Grafting, an age-old horticultural technique, has been revealed as a powerful tool against soil-borne diseases like crown gall. New research uncovers how the composition of root exudates changes when plants are grafted onto resistant rootstocks, creating a defensive mechanism that reduces the prevalence of pathogenic Agrobacterium.
Crown gall disease, a destructive plant ailment caused by Agrobacterium, has long plagued agriculture, leading to significant crop losses. Traditional control methods have proven inadequate, highlighting an urgent need for innovative solutions. Given the pervasive impact of this disease and the limitations of current strategies, there is a pressing demand to explore the complex interplay between plant roots and soil microbes, potentially unlocking new avenues for disease resistance.
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Forestry and the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences have made a breakthrough in understanding how grafting can suppress crown gall disease. Published (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae049) in the prestigious journal Horticulture Research on 23 February 2024, the study delves into the defensive alteration of root exudate composition, offering new insights into plant-pathogen interactions.
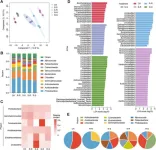
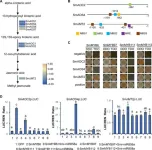
This study meticulously investigates the impact of grafting on root exudates, the biochemical substances secreted by plant roots that influence soil microbial communities. The research reveals that grafting disease-susceptible Prunus sp. onto resistant rootstock 'Haiying 1' triggers a significant reduction in pathogenic Agrobacterium. The team discovered that the root exudates from grafted plants were enriched with beneficial bacteria and depleted of the pathogen. Notably, the decrease in valine, an amino acid in root exudates, was linked to the suppression of crown gall disease. This finding is pivotal, as it suggests that the modification of root exudates through grafting can directly and positively influence the soil microbiome, thereby enhancing the plant's natural defense mechanisms against pathogens. The study's comprehensive approach, combining field experiments with biochemical and microbiome analyses, provides a robust foundation for understanding the multifaceted benefits of grafting in disease resistance.
Dr. Yunpeng Liu, corresponding author and lead researcher, emphasizes the significance of these findings: "Our research sheds light on the intricate relationship between plants and soil microbes. By understanding how grafting influences root exudates, we can develop more sustainable and effective methods to protect plants from diseases, ultimately contributing to global food security."
The research significantly advances sustainable agriculture by highlighting the natural defense mechanisms in plants. With the potential to minimize chemical pesticide use, it promotes eco-friendly farming. Grafting resistant rootstocks could become a widespread practice, enhancing crop health and yields. The discovery of root exudate compounds offers a pathway to develop precise biocontrol agents against soil-borne diseases, thereby bolstering global food security and reducing the agriculture sector's environmental footprint.
###
References
DOI
10.1093/hr/uhae049
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1093/hr/uhae049
Funding information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 32370135 and 31700548) and the Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-CSAL-202302).
About Horticulture Research
Horticulture Research is an open access journal of Nanjing Agricultural University and ranked number one in the Horticulture category of the Journal Citation Reports ™ from Clarivate, 2022. The journal is committed to publishing original research articles, reviews, perspectives, comments, correspondence articles and letters to the editor related to all major horticultural plants and disciplines, including biotechnology, breeding, cellular and molecular biology, evolution, genetics, inter-species interactions, physiology, and the origination and domestication of crops.
END
Roots of resistance: unveiling the soil-saving secrets of grafting
2024-06-07
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Insilico Medicine Founder and CEO Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD talks about AI and robotics in healthcare breakthroughs in following conferences
2024-06-07
Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and co-CEO of Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, will be attending a series of meetings in the following week, where he will be discussing bioscience innovations powered by AI and robotics.
More information about the events is listed as follows:
[1] London Tech Week 2024
Fireside Chat: The Forefront of AI Innovation in Health Tech
Time: Monday, 10th June 15:55 - 16:15 (UK time)
Location: London Olympia, Main Stage
London Tech Week is the global tech ecosystem aiming to accelerate the infinite cycle of tech innovation, which brings together the innovators ...
New: Classification Criteria for Hand OA
2024-06-07
Hand osteoarthritis mainly affects the distal interphalangeal, proximal interphalangeal, and thumb base joints,1 leading to joint pain, aching, and stiffness. Criteria developed by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) in 1990 are useful, but they cannot distinguish between interphalangeal or thumb base disease, and this is important since these two phenotypes may require different treatment strategies.
To address this, EULAR and a team of leading experts in the field set out to develop new classification criteria sets that include radiographic features. Early phases of the project used observational data to identify self-reported, ...
Perturbations simplify the study of “super photons”
2024-06-07
Thousands of particles of light can merge into a type of “super photon” under suitable conditions. Physicists call such a state a photon Bose-Einstein condensate. Researchers at the University of Bonn have now shown that this exotic quantum state obeys a fundamental theorem of physics. This finding now allows one to measure properties of photon Bose-Einstein condensates which are usually difficult to access. The study has been published in the journal Nature Communications.
If many atoms are cooled to a very low temperature confined in a small volume, they can become indistinguishable and behave like a single “super particle.” Physicists also call this ...
Decoding salvia miltiorrhiza: a molecular approach to boosting bioactive compounds
2024-06-07
Salvia miltiorrhiza, known as Danshen, is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for treating cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease. The medicinal properties of Danshen are primarily attributed to its two major bioactive compounds: tanshinones and phenolic acids. Despite their importance, the genetic and regulatory mechanisms underlying their biosynthesis remain poorly understood. Based on these challenges, there is a pressing need for in-depth research to uncover the molecular pathways involved in the production of these ...
Digital babies created to improve infant healthcare
2024-06-07
Researchers at University of Galway have created digital babies to better understand infants’ health in their critical first 180 days of life.
The team created 360 advanced computer models that simulate the unique metabolic processes of each baby.
The digital babies are the first sex-specific computational whole-body models representing newborn and infant metabolism with 26 organs, six cell types, and more than 80,000 metabolic reactions.
Real-life data from 10,000 newborns, including sex, birth weight and metabolite concentrations, enabled the creation and validation ...
Lavender's secret: genetic regulator boosts plant health and fragrance output
2024-06-07
A groundbreaking study has identified a gene that plays a dual role in enhancing both the aromatic compounds and disease resistance in lavender plants. The research uncovers how the LaMYC7 gene positively regulates the biosynthesis of linalool and caryophyllene, key for lavender's scent and its resistance to common plant pathogens.
Plants face various environmental pressures, including biotic stressors like pathogens and abiotic stressors such as extreme temperatures. Among biotic stressors, Pseudomonas syringae significantly threatens plant health worldwide. Terpenoids, including linalool and caryophyllene, play crucial roles in plant ...
How $4 billion funded the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic response
2024-06-07
New University of Virginia School of Medicine research is shedding light on how federal funding helped scientists understand the COVID-19 virus, develop new treatments and deploy lifesaving vaccines in record time.
The UVA Health researchers used advanced “machine learning” – a form of artificial intelligence – to analyze the thousands of scientific publications that resulted from the National Institutes of Health’s deployment of more than $4 billion to combat the pandemic. This analysis allowed the researchers to categorize the types ...
Advances in omics research of rosaceae
2024-06-07
A research team has provided a comprehensive overview of the applications of omics technologies in Rosaceae plants. The study highlights significant advancements in genome sequencing, transcriptome, proteomics, and metabolomics, shedding light on the genetic regulatory mechanisms underlying crucial traits such as flower color, fragrance, stress tolerance, and fruit quality. This research is invaluable for molecular breeding and improving economic traits in Rosaceae plants, potentially leading to the rapid cultivation of new varieties and germplasm.
The Rosaceae family, with its diverse species and economic importance, is a focus ...
Basic research: Inhibition of epigenetic control enzymes in immune cells as a potential new starting point in cancer immunotherapy
2024-06-07
Immunotherapy is one of the pillars in the fight against cancer and aims to enable the body's own immune system to fight a tumor. A recent study now shows that removing certain enzymes that regulate epigenetic processes from the so-called dentritic cells of the immune system influences their development and thus improves anti-tumor immunity. This finding could lead to new therapeutic strategies in immunotherapy. The study by Cristiano De Sá Fernandes from Maria Sibilia's research group at the Center for Cancer Research and the Comprehensive Cancer Center of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital was recently published in Cell Reports.
Cancer cells are the body's ...
Tracking greenhouse gas emissions in Chinese value chains with an interprovincial input–output model
2024-06-07
China’s economy has shifted from a stage of high growth to a stage of high-quality development, and the establishment of a dual-carbon target requires profound changes in the industrial structure and energy systems, as well as finding the right direction and pathway for industrial adjustment. While the potential for technological emission reduction continues to be released, the main factor affecting China’s carbon emissions is the speed and intensity of economic transformation and industrial restructuring.
A research team of Dr. GU Alun from Tsinghua University in Beijing, China, recently analyzed the correlations ...