (3%) and the group size is 30, the probability of including one or more minority members in the group is one minus the probability that all 30 members are NOT the minority. Because the probability that one person is not a minority is 0.97, the probability of minority inclusion is given by 1 – (0.97)30 (if there is no other information). The computer tells us that the result is 0.60 (60%). When the minority prevalence is 7%, it increases to 89%. These mathematical probabilities appear to be higher than those of naïve intuition.
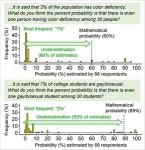
Indeed, most respondents estimated probabilities far below the mathematical probabilities. The second image shows examples of the questions and results. Approximately 90% of the respondents estimated below-mathematical probabilities, and the majority of the estimates were lower than 10%. This underestimation was repeatedly observed under a variety of conditions (online worker and student samples, revised wording, etc.).
Why are the probabilities of minority inclusion underestimated? Is this a result of prejudice or stereotyping against minorities? The answer was “No.” The same underestimation occurred even when minorities unlikely to be associated with negative stereotypes were used (e.g., people with absolute pitch and fictional minorities). Of course, the mathematical calculations cannot be performed mentally. No wonder the respondents’ estimates were inaccurate. The problem was why the estimates were not random, but strongly biased toward underestimation. Even if one does not know how to calculate it, one may have learned from daily experience that the probability of inclusion is much higher than the prevalence (e.g., the probability of including a woman in a group of randomly selected 100 individuals should be greater than 50%). However, the present results suggest that most people are unfamiliar with the concept of probability of inclusion and do not know how to think about it. Further analysis revealed that the major source of underestimation was the use of heuristics, such as ignoring group size and reporting prevalence, or calculating the expected value of the number of minorities. Although most heuristics were erroneous, some yielded relatively reasonable estimates (e.g., assuming a high probability if the expected value exceeded one).
Underestimating the probability of minority inclusion may lead to the misconception that minorities are irrelevant in our daily lives. However, there was one promising finding in the present study. When the respondents were given the mathematical probability of minority inclusion, their attitudes changed in favor of inclusive views about minorities compared to conditions in which mathematical probability was not given. Knowledge may compensate for cognitive bias.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-05
DALLAS, June 4, 2024 — According to the American Heart Association, when someone suffers a cardiac arrest, immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is critical and can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. More than 350,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur in the United States each year. Of those, 90% will not survive, according to the Association, which is working to turn more bystanders into lifesavers who can use CPR in an emergency. The American Heart Association, celebrating one hundred years of lifesaving service as a global ...
2024-06-05
FORT COLLINS, Colo., June 4, 2024 — Dr. Erin Belval, a research forester at the USDA Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Station, was awarded the Early Career Scientist Award in Fire Science from the International Association of Wildland Fire (IAWF). She received the honor last month at the 2024 International Wildland Fire Conference in Boise, Idaho.
The award recognizes promising early-career professionals who demonstrate outstanding ability in any field of wildland fire science. Belval was nominated by colleagues and peers for her outstanding contributions.
“The award is particularly meaningful because ...
2024-06-05
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Thirty by thirty. It’s an ambitious answer to growing calls for protecting more of our planet’s surface. The goal is to conserve 30% of the Earth’s oceans, lands and freshwaters by 2030. While this may seem a lofty aim, the diversity and coverage of conservation areas today might be greater than what’s currently recognized by global tracking systems.
An international team of conservation researchers and practitioners, led by scientists at UC Santa Barbara and The Nature Conservancy, has developed an inclusive inventory approach for tracking ...
2024-06-05
SUMMARY
Researchers have identified a significant change in composition and abundance of bacteria in study participants’ oral microbiomes after using a popular brand of alcohol-based mouthwash.
The oral microbiome is the community of bacteria that live in the mouth, they help us digest our food and keep our mouth healthy.
Researchers found that two species of opportunistic bacteria were significantly more abundant in the mouth after daily use of the alcohol-based mouthwash, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus anginosus. ...
2024-06-05
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – While cervical spine injuries (CSI) are uncommon in children, they can be potentially devastating, resulting in quadriplegia – paralysis below the neck affecting both arms and both legs. Detecting CSIs in a clinical setting often requires imaging such as X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, both of which expose children to radiation, which can cause other health issues over time.
In a study published today in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, researchers in the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) – led by Julie Leonard, MD, MPH at Nationwide Children’s Hospital –created a highly accurate ...
2024-06-05
University of Leeds press release
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00.01 UK BST, 5 JUNE 2024 (19.01 US ET, 4 JUNE 2024)
The second annual Indicators of Global Climate Change report, which is led by the University of Leeds, reveals that human-induced warming has risen to 1.19 °C over the past decade (2014-2023) – an increase from the 1.14 °C seen in 2013-2022 (set out in last year’s report).
Looking at 2023 in isolation, warming caused by human activity reached 1.3 °C. This ...
2024-06-05
Housing associations are being urged to step out of their traditional role to deliver change in deprived areas and help people into work or entrepreneurship.
The call comes in a whitepaper published today by the University of East Anglia (UEA), written in response to how the UK levelling up policy agenda has so far failed to deliver results for constituents in the communities it is designed to help.
It follows a £10.8M Increase Valorisation Sociale (INCREASE VS) project, which showed how housing associations can go ...
2024-06-05
Participants reacted quicker and made fewer errors during menstruation, despite believing their performance would be worse, according to new research from UCL and the Institute of Sport, Exercise & Health (ISEH).
The study, published in Neuropsychologia, is the first to assess sport-related cognition during the menstrual cycle and is part of a larger research project supported by the FIFA Research Scholarship.
The findings act as a proof-of-principle that specific types of cognition fluctuate throughout the ...
2024-06-05
Large Language Models behind popular generative AI platforms like ChatGPT gave different answers when asked to respond to the same reasoning test and didn’t improve when given additional context, finds a new study from researchers at UCL.
The study, published in Royal Society Open Science, tested the most advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) using cognitive psychology tests to gauge their capacity for reasoning. The results highlight the importance of understanding how these AIs ‘think’ before entrusting them with tasks, particularly those involving decision-making.
In recent years, the LLMs ...
2024-06-04
June 4, 2024
UMass Amherst to Join $90M US National Science Foundation large-scale research infrastructure for education
Platform brings together institutions, digital learning and a world-class team to enable research studies to inform efficacy, improvement and innovation in teaching and learning
AMHERST, Mass. – The Manning College of Information and Computer Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has joined the newly announced U.S. National Science Foundation’s (NSF) SafeInsights, a five-year, $90 million research and development infrastructure for inclusive education ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] People underestimate the probability of including at least one minority member in a group



