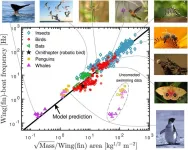
(Press-News.org) A single universal equation can closely approximate the frequency of wingbeats and fin strokes made by birds, insects, bats and whales, despite their different body sizes and wing shapes, Jens Højgaard Jensen and colleagues from Roskilde University in Denmark report in a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, publishing June 5.
The ability to fly has evolved independently in many different animal groups. To minimize the energy required to fly, biologists expect that the frequency that animals flap their wings should be determined by the natural resonance frequency of the wing. However, finding a universal mathematical description of flapping flight has proved difficult. Researchers used dimensional analysis to calculate an equation that describes the frequency of wingbeats of flying birds, insects and bats, and the fin strokes of diving animals, including penguins and whales.
They found that flying and diving animals beat their wings or fins at a frequency that is proportional to the square root of their body mass, divided by their wing area. They tested the accuracy of the equation by plotting its predictions against published data on wingbeat frequencies for bees, moths, dragonflies, beetles, mosquitos, bats, and birds ranging in size from hummingbirds to swans.
The researchers also compared the equation’s predictions against published data on fin stroke frequencies for penguins and several species of whale, including humpbacks and northern bottlenose whales. The relationship between body mass, wing area and wingbeat frequency shows little variation across flying and diving animals, despite huge differences in their body size, wing shape and evolutionary history, they found. Finally, they estimated that an extinct pterosaur (Quetzalcoatlus northropi) — the largest known flying animal — beat its 10 meter-square wings at a frequency of 0.7 hertz.
The study shows that despite huge physical differences, animals as distinct as butterflies and bats have evolved a relatively constant relationship between body mass, wing area and wingbeat frequency. The researchers note that for swimming animals they didn’t find publications with all the required information; data from different publications was pieced together to make comparisons, and in some cases animal density was estimated based on other information. Furthermore, extremely small animals — smaller than any yet discovered — would likely not fit the equation, because the physics of fluid dynamics changes at such a small scale. This could have implications in the future for flying nanobots. The authors say that the equation is the simplest mathematical explanation that accurately describes wingbeats and fin strokes across the animal kingdom.
The authors add: “Differing almost a factor 10000 in wing/fin-beat frequency, data for 414 animals from the blue whale to mosquitoes fall on the same line. As physicists, we were surprised to see how well our simple prediction of the wing-beat formula works for such a diverse collection of animals.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0303834
Citation: Jensen JH, Dyre JC, Hecksher T (2024) Universal wing- and fin-beat frequency scaling. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0303834. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303834
Author Countries: Denmark
Funding: The work was supported by the VILLUM Foundation’s Matter grant VIL16515. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Flapping frequency of birds, insects, bats and whales described by universal equation
The wing and fin beats of flying and diving animals can be predicted using just body mass and wing area
2024-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pro-inflammatory diets are associated with higher levels of the heart failure biomarker NT-proBNP, with potential implications for cardiovascular risk, per study of more than 10,000 US adults
2024-06-05
Pro-inflammatory diets are associated with higher levels of the heart failure biomarker NT-proBNP, with potential implications for cardiovascular risk, per study of more than 10,000 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304289
Article Title: Association between dietary inflammatory index and NT-proBNP levels in US adults: A cross-sectional analysis
Author Countries: China
Funding: The study was funded by the Yan'an Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant No. 2022SLSFGG-025).The funders ...
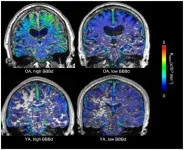
Normal ageing might be associated with increased blood-brain barrier permeability in regions also vulnerable in Alzheimer's Disease, in small study comparing healthy brains of the young and old
2024-06-05
Normal ageing might be associated with increased blood-brain barrier permeability in regions also vulnerable in Alzheimer's Disease, in small study comparing healthy brains of the young and old
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299764
Article Title: Associations between regional blood-brain barrier permeability, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in cognitively normal older adults
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported ...
Evidence-based design or Feng Shui in hospital rooms might benefit patients
2024-06-05
In an online study, virtual hospital rooms designed according to the principles of evidence-based design or the principles of Feng Shui were associated with greater potential benefit for viewers than virtual representations of standard hospital rooms. Emma Zijlstra of Hanze University of Applied Sciences in the Netherlands and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 5.
Hospital designers might consider employing specific design principles in an effort to improve patients’ experiences. Growing evidence suggests ...
US Islamist extremist co-offenders form close-knit groups driven by mutual contacts, homophily effects
2024-06-05
The formation of relationships within violent US Islamist extremist groups is highly driven by mutual contacts and the tendency for people to bond with others similar to themselves, according to new research. Anina Schwarzenbach, formally of Harvard University and the University of Maryland (currently affiliated with the University of Bern) and Michael Jensen of the University of Maryland present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 5, 2024.
Prior research on social structures within extremist networks have primarily ...
Simple headlines attract more online news readers
2024-06-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Online news consumers tend to click on simpler headlines that use more common words and more readable writing, a new study finds.
Researchers evaluated more than 30,000 real-world field experiments from the Washington Post and the online news site Upworthy to see how readers reacted to headlines of varying complexity.
In addition, a follow-up experiment showed that average readers paid more attention to simpler headlines and processed them more deeply – unlike journalists, who paid just as much attention to complex headlines.
The results show ...
Researchers unveil pioneering approach to combat age-related vision loss
2024-06-05
June 5, 2024 (Cambridge, MA) - Cirrus Therapeutics, the University of Bristol, and London’s Global University Institute of Ophthalmology have discovered a revolutionary treatment for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the leading cause of vision loss among older adults.
Featured on the cover of the journal Science Translational Medicine, this breakthrough research reveals that boosting a specific protein, IRAK-M, in retinal cells could offer a new and highly effective therapy for AMD.
AMD ...
MSU research: What makes a good headline?
2024-06-05
EAST LANSING, Mich. – The competition for online attention in today’s news environment is fierce. High-quality news from credible sources must compete for attention with misinformation and a rapidly increasing amount of partisan content.
How can a news organization stand out as a reputable and trustworthy outlet while driving readers to its site?
The answer is simple: literally.
According to research from Michigan State University, news readers engage more with simple writing, suggesting journalists ...
Scientists identify ‘missing piece’ required for blood stem cell self-renewal
2024-06-05
UCLA scientists have identified a protein that plays a critical role in regulating human blood stem cell self-renewal by helping them sense and interpret signals from their environment.
The study, published in Nature, brings researchers one step closer to developing methods to expand blood stem cells in a lab dish, which could make life-saving transplants of these cells more available and increase the safety of blood stem cell-based treatments, such as gene therapies.
Blood stem cells, also known as hematopoietic stem cells, have the ability to make copies of themselves via a process called ...
Father's diet before conception influences children's health
2024-06-05
Dr. Raffaele Teperino, head of the "Environmental Epigenetics" research group at Helmholtz Munich, along with his research team, has examined the impact of paternal diet on children's health – specifically, the influence of diet before conception. The researchers focused on special small RNA molecules in sperm, known as mitochondrial tRNA fragments (mt-tsRNAs, see background). These RNAs play a key role in the inheritance of health traits by regulating gene expression.
For their study, the researchers used data from the LIFE Child cohort, which includes information from over 3,000 families. The analyses showed ...
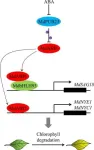
Fountain of youth for plants: E3 ligase's role in leaf longevity
2024-06-05
A new study uncovers the intricate molecular mechanisms that regulate leaf senescence in apple plants, focusing on the crucial role of the E3 ligase enzyme, MdPUB23, and its interaction with the ABI5 protein. This research provides valuable insights into how plants manage stress responses and maintain growth, offering potential applications in improving crop yield and stress resistance.
Leaf senescence is a vital phase in the life cycle of plants, impacting overall plant health and yield. Abscisic acid (ABA) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Flapping frequency of birds, insects, bats and whales described by universal equationThe wing and fin beats of flying and diving animals can be predicted using just body mass and wing area