(Press-News.org) When college athletes are evaluated for a possible concussion, the diagnosis is based on an athletic trainer or team physician’s assessment of three things: the player’s symptoms, physical balance and cognitive skills.
Research published today suggests that almost half of athletes who are ultimately diagnosed with a concussion will test normally on the recommended cognitive-skills test.
“If you don’t do well on the cognitive exam, it suggests you have a concussion. But many people who are concussed do fine on the exam,” said Dr. Kimberly Harmon, the study’s lead author. She is a professor of family medicine and section head of sports medicine at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The study findings appear in JAMA Network Open.
Harmon said her sideline experiences as a team physician for the UW Huskies caused her to wonder how to accurately interpret the cognitive-screening portion of the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool (SCAT). Introduced in 2004 by the Concussion in Sport Group, the SCAT (now in its fifth iteration, SCAT5) was intended to standardize the gathering of information from athletes with a potential head injury.
The SCAT first prompts an athlete about whether they are experiencing any of 22 symptoms such as headache, nausea or blurred vision, and symptom severity. Then the tool tests the athlete’s cognition in several ways.
First come questions of orientation. (What day is it? What month is it?) Then a test of immediate memory, in which a list of 10 words is read aloud to the athlete, who is asked to restate the list. This sequence is repeated three times. Then the athlete’s concentration is tested by having to repeat short sequences of numbers in reverse order. Then comes a prescribed evaluation of the athlete’s balance, after which the athlete is again asked to recall the 10 words from the first list.
In Harmon’s experience as a team physician, she saw that “some people were concussed and they did well on the recall tests. Some people weren’t concussed and they didn’t do well. So I thought we should study it,” she said.
The study involved 92 NCAA Division I athletes who sustained a concussion between July 13, 2020, and Dec. 31, 2022, and who had a concussion evaluation within 48 hours. The investigators also recruited 92 of the concussed players’ teammates as matched control subjects, each of whom was given the SCAT5 screening within two weeks of the incident concussion.
All athletes in the study had previously completed NCAA-required baseline concussion screenings. The investigators found no significant differences in baseline scores between the athletes with and without concussion.
Harmon and colleagues analyzed the study participants’ SCAT5 responses and found that the word-recall tests had little predictive value for concussion. In fact, almost half (45%) of the concussed athletes performed at or above their baseline cognitive-test results, the researchers reported.
Instead, the study showed that the most accurate predictor of concussion were the athletes’ responses to questions about their symptoms.
“If you get hit in the head and go to the sideline and say, ‘I have a headache. I’m dizzy. I don’t feel right,’ I can say with pretty good assurance that you have a concussion,” Harmon said. “I don’t need to do any testing. The problem is that some athletes don’t want to come out. They don’t report their symptoms or may not recognize their symptoms. So then you need an objective, accurate test to tell you whether you can safely put the athlete back on the field. We don’t have that right now.”
During in-game evaluations for a concussion, team trainers and physicians must quickly synthesize the available evidence and make their best clinical judgment about a player’s health. The responsibility for a safety-first decision, though, also lies in part with the athletes, the study’s authors wrote:
“Although an increase in symptoms is highly suggestive of concussion, this relies on accurate reporting by the athlete who may not report symptoms because of a desire to return to play, a fear of letting teammates down, minimizing the seriousness of concussion, difficulty discerning symptoms, a delay in symptom development, or other reasons.”
“We are still short of the holy grail, which is an objective test for concussion,” Harmon said. “For now, this study shows how important it is for athletes to disclose their symptoms.”
The study was funded in part by the Jack and Luellen Cherneski and the Chisholm Foundation.
END
Cognitive test is poor predictor of athletes’ concussion
Part of the NCAA’s standardized concussion evaluation fails to distinguish athletes who were actually injured, a study shows.
2024-06-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Buck researchers explore how the immune system goes awry during space travel and the implications for human aging on earth
2024-06-11
As long as humans have been traveling into space, astronauts have experienced significant health effects from the extreme conditions of space flight, notably the reduction of gravity.
Two Buck scientists led a team that has revealed for the first time how the lack of gravity affects the cells of the immune system at single cell resolution. As co-senior authors, along with Christopher E. Mason, PhD of Weill Cornell Medical College, Associate Professor David Furman, PhD and Associate Professor Daniel Winer, MD, published in the ...
Social determinants of health linked with youth-onset prediabetes
2024-06-11
Food insecurity, low household income and not having private health insurance are associated with higher rates of prediabetes in adolescents, independent of race and ethnicity, according to a new JAMA Network Open study by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC researchers.
The findings suggest that screening for social determinants of health — the non-medical factors that influence a person's health and risk of disease — may help identify youth at risk of prediabetes, which could ultimately improve early interventions that prevent progression to type 2 diabetes.
“This study underscores the importance ...
Harvard, Google DeepMind researchers create realistic virtual rodent
2024-06-11
The agility with which humans and animals move is an evolutionary marvel that no robot has yet been able to closely emulate. To help probe the mystery of how brains control movement, Harvard neuroscientists have created a virtual rat with an artificial brain that can move around just like a real rodent.
Bence Ölveczky, professor in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, led a group of researchers who collaborated with scientists at Google’s DeepMind AI lab to build a biomechanically realistic digital model of a rat. Using high-resolution data recorded from ...
Scientists unlock secrets of how the third form of life makes energy
2024-06-11
Scientists unlock secrets of how the third form of life makes energy.
An international scientific team has redefined our understanding of archaea, a microbial ancestor to humans from two billion years ago, by showing how they use hydrogen gas.
The findings, published today in Cell, explain how these tiny lifeforms make energy by consuming and producing hydrogen. This simple but dependable strategy has allowed them to thrive in some of Earth’s most hostile environments for billions of years.
The paper, led by Monash University Biomedicine Discovery Institute scientists, including ...
Would astronauts’ kidneys survive a roundtrip to Mars?
2024-06-11
The structure and function of the kidneys is altered by space flight, with galactic radiation causing permanent damage that would jeopardise any mission to Mars, according to a new study led by researchers from UCL.
The study, published in Nature Communications, is the largest analysis of kidney health in space flight to date and includes the first health dataset for commercial astronauts. It is published as part of a Nature special collection of papers on space and health.
Researchers have known that space flight causes certain health issues since the 1970s, in the ...
Depressive symptoms may hasten memory decline in older people
2024-06-11
Depressive symptoms are linked to subsequent memory decline in older people, while poorer memory is also linked to an increase in depressive symptoms later on, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL and Brighton and Sussex Medical School.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, looked at 16 years of longitudinal data from 8,268 adults in England with an average age of 64.
The researchers concluded that depression and memory were closely interrelated, with both seeming to affect each other.
Senior author Dr Dorina Cadar, of the UCL Department of Behavioural Science & Health and Brighton and Sussex Medical School, said: “It is ...
New technique could help build quantum computers of the future
2024-06-11
Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems in human health, drug discovery, and artificial intelligence millions of times faster than some of the world’s fastest supercomputers. A network of quantum computers could advance these discoveries even faster. But before that can happen, the computer industry will need a reliable way to string together billions of qubits – or quantum bits – with atomic precision.
Connecting qubits, however, has been challenging for the research community. Some methods form qubits by placing ...
Trash-sorting robot mimics complex human sense of touch
2024-06-11
WASHINGTON, June 11, 2024 – Today’s intelligent robots can accurately recognize many objects through vision and touch. Tactile information, obtained through sensors, along with machine learning algorithms, enables robots to identify objects previously handled.
However, sensing is often confused when presented with objects similar in size and shape, or objects unknown to the robot. Other factors restrictive to robot perception include background noise and the same type of object with different shapes and sizes.
In Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Tsinghua University worked to break through the difficulties ...
Shedding light on the origin of a genetic variant underlying fungal infections
2024-06-11
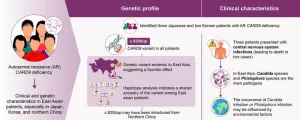
Researchers from Japan uncover the genetic diversity and regional patterns of CARD9 deficiency in patients susceptible to fungal diseases
Tokyo, Japan – Fungal infections pose life-threatening risks, especially when vital organs or the central nervous system are affected. Individuals harboring variants in the CARD9 gene are particularly susceptible to invasive fungal infections, given that the protein coded by this gene serves as a critical regulator of the immune system. A recent discovery ...
Humanitarian organizations showed flexibility and grit during COVID supply chain disruptions: study
2024-06-11
When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, it sent shock waves across global supply chains. But manufacturers and other businesses weren’t the only ones hit hard: local and international aid organizations, tasked with providing humanitarian assistance during times of crisis, suddenly had a major crisis of their own. How would they get the supplies they needed to carry out their crucial work?
According to a new study by the UBC Sauder School of Business, the organizations showed remarkable nimbleness and ingenuity — and while the pandemic was an unusual event, their approaches can provide powerful insights ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Cognitive test is poor predictor of athletes’ concussionPart of the NCAA’s standardized concussion evaluation fails to distinguish athletes who were actually injured, a study shows.