Groundbreaking study uncovers new insights into alternative splicing and disease associations
2024-06-12
(Press-News.org)
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers harness long-read RNA sequencing to decode genetic intricacies and disease links.
Tokyo, Japan – Alternative splicing, a process where a single gene can give rise to multiple different proteins via inclusion or exclusion of certain segments of the gene sequence, is known to occur in over 90% of human genes. This leads to the production of numerous transcript isoforms (splice variants of an expressed gene) crucial for protein function and cellular processes. Despite previous research on mechanisms underlying alternative splicing and genetic variants affecting splicing, understanding the complete diversity of isoforms has been challenging.
In a study published on 28 May 2024 in Nature Communications, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) in Japan revealed significant new insights into alternative splicing and its association with complex diseases, especially immune-mediated diseases. This research highlights the limitations of traditional short-read sequencing methods in capturing the full spectrum of isoform diversity, emphasizing the revolutionary potential of long-read sequencing technology.
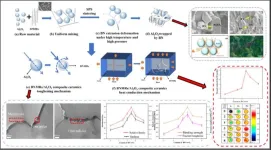
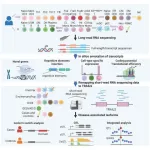
The study employed long-read RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), a technique that can determine the base sequence of long regions of RNA molecules, to map RNA transcripts in 29 immune cell subsets from a healthy individual. Long-read sequencing technology, compared to widely-used short-read sequencing technology, can improve mapping accuracy, genome assembly, and structural variation detection. This approach allowed for the identification of novel isoforms, the understanding of cell-type-specific splicing patterns, and the exploration of the role of repetitive DNA sequences in isoform diversity. It involved a comprehensive characterization of transcript isoforms within the purified immune cell subsets, followed by validation with additional peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Researchers compiled this information into a database, which they named TRAILS. Put simply, TRAILS is a database that contains the full-length structure of expressed genes in human immune cells.
One of the study's significant findings was the identification of numerous readthrough transcripts, such as a novel isoform at the TOMM40-APOE locus linked to Alzheimer's disease. This highlights the importance of these understudied isoforms in disease genetics. Additionally, the research revealed cell-type-specific splicing patterns and their impact on gene function, particularly through 3'-UTR regions, along with the relationship between transcript features and translational efficiency.
Furthermore, using TRAILS, researchers performed an integrated analysis of paired RNA-seq and genotype data and identified several transcripts associated with the risk of developing immune-related diseases. The number of disease-linked transcripts identified by TRAILS was greater than that of the widely used public atlas, GENCODE, indicating the utility of TRAILS specifically for immune cells.
Professor Yuta Kochi, the lead author of the study, explains, “We leveraged integrative genetic analyses to identify isoforms associated with specific diseases. These disease-associated transcripts include previously unknown transcripts that, combined with the detailed transcript information in our extensive database, allowed us to infer the mechanism of the disease.”
Dr. Jun Inamo, the first author, highlights, “These findings advance our understanding of the association between alternative splicing and disease genetics. By uncovering previously unknown isoforms and exploring their implications in disease pathways, our study could pave the way for more targeted and effective interventions for complex diseases.”
This study marks a crucial milestone in genomic research, emphasizing the importance of understanding alternative splicing in unraveling the complexities of human genetics. It advances our understanding of immune system complexities and disease mechanisms and provides insights into human genome evolution and immune system functions. By linking genomic data with functional analysis, TRAILS aids in our understanding of the pathology of immune-mediated diseases and other conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
The discoveries made in this research thus have the potential to revolutionize the genomic field, offering hope for improved diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in the future.
###
The article, “Long-read sequencing for 29 immune cell subsets reveals disease-linked isoforms” was published in Nature Communications at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48615-4
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-12
Many modern bridges use orthotropic steel bridge decks (OSBD), the decks being the surface sections of the bridge. OSBDs were designed to be lightweight and economical. However, this design has shown increasing issues with pavement cracking and fatigue damage at the welds that connect the bridge deck to the bridge superstructure. Fatigue damage is damage that accrues over time with use.
To ameliorate these problems, a new bridge deck was designed. The composite bridge deck system (CBD) added a layer of concrete to decrease the probability of damage due to fatigue. More recently the use of high-performance materials, such as ultra-high-performance ...
2024-06-12
In recent years, the high complexity of integrated devices has made heat accumulation increasingly critical and has resulted in higher heat dissipation requirements for substrates and packaging materials. In this study, boron nitride microribbon (BNMR)/Al2O3 composite ceramics are prepared using spark plasma sintering (SPS). This study examines the effect of varying the amount of toughened phase BNMR on the density, mechanical properties, dielectric constant, and thermal conductivity of BNMR/Al2O3 composite ceramics while also exploring the mechanisms behind the toughening and increased ...
2024-06-12
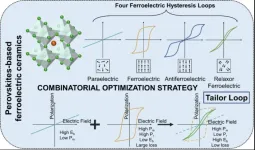
With the escalating impacts of climate change and depletion of resources, dielectric capacitors are emerging as promising high-demanded candidates for high-performance energy storage devices. However, due to the shortcomings of various dielectric ceramics (e.g., paraelectrics, ferroelectrics, and antiferroelectrics), their low polarizability, low breakdown strength, and large hysteresis loss limit their standalone use in the advancing of energy storage ceramics. Therefore, synthesizing novel perovskite-based materials that exhibit high energy density, high energy efficiency, and low loss is crucial in achieving superior energy ...
2024-06-12
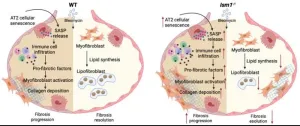
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic and progressive lung disease marked by the thickening and scarring of lung tissue with unclear etiology. Affecting around five million people worldwide, IPF causes severe respiratory problems and greatly diminishes the quality of life. Despite ongoing medical research, the exact cause of IPF is still unknown, and treatment options are limited. The prognosis for IPF is grim, with only about 20% of patients surviving five years post-diagnosis, highlighting the critical need for better therapies and a deeper understanding ...
2024-06-12
Thermoelectric technology, which enables the direct conversion of heat into electricity, has emerged as a promising alternative energy source. Notably, this technology can efficiently convert body heat into electrical energy, garnering significant attention in the field of wearable electronics. However, the dense structure of most thermoelectric materials results in ultra-low moisture permeability. In practical applications, insufficient moisture permeability can trap heat and humidity, fostering bacterial growth and potentially causing skin lesions. Hence, developing thermoelectric materials with superior moisture permeability is crucial.
A team led by ...
2024-06-12
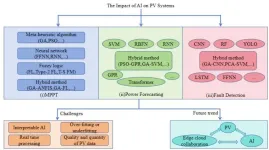
Artificial intelligence is poised to bring photovoltaic systems into a new era through revolutionary improvements in efficiency, reliability, and predictability of solar power generation.
In their paper published on May 8 in CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research, a research team from Chinese and Malaysian universities explored the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) technology on photovoltaic (PV) power generation systems and their applications from a global perspective.
“The overall message is an optimistic outlook on how AI can lead to more sustainable and efficient energy solutions,” said Xiaoyun Tian from ...
2024-06-12
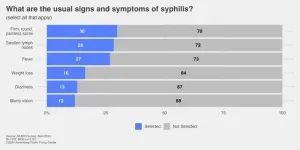
PHILADELPHIA – Syphilis cases are on the rise around the globe, but many Americans don’t know the symptoms.
In January, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that syphilis cases had risen 80 percent over the five years from 2018 to 2022, totaling more than 200,000 in 2022, the last year for which data are available.
Yet just over half of U.S. adults (54%) know that a case of syphilis can be permanently cured and most either mistakenly think there is a vaccine to prevent it (16%) or are unsure (45%), according to the Annenberg Public Policy ...
2024-06-12
The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters today announced the 2024 Kavli Prize Laureates in the fields of astrophysics, nanoscience, and neuroscience. The 2024 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience honors McGovern Investigator and MIT neuroscientist Nancy Kanwisher, UC Berkeley neurobiologist Doris Tsao, and Rockefeller University neuroscientist Winrich Freiwald for their discovery of a highly localized and specialized system for representation of faces in human and non-human primate neocortex. The neuroscience laureates ...
2024-06-12
Eight scientists from three countries are honored for their research that has broadened our understanding of the big, the small and the complex.
June 12, 2024 (Oslo, Norway) — The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters today announced the 2024 Kavli Prize Laureates in the fields of astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscience. Eight scientists from three countries are honored for their research that has broadened our understanding of the big, the small and the complex. The laureates in each field will share $1 million USD.
The ...
2024-06-12
Washington, D.C—The nasal microbiota of intensive care unit (ICU) patients effectively distinguishes sepsis from non-septic cases and outperforms analyzing the gut microbiota to predict sepsis, according to a new study published in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“These findings have implications for the development of diagnostic strategies and advancements in critical care medicine,” said corresponding study author Xiaolong He, M.D., Ph.D., a professor at the Microbiome Medicine Center, Department of Laboratory Medicine, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Groundbreaking study uncovers new insights into alternative splicing and disease associations