(Press-News.org)
Researchers at University of Galway have created digital babies to better understand infants’ health in their critical first 180 days of life.
The team created 360 advanced computer models that simulate the unique metabolic processes of each baby.
The digital babies are the first sex-specific computational whole-body models representing newborn and infant metabolism with 26 organs, six cell types, and more than 80,000 metabolic reactions.
Real-life data from 10,000 newborns, including sex, birth weight and metabolite concentrations, enabled the creation and validation of the models, which can be personalised - enabling scientists to investigate an individual infant’s metabolism for precision medicine applications.
The work was conducted by a team of scientists at University of Galway’s Digital Metabolic Twin Centre and Heidelberg University, led by APC Microbiome Ireland principal investigator Professor Ines Thiele.
The team’s research aims to advance precision medicine using computational modelling. They describe the computational modelling of babies as seminal, as it enhances understanding of infant metabolism and creates opportunities to improve the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions during the early days of a baby’s life, such as inherited metabolic diseases.
Lead author Elaine Zaunseder, Heidelberg University, said: “Babies are not just small adults - they have unique metabolic features that allow them to develop and grow up healthy. For instance, babies need more energy for regulating body temperature due to, for example, their high surface-area-to-mass ratio, but they cannot shiver in the first six months of life, so metabolic processes must ensure the infant keeps warm.
“Therefore, an essential part of this research work was to identify these metabolic processes and translate them into mathematical concepts that could be applied in the computational model. We captured metabolism in an organ-specific manner, which offers the unique opportunity to model organ-specific energy demands that are very different in infants compared to adults.
“As nutrition is the fuel for metabolism, we can use breast milk data from real newborns in our models to simulate the associated metabolism throughout the baby’s entire body, including various organs. Based on their nutrition, we simulated the development of digital babies over six months and showed that they will grow at the same rate as real-world infants.”
Professor Ines Thiele, study lead on the project, said: “New-born screening programmes are crucial for detecting metabolic diseases early on, enhancing infant survival rates and health outcomes. However, the variability observed in how these diseases manifest in babies underscores the urgent need for personalised approaches to disease management.
“Our models allow researchers to investigate the metabolism of healthy infants as well as infants suffering from inherited metabolic diseases, including those investigated in newborn screening. When simulating the metabolism of infants with a disease, the models showed we can predict known biomarkers for these diseases. Furthermore, the models accurately predicted metabolic responses to various treatment strategies, showcasing their potential in clinical settings.”
Elaine Zaunseder added: “This work is a first step towards establishing digital metabolic twins for infants, providing a detailed view of their metabolic processes. Such digital twins have the potential to revolutionise paediatric healthcare by enabling tailored disease management for each infant's unique metabolic needs.”
The research was published this week in Cell Metabolism
This work was led by University of Galway and completed as part of a collaboration with Heidelberg University, Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies and Heidelberg University Hospital, Germany.
Ends
END
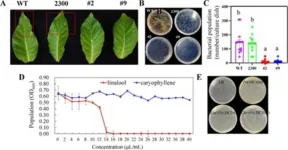
A groundbreaking study has identified a gene that plays a dual role in enhancing both the aromatic compounds and disease resistance in lavender plants. The research uncovers how the LaMYC7 gene positively regulates the biosynthesis of linalool and caryophyllene, key for lavender's scent and its resistance to common plant pathogens.
Plants face various environmental pressures, including biotic stressors like pathogens and abiotic stressors such as extreme temperatures. Among biotic stressors, Pseudomonas syringae significantly threatens plant health worldwide. Terpenoids, including linalool and caryophyllene, play crucial roles in plant ...
New University of Virginia School of Medicine research is shedding light on how federal funding helped scientists understand the COVID-19 virus, develop new treatments and deploy lifesaving vaccines in record time.
The UVA Health researchers used advanced “machine learning” – a form of artificial intelligence – to analyze the thousands of scientific publications that resulted from the National Institutes of Health’s deployment of more than $4 billion to combat the pandemic. This analysis allowed the researchers to categorize the types ...
A research team has provided a comprehensive overview of the applications of omics technologies in Rosaceae plants. The study highlights significant advancements in genome sequencing, transcriptome, proteomics, and metabolomics, shedding light on the genetic regulatory mechanisms underlying crucial traits such as flower color, fragrance, stress tolerance, and fruit quality. This research is invaluable for molecular breeding and improving economic traits in Rosaceae plants, potentially leading to the rapid cultivation of new varieties and germplasm.
The Rosaceae family, with its diverse species and economic importance, is a focus ...
Immunotherapy is one of the pillars in the fight against cancer and aims to enable the body's own immune system to fight a tumor. A recent study now shows that removing certain enzymes that regulate epigenetic processes from the so-called dentritic cells of the immune system influences their development and thus improves anti-tumor immunity. This finding could lead to new therapeutic strategies in immunotherapy. The study by Cristiano De Sá Fernandes from Maria Sibilia's research group at the Center for Cancer Research and the Comprehensive Cancer Center of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital was recently published in Cell Reports.
Cancer cells are the body's ...
China’s economy has shifted from a stage of high growth to a stage of high-quality development, and the establishment of a dual-carbon target requires profound changes in the industrial structure and energy systems, as well as finding the right direction and pathway for industrial adjustment. While the potential for technological emission reduction continues to be released, the main factor affecting China’s carbon emissions is the speed and intensity of economic transformation and industrial restructuring.
A research team of Dr. GU Alun from Tsinghua University in Beijing, China, recently analyzed the correlations ...
Fukuoka, Japan—In a paper published in Geophysical Research Letters, researchers have discovered that the turbulence in the thermosphere exhibits the same physical laws as the wind in the lower atmosphere. Furthermore, wind in the thermosphere predominantly rotates in a cyclonic direction, in that it rotates counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
The findings reveal a new unified principle for the Earth’s varied environmental systems and can potentially improve future forecasting of both earth and space weather.
One time or another we’ve tuned in to see the latest weather forecast, and while ...
Neurons communicate electrically so to understand how they produce brain functions such as memory, neuroscientists must track how their voltage changes—sometimes subtly—on the timescale of milliseconds. In a new paper in Nature Communications, MIT researchers describe a novel image sensor with the capability to substantially increase that ability.
The invention led by Jie Zhang, a postdoctoral scholar in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory lab of Sherman Fairchild Professor Matt ...
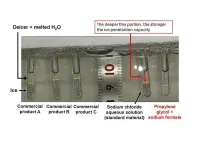
The dangers of frozen roads, airplane engines, and runways are well known, but the use of commercial products often means short-term safety over long-term environmental degradation. Seeking a better product, Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have developed a deicing mixture offering higher performance than deicers on the market while also having less impact on the environment.
The team, made up of graduate student Kai Ito, Assistant Professor Arisa Fukatsu, Associate Professor Kenji Okada, and Professor Masahide Takahashi of the Graduate School of Engineering, used machine learning to analyze ice melting mechanisms of aqueous solutions of 21 salts and 16 organic ...
Cells are signalled to have nutrients in excess, and this leads to malfunction and inflammation in organs such as the pancreas, the liver and the kidneys.
The finding, by CNIO researchers, are published in Nature Aging. It suggests that an intervention on the inflammation alone can relieve symptoms and increase survival.
The research has been conducted on animal models, but comparing their molecular processes with blood samples from people in their seventies indicates that they can be extrapolated to human aging.
The reality of a population who is ageing at an accelerated rate makes it a priority to understand what happens in the body over time, ...
An international research team led by scientists from the University of Liège has discovered an interesting new therapeutic target for the treatment of melanoma resistant to targeted therapies. Inhibition of the VARS enzyme could prevent this therapeutic resistance by resensitising tumours resistant to these targeted therapies.
Melanoma is one of the most serious and aggressive forms of skin cancer. When diagnosed early, melanoma is surgically removed. However, once metastases (i.e. secondary distant tumours) have developed, ...