(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND, Ohio (June 12, 2024)—Kidneys play a critical role in overall health by removing waste products from the blood. When they fail to sufficiently filter out foreign elements, several serious, lifethreatening, medical conditions can result. A new study suggests that chronic kidney disease may also be linked with tooth loss. Results of the survey are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
A woman’s glomerular filtration rate shows how well her kidneys are functioning. Kidney function decreases with time after menopause and is associated with declining reproductive hormone levels. These hormone changes during menopause also often lead to abdominal obesity, which is an independent risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease and also linked with a higher risk of tooth loss.
The consequences of kidney disease are numerous, including an increased probability of experiencing problems with bone and cardiovascular health. Tooth loss, which reflects oral health status, is also associated with systemic diseases, such as diabetes, thyroid disease, and osteoporosis, and is independently associated with an increased risk of stroke. Excessive tooth loss can also impair chewing and speech.
Previous studies have identified an association between kidney function and tooth count. This newest study involving nearly 65,000 participants, however, is the first known to evaluate the association between chronic kidney disease and tooth loss in postmenopausal women across the ages. It concluded that the glomerular filtration rate, a measure of kidney function, is significantly associated with having at least 20 (of a total of 28) adult teeth, suggesting that chronic kidney disease and tooth loss are significantly associated, especially in postmenopausal women aged 66 to 79 years.
These findings suggest that preventing and managing mineral and bone metabolism disorders in postmenopausal women with chronic kidney disease are crucial to prevent tooth loss. It is also important to address kidney disease progression, as the consequences affect multiple body systems beyond just oral health.
Survey results are published in the article “Chronic kidney disease in postmenopausal women is associated with tooth loss.”
“This study highlights the known link between chronic kidney disease and bone metabolism. Increased attention to oral and bone health is warranted in postmenopausal women with chronic kidney disease, in addition to meticulous efforts aimed at preserving kidney function. Conversely, oral health is a window to overall health, and good oral hygiene is important for women of all ages,” says Dr. Stephanie Faubion, medical director for The Menopause Society.
For more information about menopause and healthy aging, visit www.menopause.org. The Menopause Society (formerly The North American Menopause Society) is dedicated to empowering healthcare professionals and providing them with the tools and resources to improve the health of women during the menopause transition and beyond. As the leading authority on menopause since 1989, the nonprofit, multidisciplinary organization serves as the independent, evidence-based resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, the media, and the public and leads the conversation about improving women’s health and healthcare experiences. To learn more, visit menopause.org.
END
New study suggests kidney function is associated with tooth loss in postmenopausal women
Low tooth count is linked with systemic diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disease, and osteoporosis, plus an increased risk of stroke
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
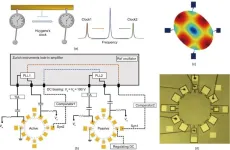
Breakthrough MEMS Huygens clock improves timekeeping precision and stability
2024-06-12
In a significant development for the miniaturization of electronic devices, a new study published in Engineering has reported the creation of a Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) clock that offers improved precision and stability. The clock, which utilizes the synchronization principle discovered by the Christiaan Huygens, consists of two synchronized MEMS oscillators and a frequency compensation system.
The research details how the MEMS Huygens clock enhances short-time stability, with the Allan deviation – a measure of the clock’s accuracy over time – improving by a factor of 3.73 from 19.3 ppb to 5.17 ppb at 1 second. The clock's long-term ...
HKUMed’s world-first ‘Liver-in-Cube’ wins a gold medal at International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva, advancing precise cancer treatment
2024-06-12
Background
Liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer and third leading cause of cancer death globally. According to Hong Kong Cancer Registry data, there are approximately 1,800 new cases of liver cancer each year, with over 1,500 deaths, over 80% of which are advanced cases at first diagnosis. Patients with advanced liver cancer who are not suitable for surgical operations have limited treatment options. Traditional chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy for treating advanced liver cancer often have a low response rate and severe side effects, thereby limiting their efficacy and hindering the patient’s quality ...
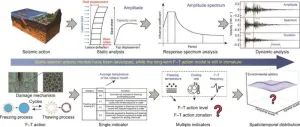
Nationwide zonation and durability assessment of China’s plateau infrastructure under freeze–thaw cycles
2024-06-12
In a bid to tackle the enduring problem of infrastructure durability in the face of relentless freeze–thaw (F–T) cycles, a team of researchers has published a new study in Engineering. The study focuses on the Chinese Plateau region, where the harsh effects of F–T cycles on concrete structures have led to concerns regarding their aging and subsequent performance deterioration.
The authors of the study emphasize that the existing national standards for designing frost-resistant concrete structures are insufficient, as they rely primarily on the coldest monthly average temperature without accounting for the intricate spatiotemporal variations, amplitude, and ...
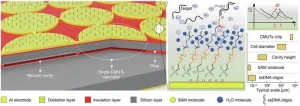
Innovative CMUT-based resonant biosensor offers enhanced DNA detection specificity
2024-06-12
In the latest study, researchers have successfully demonstrated a novel biosensor capable of detecting single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides with high specificity without needing external labels. This advancement paves the way for more accessible and efficient point-of-care diagnostics, as reported in a recent study published in Engineering.
The biosensor in question is based on capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTs), which have shown promise for developing miniaturized, high-performance biosensing platforms. However, previous ...
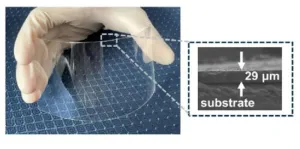
Transparent organic–inorganic hybrid photoresist with highly tunable refractive index for advanced display
2024-06-12
Researchers at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT) and BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd. (BOE) have developed a novel type of transparent organic–inorganic hybrid photoresist with highly tunable refractive index. The study published in Engineering presents the synthesis of transparent photoresist made of titanium dioxide nanoparticle-embedded acrylic resin with a tunable refractive index of up to 2.0 (589 nm) after being cured by ultraviolet (UV) light, while maintaining both a high transparency of over 98% in the visible ...
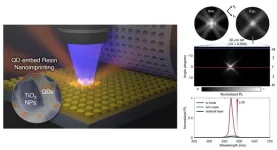
Quantum dots and metasurfaces: Deep connections in the nano world
2024-06-12
In relationships, sharing closer spaces naturally deepens the connection as bonds form and strengthen through increasing shared memories. This principle applies not only to human interactions but also to engineering. Recently, an intriguing study was published demonstrating the use of quantum dots to create metasurfaces, enabling two objects to exist in the same space.
Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Department of Chemical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering, ...
Researchers at Houston Methodist find survival improves with open radical hysterectomy in early-stage cancer
2024-06-12
Early-stage cervical cancer patients see better survival and decreased recurrence rates after open radical hysterectomy than minimally invasive laparoscopic approaches, according to a 5-year study led by Houston Methodist researchers and published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“The findings from this and an initial study in 2018 led to the change in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines established that same year that for radical hysterectomy we routinely perform an open approach. This latest study reaffirms this recommendation,” ...
Rise in global number of patient harms from 11 million to 18 million (59%) in 30 years
2024-06-12
The proportion of patient harms associated with medical procedures, treatment, and contact with healthcare systems rose by 59%, from 11 million to 18 million globally between 1990 and 2019, finds a data analysis published online in the journal BMJ Quality & Safety.
They outpaced the increase in the world’s population of 45% over the same period. And older people bore the brunt of these incidents, with the steepest rise among 65-69 year olds, the findings show.
In developed nations, over 50% of inpatient ...
Few UK people likely to be suitable for new Alzheimer’s drugs when they come on stream
2024-06-12
Few people in the UK with early stage Alzheimer’s disease are likely to be suitable for the latest drugs which aim to halt progress of the condition, yet many are nevertheless likely to be referred for these treatments, finds research published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The disease-modifying drugs, lecanemab and donanemab, slow cognitive decline in people with early stage Alzheimer’s disease. And they have been granted ‘breakthrough therapy’ ...
Retraction notice of previously press released research
2024-06-12
The research “Acupuncture for low back and/or pelvic pain during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials,” published in the open access journal BMJ Open in 2022, has been retracted.
This research was press released in November 2022 under the title of “Acupuncture can relieve lower back/pelvic pain often experienced during pregnancy.”
Following publication of the research, various issues concerning its design and reporting methods came to light, none of which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] New study suggests kidney function is associated with tooth loss in postmenopausal womenLow tooth count is linked with systemic diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disease, and osteoporosis, plus an increased risk of stroke