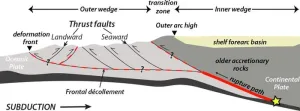
(Press-News.org) Off the coasts of southern British Columbia, Washington, Oregon and northern California lies a 600 mile-long strip where the Pacific Ocean floor is slowly diving eastward under North America. This area, called the Cascadia Subduction Zone, hosts a megathrust fault, a place where tectonic plates move against each other in a highly dangerous way. The plates can periodically lock up and build stress over wide areas―eventually to be released when they finally lurch against each other. The result: the world’s greatest earthquakes, shaking both seabed and land, and generating tsunamis 100 feet high or more. Such a fault off Japan caused the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster. Similar zones exist off Alaska, Chile and New Zealand, among other places. At Cascadia, big quakes are believed to come roughly every 500 years, give or take a couple hundred. The last occurred in 1700.
Scientists have long been working to understand the Cascadia Subduction Zone’s subterranean structures and mechanics, in order to delineate places most susceptible to quakes, how big they might be and what warning signs they might produce. There is no such thing as predicting an earthquake; rather, scientists try to forecast probabilities of multiple scenarios, hoping to help authorities design building codes and warning systems to minimize the damage when something happens.
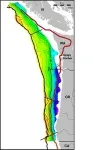
A newly published study promises to greatly advance this effort. A research vessel towing an array of the latest geophysical instruments along almost the entire zone has produced the first comprehensive survey of the many complex structures beneath the seafloor. These include the geometry of the down-going ocean plate and overlying sediments, and the makeup of the overriding North American plate. The study was just published in the journal Science Advances.
“The models currently in use by public agencies were based on a limited set of old, low-quality 1980s-era data,” said Suzanne Carbotte, a marine geophysicist at Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, who led the research. “The megathrust has a much more complex geometry than previously assumed. The study provides a new framework for earthquake and tsunami hazard assessment.”
With funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation, the data was gathered during a 41-day cruise in 2021 by Lamont’s research vessel, the Marcus G. Langseth. Researchers aboard the ship penetrated the seafloor with powerful sound pulses and read the echoes, which were then converted into images, somewhat similar to how physicians create interior scans of the human body.
One key finding: the megathrust fault zone is not just one continuous structure, but is divided into at least four segments, each potentially somewhat insulated against movements of the others. Scientists have long debated whether past events, including the 1700 quake, ruptured the entire zone or just part of it—a key question, because the longer the rupture, the bigger the quake.
The data show that the segments are divided by buried features including big faults, where opposing sides slide against each other perpendicular to the shore. This might help buffer against movement on one segment translating to the next. “We can’t say that this definitely means only single segments will rupture, or that definitely the whole thing will go at once,” said Harold Tobin, a geophysicist at the University of Washington and coauthor of the study. “But this does upgrade evidence that there are segmented ruptures.”
The imagery also suggests the causes of the segmentation: the rigid edge of the overriding North American continental plate is composed of many different kinds of rocks, formed at different times over many tens of millions of years, with some being denser than others. This variety in the continental rocks causes the incoming, more pliable oceanic plate to bend and twist to accommodate differences in overlying pressure. In some places, segments go down at relatively steep angles, in others at shallow ones.
The researchers zeroed in on one segment in particular, which runs from southern Vancouver Island alongside Washington state, more or less ending at the Oregon border. The subterranean topography of other segments is relatively rough, with oceanic features like faults and subducted seamounts rubbing up against the upper plate—features that might erode the upper plate and limit how far any quake may propagate within the segment, thus limiting the quake’s size. In contrast, the Vancouver-Washington segment is quite smooth. This means that it may be more likely to rupture along its entire length at once, making it potentially the most dangerous section.
Also in this segment, the seafloor is subducting under the continental crust at a shallow angle relative to the other segments. In the other segments, most of the earthquake-prone interface between the plates lies offshore, but here the study found the shallow subduction angle means it probably extends directly under Washington’s Olympic Peninsula. This might magnify any shaking on land. "It requires a lot more study, but for places like Tacoma and Seattle, it could mean the difference between alarming and catastrophic," said Tobin.
With funding from the U.S. Geological Survey, a consortium of state and federal agencies and academic institutions has already been poring over the data since it became available to sort through the implications.
As for tsunami hazard, that is “still a work in progress,” said Kelin Wang, a research scientist at the Geological Survey of Canada who was not involved in the study. Wang’s group is using the data to model features of the seafloor off Vancouver Island that might generate tsunamis. (In general, a tsunami occurs when the deep seafloor moves up or down during a quake, sending a wave to the surface that concentrates its energy and gathers height as it reaches shallower coastal waters.) Wang said his results will go to another group that models tsunamis themselves, and after that to another group that analyzes the hazards on land.
Practical assessments that could affect building codes or other aspects of preparedness may be published as early as next year, say the researchers. “There’s a whole lot more complexity here than was previously inferred,” said Carbotte.
# # #
Lead author contact:
Suzanne Carbotte carbotte@ldeo.columbia.edu
More information:
Kevin Krajick, Senior editor, science news, Columbia Climate School/Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory kkrajick@ei.columbia.edu 917-361-7766
END
Scientists at the University of Dundee have uncovered the inner relay of a molecular switch that protects the brain against the development of Parkinson’s disease.
The research provides new potential strategies to develop drugs that may benefit patients with Parkinson’s.
Parkinson’s is the fastest growing brain disorder in the world, however, there are currently no treatments that can slow or arrest the condition.
Previous research conducted at the University had found a gene called PINK1 is central to protecting brain cells against stress. In patients ...
While smell plays a considerable role in the social interactions of humans—for instance, signaling fear or generating closeness—for ants, it is vitally important. Researchers from New York University and the University of Florida found that a key protein named Orco, essential for the function of olfactory cells, is also critical for the cells’ survival in ants.
Their study showed that mutating the orco gene in Harpegnathos saltator jumping ants dramatically decreased the number of olfactory neurons, suggesting that Orco is necessary for the development and life of these cells. The findings, published in Science Advances, offer insights into the cellular ...
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have provided a simple and comprehensive – if less dramatic – explanation for bright radar reflections initially interpreted as liquid water beneath the ice cap on Mars’ south pole.
Their simulations show that small variations in layers of water ice – too subtle for ground-penetrating radar instruments to resolve – can cause constructive interference between radar waves. Such interference can produce reflections whose intensity and variability match observations to date – not only in the area proposed to be liquid water, but across the so-called south ...
Toronto, ON, Canada - A new study conducted by researchers at the University of Toronto has unveiled a significant association between the use of photo filters on social media and increased symptoms of muscle dysmorphia among adolescents and young adults in Canada. This study, which analyzed data from 912 participants from the Canadian Study of Adolescent Health Behaviors, emphasizes the growing concern over the impact of digital image manipulation on body image and mental health.
The research reveals that the use of photo filters, commonly found on apps like Snapchat, Instagram, and TikTok, is linked to greater muscle dysmorphia symptomatology, a condition marked ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Feed costs for producing broiler chickens accounts for 60% to 70% of total production costs, and stump waste from the production of button mushrooms comprises nearly 30% of total mushroom weight. Marrying the two has the potential to reduce both cost and waste, especially in Pennsylvania, which is a national leader in the production of broiler chickens and button mushrooms.
To learn whether the two are compatible, a team of Penn State researchers conducted a new study to determine how supplementing the feed of broilers with mushroom stump waste affected the growth and health of the chickens.
In findings ...
New eye-tracking research has shown that simply looking at natural elements during urban walks can offer significant mental health benefits.
The study, by Bangor University and Technion- Israel Institute of Technology, published in the scientific journal People and Nature, involved city-dwellers, and showed how paying visual attention to greenery, rather than human-made structures, can alleviate anxiety and enhance restorative feelings.
The 117 urban residents who took part in the study, were guided on a 45-minute urban walk, while wearing eye-tracking ...
By Devon McPhee
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Scientists have a handful of standard research organisms, including fruit flies and mice, that they use to study the evolutionary development (evo-devo) of animal lineages over time. Yet the more research organisms they can study, the deeper our understanding of life and the more knowledge we have to advance biomedicine and ecological conservation.
Researchers at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), Woods Hole, and the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn (SZS) in Naples, Italy, have added to the evo-devo toolbox by establishing Holothuria tubulosa, ...
In the relentless fight against cancer, a new technology promises to shed light on how we track and understand the spread of this disease within the body. A research team from Northeastern University and Dartmouth College recently developed a remarkable tool called "diffuse in vivo flow cytometry" (DiFC), which allows for the noninvasive detection and counting of rare cancer cells circulating in the bloodstream.
Monitoring cancer spread in real time
In a recent publication in the Journal of Biomedical Optics (JBO), the research team detailed their innovative two-color DiFC system, capable of simultaneously detecting two distinct populations of cancer ...
East Hanover, NJ – June 7, 2024 –May job numbers showed gains for people with disabilities, who continue to engage with the labor market at historic levels, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). Increases in both labor force participation and employment indicate that people with disabilities are not only striving to work but succeeding in finding jobs. ...
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, has joined with the IEEE Computer Society (IEEE-CS) and the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) to develop “Computer Science Curricula 2023” (CS2023). CS2023 provides a comprehensive guide outlining the knowledge and competencies students should attain for degrees in computer science and related disciplines at the undergraduate level.
Establishing uniform curricular guidelines for computer science disciplines is viewed as being essential to the ongoing vitality of the field and the future success of the students ...