(Press-News.org) In relationships, sharing closer spaces naturally deepens the connection as bonds form and strengthen through increasing shared memories. This principle applies not only to human interactions but also to engineering. Recently, an intriguing study was published demonstrating the use of quantum dots to create metasurfaces, enabling two objects to exist in the same space.
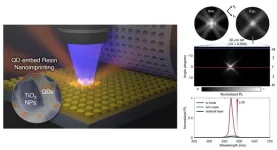
Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Department of Chemical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering, PhD candidates Minsu Jeong, Byoungsu Ko, and Jaekyung Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Chunghwan Jung, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) employed Nanoimprint Lithography (NIL) to fabricate metasurfaces embedded with quantum dots, enhancing their luminescence efficiency. Their research was recently published in the online edition of Nano Letters, an international journal in nanotechnology.
NIL, a process for creating optical metasurfaces, utilizes patterned stamps to quickly transfer intricate patterns at the nanometer (nm) scale. This method offers cost advantages over electron beam lithography and other processes and has the advantage of enabling the creation of metasurfaces using materials that are not available in conventional processes.
Metasurfaces have recently been the focus of extensive research for their ability to control the polarization and emission direction of light from quantum dots. Quantum dots, which are nanoscale semiconductor particles, are highly efficient light emitters capable of emitting light at precise wavelengths. This makes them widely used in applications such as QLEDs and quantum computing. However, conventional processes cannot embed quantum dots within metasurfaces. As a result, research has often involved fabricating metasurfaces and quantum dots separately and then combining them, which imposes limitations on controlling the luminescence of the quantum dots.
In this study, the researchers integrated quantum dots with titanium dioxide (TiO2), a material used in the NIL process, to create a metasurface. Unlike conventional methods, which involve separately fabricating the metasurface and quantum dots before combining them, this approach embeds the quantum dots directly within the metasurface during its creation.
The resulting metasurface enhances the proportion of photons emitted from the quantum dots that couple with the resonance mode of the metasurface. This advancement allows for more effective control over the specific direction of light emitted from the quantum dots compared to previous methods.
Experiments demonstrated that the more photons emitted from the quantum dots that were coupled to the resonant modes of the metasurface, the higher the luminescence efficiency. The team's metasurface achieved up to 25 times greater luminescence efficiency compared to a simple coating of quantum dots.
Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH who led the research stated, "The use of luminescence-controlled metasurfaces will enable sharper, brighter displays and more precise, sensitive biosensing." He added, "Further research will allow us to control luminescence more effectively, leading to advances in areas such as nano-optical sensors, optoelectronic devices, and quantum dot displays."
The research was conducted with support from POSCO N.EX.T IMPACT, the Samsung Future Technology Incubation Program, and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
END
Quantum dots and metasurfaces: Deep connections in the nano world
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers at Houston Methodist find survival improves with open radical hysterectomy in early-stage cancer
2024-06-12
Early-stage cervical cancer patients see better survival and decreased recurrence rates after open radical hysterectomy than minimally invasive laparoscopic approaches, according to a 5-year study led by Houston Methodist researchers and published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“The findings from this and an initial study in 2018 led to the change in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines established that same year that for radical hysterectomy we routinely perform an open approach. This latest study reaffirms this recommendation,” ...
Rise in global number of patient harms from 11 million to 18 million (59%) in 30 years
2024-06-12
The proportion of patient harms associated with medical procedures, treatment, and contact with healthcare systems rose by 59%, from 11 million to 18 million globally between 1990 and 2019, finds a data analysis published online in the journal BMJ Quality & Safety.
They outpaced the increase in the world’s population of 45% over the same period. And older people bore the brunt of these incidents, with the steepest rise among 65-69 year olds, the findings show.
In developed nations, over 50% of inpatient ...
Few UK people likely to be suitable for new Alzheimer’s drugs when they come on stream
2024-06-12
Few people in the UK with early stage Alzheimer’s disease are likely to be suitable for the latest drugs which aim to halt progress of the condition, yet many are nevertheless likely to be referred for these treatments, finds research published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The disease-modifying drugs, lecanemab and donanemab, slow cognitive decline in people with early stage Alzheimer’s disease. And they have been granted ‘breakthrough therapy’ ...
Retraction notice of previously press released research
2024-06-12
The research “Acupuncture for low back and/or pelvic pain during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials,” published in the open access journal BMJ Open in 2022, has been retracted.
This research was press released in November 2022 under the title of “Acupuncture can relieve lower back/pelvic pain often experienced during pregnancy.”
Following publication of the research, various issues concerning its design and reporting methods came to light, none of which ...
Preparing for a world where Alzheimer’s disease is treatable
2024-06-12
Under strict embargo until Tuesday 11 June 2024 at 23.30 hours UK (BST) time
Preparing for a world where Alzheimer’s disease is treatable
Peer-reviewed | Observational study | People
Drugs with the potential to change the course of Alzheimer’s disease are expected to be approved by mid-year in the UK. Healthcare services may need to change to ensure that all patients have equitable access to these new modifying anti-amyloid therapies, according to research led by Queen Mary University of London and University College London (UCL).
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia. Of the 944,000 people living ...
Robot radiotherapy could improve treatments for eye disease
2024-06-12
Researchers from King’s, with doctors at King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, have successfully used a new robot system to improve treatment for debilitating eye disease.
The custom-built robot was used to treat wet neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD), administering a one-off, minimally invasive dose of radiation, followed by patients’ routine treatment with injections into their eye.
In the landmark trial, published today in The Lancet, it was found that patients then needed fewer injections to effectively control the disease, potentially saving around ...
Millions of insects migrate through 30-metre Pyrenees pass
2024-06-12
Over 17 million insects migrate each year through a single mountain pass on the border between France and Spain, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied migrating insects in the Pass of Bujaruelo, a 30-metre gap between two high peaks in the Pyrenees.
The team visited the pass each autumn for four years, monitoring the vast number and variety of day-flying insects heading south.
The findings for this single pass suggest that billions of insects cross the Pyrenees each year, making it a key location for many migrating species.
The migrating insects ...
Should celebrities and influencers turn off their social media comments? A new study suggests they are less persuasive and likable when they do
2024-06-12
Researchers from University of Alabama and Vanderbilt University published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the negative consequences that celebrities and influences incur when they disable social media comments.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “No Comments (From You): Understanding the Interpersonal and Professional Consequences of Disabling Social Media Comments” and is authored by Michelle Daniels and Freeman Wu.
Celebrities and influencers like Addison Rae, Hailey Bieber, ...
Painful truth about knee osteoarthritis: Why inactivity may be more complex than we think
2024-06-12
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a common cause of pain and joint stiffness. And while physical activity is known to ease symptoms, only one in 10 people regularly exercise.
Understanding what contributes to patients’ inactivity is the focus of a world first study from the University of South Australia. Here, researchers have found that people with knee OA unconsciously believe that activity may be dangerous to their condition, despite medical advice telling them otherwise.
The study found that of those surveyed, 69% of people with knee pain had stronger implicit (unconscious) beliefs that exercise ...
New study finds human-caused nitrous oxide emissions grew 40 percent from 1980-2020, greatly accelerating climate change
2024-06-12
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (6/11/24) – Emissions of nitrous oxide – a greenhouse gas more potent than carbon dioxide or methane – continued unabated between 1980 and 2020, a year when more than 10-million metric tons were released into the atmosphere primarily through farming practices, according to a new report by the Global Carbon Project.
Agricultural production accounted for 74 percent of human-driven nitrous oxide emissions in the 2010s – attributed primarily to the use of chemical fertilizers and ...