(Press-News.org) A recent study published in IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution explores how artificial intelligence—in particular machine learning techniques—can be leveraged as powerful tools for the electric power and energy industry, and for managing its assets.
By showcasing practical applications and success stories, the study demonstrates the growing acceptance of machine learning as a valuable technology for current and future business needs in the power sector. It also assesses the barriers and difficulties of implementing large-scale machine learning techniques in practical settings, while exploring potential solutions.
“To support the power sector in its goal of efficient asset management, we must keep investigating and developing machine learning–based strategies. By doing this, we can ensure sustainable, dependable, and effective energy networks for the future while fostering resilient power systems that satisfy the changing demands of a changing world,” the authors wrote.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1049/gtd2.13183
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution is a fully open access and influential journal for the best research in the field. We empower the discussion and publication of current practice and future developments in electric power generation, transmission and distribution which is highly read and cited worldwide.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
How can artificial intelligence be applied to the business needs of the electric power industry?
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Could a novel liver patch help treat and prevent liver disease?
2024-06-12
As described in research published in the Biotechnology Journal, investigators have developed a novel patch that can help liver tissue regenerate.
The patch is a combination of decellularized liver matrix, a liver growth factor, and an anticoagulant. In lab tests with liver cells, the patch helped liver cells regain function after exposure to a toxin.
In rats, patches attached to the liver and gut promoted recovery from liver fibrosis, with notable decreases in scarring and inflammation.
“The decellularized liver matrix–based hepatic patch has demonstrated the ability to ...
Do psychiatric conditions increase the risk of early death in individuals with anorexia nervosa?
2024-06-12
A new study published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders found that mortality rates are high in patients with anorexia nervosa and nearly double in the presence of psychiatric conditions.
For the study, investigators analyzed data on all individuals diagnosed with anorexia nervosa in Denmark in 1977-2018. This included 14,774 patients who were followed for a median time of 9.1 years (and up to 40 years) and were matched 1:10 with age- and sex-matched individuals in the general population.
Individuals with ...
Study demonstrates sustained reduction in child mortality following educational interventions in low-resourced countries
2024-06-12
Pediatric intensive care units (PICUs) in low and middle-income countries see elevated mortality rates, often 10 times higher than those in high-income countries. One leading risk factor is the high incidence of unplanned intubation — a procedure that inserts a tube into the child’s airway — which can lead to complications like hypoxia and ventilator-associated pneumonia. Interventions that improve clinical practices can help reduce child mortality in countries with limited resources.
In a new study published June 12th in Frontiers of Public Health, investigators from Mass ...
Scientists engineer human antibodies that could neutralize black widow toxin
2024-06-12
There are various types of widow spiders, including black, red, and brown varieties in North and South America, the Australian redback spider, and several button spider species that inhabit South Africa. In Europe, Latrodectus tredecimguttatus – the European black widow – inhabits the Mediterranean region, but recently and due to the changing climate, the widows have been expanding their habitat.
Widow spiders’ bites can cause latrodectism, a disease where the spider’s venom, a neurotoxin known as alpha-latrotoxin, attacks the nervous system and causes symptoms like severe ...
How feeling younger impacts dementia caregivers and their loved ones
2024-06-12
The felt age of spousal caregivers is connected to the felt age of their loved ones living with dementia, according to a study from the University of Surrey. This perceived age in people with dementia and their caregivers is related to their own wellbeing, satisfaction with life, and self-confidence.
Felt age is defined as how old someone feels compared to their real age. It's measured by asking people to report whether they feel younger, the same, or older than their actual age. This concept helps understand how people see their own ageing, which can affect their mental and physical health and predict important ...
Towards a new era in flexible piezoelectric sensors for both humans and robots
2024-06-12
Flexible piezoelectric sensors are essential to monitor the motions of both humans and humanoid robots. However, existing designs are either are costly or have limited sensitivity. In a recent study, researchers from Japan tackled these issues by developing a novel piezoelectric composite material made from electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers combined with dopamine. Sensors made from this material showed significant performance and stability improvements at a low cost, promising advancements ...
New study suggests kidney function is associated with tooth loss in postmenopausal women
2024-06-12
CLEVELAND, Ohio (June 12, 2024)—Kidneys play a critical role in overall health by removing waste products from the blood. When they fail to sufficiently filter out foreign elements, several serious, lifethreatening, medical conditions can result. A new study suggests that chronic kidney disease may also be linked with tooth loss. Results of the survey are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
A woman’s glomerular filtration rate shows how well her kidneys are functioning. ...
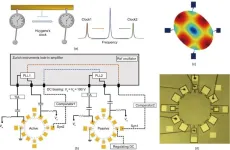
Breakthrough MEMS Huygens clock improves timekeeping precision and stability
2024-06-12
In a significant development for the miniaturization of electronic devices, a new study published in Engineering has reported the creation of a Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) clock that offers improved precision and stability. The clock, which utilizes the synchronization principle discovered by the Christiaan Huygens, consists of two synchronized MEMS oscillators and a frequency compensation system.
The research details how the MEMS Huygens clock enhances short-time stability, with the Allan deviation – a measure of the clock’s accuracy over time – improving by a factor of 3.73 from 19.3 ppb to 5.17 ppb at 1 second. The clock's long-term ...
HKUMed’s world-first ‘Liver-in-Cube’ wins a gold medal at International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva, advancing precise cancer treatment
2024-06-12
Background
Liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer and third leading cause of cancer death globally. According to Hong Kong Cancer Registry data, there are approximately 1,800 new cases of liver cancer each year, with over 1,500 deaths, over 80% of which are advanced cases at first diagnosis. Patients with advanced liver cancer who are not suitable for surgical operations have limited treatment options. Traditional chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy for treating advanced liver cancer often have a low response rate and severe side effects, thereby limiting their efficacy and hindering the patient’s quality ...
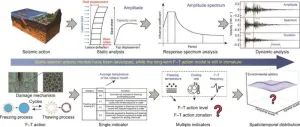
Nationwide zonation and durability assessment of China’s plateau infrastructure under freeze–thaw cycles
2024-06-12
In a bid to tackle the enduring problem of infrastructure durability in the face of relentless freeze–thaw (F–T) cycles, a team of researchers has published a new study in Engineering. The study focuses on the Chinese Plateau region, where the harsh effects of F–T cycles on concrete structures have led to concerns regarding their aging and subsequent performance deterioration.
The authors of the study emphasize that the existing national standards for designing frost-resistant concrete structures are insufficient, as they rely primarily on the coldest monthly average temperature without accounting for the intricate spatiotemporal variations, amplitude, and ...