(Press-News.org) Eight scientists from three countries are honored for their research that has broadened our understanding of the big, the small and the complex.
June 12, 2024 (Oslo, Norway) — The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters today announced the 2024 Kavli Prize Laureates in the fields of astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscience. Eight scientists from three countries are honored for their research that has broadened our understanding of the big, the small and the complex. The laureates in each field will share $1 million USD.
The 2024 Kavli Prizes recognize groundbreaking science for the discovery and characterization of extra-solar planets and their atmospheres; foundational research integrating synthetic nanoscale materials for biomedical use; and the localization of areas in the brain specialized for face recognition and processing.
The 2024 Kavli Prize Laureates are:
Kavli Prize in Astrophysics: David Charbonneau (Canada/USA) and Sara Seager (Canada/USA)
Kavli Prize in Nanoscience: Robert S. Langer (USA), Armand Paul Alivisatos (USA) and Chad A. Mirkin (USA)
Kavli Prize in Neuroscience: Nancy Kanwisher (USA), Winrich Freiwald (Germany), and Doris Tsao (USA)
“The Kavli Prize 2024 honors outstanding researchers doing fundamental science that moves the world forward. They are exploring planets outside our solar system; they have broadened the scientific field of nanoscience towards biomedicine; and they are adding to our understanding of the neurological basis of face recognition,” said Lise Øvreås, president at The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters.
Astrophysics: Searching for life beyond Earth
The 2024 Kavli Prize in Astrophysics honors Sara Seager and David Charbonneau for discoveries of exoplanets and the characterization of their atmospheres. They pioneered methods for the detection of atomic species in planetary atmospheres and the measurement of their thermal infrared emission, setting the stage for finding the molecular fingerprints of atmospheres around both giant and rocky planets. Their contributions have been key to the enormous progress seen in the last 20 years in the exploration of myriad exo-planets.
“Humans have always looked towards the stars for discoveries. The pivotal research conducted by Seager and Charbonneau has been an important first step towards finding new planets and strong evidence of life elsewhere in the universe,” remarked Viggo Hansteen, Chair of the Astrophysics Committee.
David Charbonneau led the team that used the transit method to discover a giant exoplanet (HD 209458b). He pioneered the application of space-based observatories to perform the first studies of the atmosphere of giant extrasolar planets. This new method measures the tiny amount of light blocked by such a planet as it passes in front of its host star. Charbonneau has also used the transit method to study exoplanetary atmospheres, measuring molecular spectra using both filtered starlight and infrared emission from the planets themselves. He demonstrated these two approaches with observations from the Hubble Space Telescope in 2002 and the Spitzer Space Telescope three years later.
Sara Seager pioneered the theoretical study of planetary atmospheres and predicted the presence of atomic and molecular species detectable by transit spectroscopy, most notably the alkali gases. She predicted how transits could be used to measure atomic and molecular characteristics in exoplanetary atmospheres, which is crucial for identifying biomarkers – signs of life. Seager made outstanding contributions to the understanding of planets with masses below that of Neptune. She also carried out extensive research on starshades – enormous petal-like structures designed to shield space observatories from the glare of a faraway Sun-like star – and was among the first to recognize their importance in detecting and characterizing the faint light from any Earth-like planet orbiting the star.
Nanoscience: Integrating nanomaterials for biomedical advances
The 2024 Kavli Prize in Nanoscience honors Robert S. Langer, Armand Paul Alivisatos and Chad A. Mirkin who each revolutionized the field of nanomedicine by demonstrating how engineering nanoscale materials can advance biomedical research and application. Their discoveries contributed foundationally to the development of therapeutics, vaccines, bioimaging and diagnostics.
“The three scientists, Langer, Alivisatos and Mirkin, have broadened the scientific field of nanoscience, building from fundamental research. By scientific curiosity they have become inventors for the future of nanoscience and biomedicine,” stated Bodil Holst, Chair of the Nanoscience Committee.
Robert S. Langer was the first to develop nano-engineered materials that enabled the controlled release, or regular flow, of drug molecules. This capability has had an immense impact for the treatment of a range of diseases, such as aggressive brain cancer, prostate cancer and schizophrenia. His work also showed that tiny particles, containing protein antigens, can be used in vaccination, and was instrumental in the development of the delivery of mRNA vaccines.
Armand Paul Alivisatos demonstrated that semiconductor nanocrystals, or quantum dots (nanoparticles that possess bright, size-dependent light-emitting properties), can be used as multicolor probes in bioimaging. Essential to this achievement was the synthesis of biocompatible nanocrystals. Semiconductor nanocrystals became the basis for the widely used research and diagnostic tools such as live cell tracking, labelling and in vivo imaging.
Chad A. Mirkin engineered spherical nucleic acids (SNA) using a gold nanoparticle as the core, and a cloud of radially distributed DNA or RNA strands as the shell. He was then able to show how SNAs can be combined to create larger structures and how they can be used in biodiagnostics. His discovery led to the development of fast, automated point-of-care medical diagnostic systems.
Neuroscience: Understanding recognition of faces
The 2024 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience honors Nancy Kanwisher, Doris Tsao and Winrich Freiwald for the discovery of a specialized system within the brain to recognize faces. Their discoveries have provided basic principles of neural organization and made the starting point for further research on how the processing of visual information is integrated with other cognitive functions.
“Kanwisher, Freiwald and Tsao together discovered a localized and specialized neocortical system for face recognition. Their outstanding research will ultimately further our understanding of recognition not only of faces, but objects and scenes,” commented Kristine Walhovd, Chair of the Neuroscience Committee.
Nancy Kanwisher was the first to prove that a specific area in the human neocortex is dedicated to recognizing faces, now called the fusiform face area. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) she found individual differences in the location of this area and devised an analysis technique to effectively localize specialized functional regions in the brain. This technique is now widely used and applied to domains beyond the face recognition system.
Elaborating on Kanwisher’s findings, Winrich Freiwald and Doris Tsao studied macaques and mapped out six distinct brain regions, known as the face patch system, including these regions’ functional specialization and how they are connected. By recording the activity of individual brain cells, they revealed how cells in some face patches specialize in faces with particular views.
Tsao proceeded to identify how the face patches work together to identify a face, through a specific code that enables single cells to identify faces by assembling information of facial features. For example, some cells respond to the presence of hair, others to the distance between the eyes.
Freiwald uncovered that a separate brain region, called the temporal pole, accelerates our recognition of familiar faces, and that some cells are selectively responsive to familiar faces.
More details available at www.kavliprize.org
Kavli Prize Committees
Astrophysics
Viggo Hansteen (Chair), University of Oslo, Norway
Francoise Combes, Observatoire de Paris, France
Martha Haynes, Cornell University, USA
Thomas Henning, Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Germany
Max Pettini, University of Cambridge, UK
Nanoscience
Bodil Holst (Chair), University of Bergen, Norway
Daniel Esteve, CEA, France
Naomi Halas, Rice University, USA
Shuit-Tong Lee, Soochow University, China
Tanja Weil, Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Germany
Neuroscience
Kristine B. Walhovd (Chair), University of Oslo, Norway
Angela Friederici, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Germany
John O’Keefe, University College London, UK
Christine Petit, Institut Pasteur, France
Marcus Raichle, Washington University School of Medicine, USA
About The Kavli Prize
The Kavli Prize is a partnership among The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters, The Norwegian Ministry of Education and Research, and The Kavli Foundation (USA). The Kavli Prize honors scientists for breakthroughs in astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscience that transform our understanding of the big, the small and the complex. Three one-million-dollar prizes are awarded every other year in each of the three fields. The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters selects the laureates based on recommendations from three independent prize committees whose members are nominated by The Chinese Academy of Sciences, The French Academy of Sciences, The Max Planck Society of Germany, The U.S. National Academy of Sciences, and The Royal Society, UK.
All 2024 Kavli Prize Laureates
Kavli Prize in Astrophysics:
David Charbonneau (Canada/USA), Harvard University
Sara Seager (Canada/USA), Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
Kavli Prize in Nanoscience:
Armand Paul Alivisatos (USA), University of Chicago
Robert S. Langer (USA), Koch Institute of Integrative Cancer Research at MIT
Chad A. Mirkin (USA), Northwestern University
Kavli Prize in Neuroscience:
Winrich Freiwald (Germany/USA), The Rockefeller University
Nancy Kanwisher (USA), Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Doris Tsao (USA), The University of California, Berkeley
For more information, please contact:
Marina Tofting (Norway)
The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters
(+ 47) 938 66 312
marina.tofting@dnva.no
Stacey Bailey (United States)
The Kavli Foundation
(+1) 310 739 2859
sbailey@kavlifoundation.org
END
2024 Kavli Prize Laureates named in astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscience
Eight scientists from three countries are honored for their research that has broadened our understanding of the big, the small and the complex.
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nasal microbiota is potential diagnostic biomarker for sepsis
2024-06-12
Washington, D.C—The nasal microbiota of intensive care unit (ICU) patients effectively distinguishes sepsis from non-septic cases and outperforms analyzing the gut microbiota to predict sepsis, according to a new study published in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“These findings have implications for the development of diagnostic strategies and advancements in critical care medicine,” said corresponding study author Xiaolong He, M.D., Ph.D., a professor at the Microbiome Medicine Center, Department of Laboratory Medicine, ...
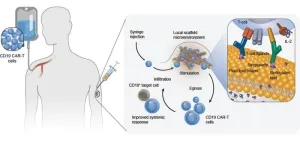
Boosting CAR-T cell therapies from under the skin
2024-06-12
T-cell stimulating biomaterial that slowly biodegrades under the skin stimulates CAR-T cells in the body to improve therapeutic efficacy in an aggressive mouse tumor model.
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — CAR-T cell therapies are transforming the treatment of previously incurable blood cancers. Six approved CAR-T products have been administered to more than 20,000 people, and more than 500 clinical trials are underway. However, according to a recent study out of the Massachusetts General Hospital, ...
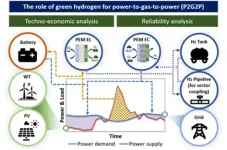
Overcoming the volatility of renewable energy, green hydrogen is 'the best'
2024-06-12
A research team in Korea Institute of Energy Research has successfully demonstrated the effectiveness of a green hydrogen system used to supplement the volatility of renewable energy.
*Green hydrogen: Hydrogen obtained by electrolysis of water, in which electrical energy derived from renewable sources such as solar and wind power is applied to water to produce hydrogen and oxygen. This production method is an environmentally friendly hydrogen production process with no carbon dioxide emissions.
Dr. Joungho Park and his research team at the Energy ...
Redefining "hormonal": The new nonprofit empowering women
2024-06-12
Hormonally.org is a digital platform that provides free-to-access, evidence-based resources designed to empower women (and all those affected by hormones) to seek the appropriate care, treatment, and support they deserve. Hormonally’s mission is to make access to information on women’s hormonal health a more equitable experience for all.
The new nonprofit organization offers accessible information and a safe place to discuss and discover everything from the first period to post-menopause. Hormonally ...
MD Anderson and Sibylla Biotech announce strategic collaboration to discover and develop small-molecule protein degraders
2024-06-12
HOUSTON and MILAN ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Sibylla Biotech today announced a strategic collaboration agreement to discover and develop novel small-molecule cancer therapies known as folding interfering degraders (FIDs), which disrupt the proper folding of target proteins and lead to their degradation.
Under the agreement, Sibylla and MD Anderson will jointly conduct discovery and development work from target identification through drug candidate nomination on selected proteins, with the potential ...
Uncovering the nature of emergent magnetic monopoles
2024-06-12
Magnetic monopoles are elementary particles with isolated magnetic charges in three dimensions. In other words, they behave as isolated north or south poles of a magnet. Magnetic monopoles have attracted continuous research interest since physicist Paul Dirac’s first proposal in 1931. However, real magnetic monopoles have not yet been observed and their existence remains an open question. On the other hand, scientists have discovered quasi-particles that mathematically behave as magnetic monopoles in condensed ...
New study shows long-term effectiveness of gastric bypass in treating type 2 diabetes and obesity
2024-06-12
SAN DIEGO – June 12, 2024 -- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, a type of weight-loss surgery, kept type 2 diabetes in remission for up to 15 years and most of the weight off for up to 20 years in one of the largest long-term studies of patients undergoing the procedure. The study* was presented today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Researchers from Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, PA analyzed diabetes remission rates and weight-loss outcomes of 2,045 patients who had a gastric bypass at their center between 2001 and 2008 ...
Hokkaido University scientist recognized in award from the Royal Society of Chemistry
2024-06-12
The NSF Center for Molecularly Optimized Networks team, of which Professor Jian Ping Gong of the Faculty of Advanced Life Science and the Institute for Chemical Reaction Design and Discovery (WPI-ICReDD) at Hokkaido University is a member, has won a Horizon Prize from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC)’s Prizes portfolio is one of the oldest and most prestigious in the world, recognizing achievements by individuals, teams and organizations in advancing the chemical sciences. They reward those undertaking excellent work in the chemical sciences from across the world. The NSF Center for Molecularly Optimized Networks team, including Professor ...
Cocaine trafficking threatens critical bird habitats
2024-06-12
ITHACA, N.Y. – In addition to its human consequences, cocaine trafficking harms the environment and threatens habitats important to dozens of species of migratory birds, according to a new study.
Two-thirds of the areas that are most important to forest birds – including 67 species of migratory birds that breed in the U.S. and Canada and overwinter in Central America – are at increased risk from cocaine trafficking activities, according to the study, “Intersection of Narco-Trafficking, Enforcement and Bird Conservation ...
Humans are the elephant in the room where conservation is debated
2024-06-12
Humans are outsized actors in the world’s wild places where there are struggles to preserve and protect vital natural resources and animals, birds and plants. Yet people and their plus-sized footprint are rarely discussed in models seeking to predict and plan for trajectories of endangered species.
Sustainability scholars at Michigan State University in this week’s journal Nature Ecology and Evolution reveal the decades-long gaps in research and propose a new way of creating accurate visions for endangered species.
To map and predict species ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] 2024 Kavli Prize Laureates named in astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscienceEight scientists from three countries are honored for their research that has broadened our understanding of the big, the small and the complex.