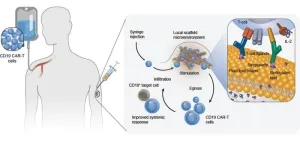
T-cell stimulating biomaterial that slowly biodegrades under the skin stimulates CAR-T cells in the body to improve therapeutic efficacy in an aggressive mouse tumor model.
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — CAR-T cell therapies are transforming the treatment of previously incurable blood cancers. Six approved CAR-T products have been administered to more than 20,000 people, and more than 500 clinical trials are underway. However, according to a recent study out of the Massachusetts General Hospital, among 100 patients suffering from lymphomas, myelomas or B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias that were treated with CAR-T cell therapies, 24% only had partial responses, and 20% were not responsive at all – and these are typical success rates for patients treated with CAR-T therapies.
CAR-T cells are created from a patient’s own immune T cells by introducing so-called “chimeric antigen receptors” (CARs) to their molecular repertoires that enable them to seek out and kill specific cancer cells. Following their laborious and costly engineering and amplification outside the body, they are re-administered to the same patient as a living therapeutic.
Oncological researchers suspect that disappointing treatment results can be the result of several circumstances, including poor quality of the CAR-T cell products that are administered to patients, or the CAR-T cells not persisting sufficiently long in patients or becoming exhausted in their tumor-fighting abilities. New therapeutic strategies are urgently needed that can help overcome these shortcomings and further boost the quality and efficacy of CAR-T cells during their manufacturing or even in the patients' bodies.
Now, a research team at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) has developed a simple intervention in the form of a biodegradable scaffold material that can be locally injected under the skin and used to restimulate CAR-T cells after their administration to increase their therapeutic efficacy. In mice that developed an aggressive blood tumor and were treated with a non-curative dose of CAR-T cells, the team’s “T-cell enhancing scaffolds” (TES) significantly curbed tumor growth and prolonged the animals’ survival. The improved therapeutic efficacy of the CAR-T cells was due to TES’ ability to increase the numbers of CAR-T cells in the blood circulation, as well as steer their differentiation into tumor-killing subtypes of T cells. The findings are published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“Although our strategy needs to be translated to human needs and settings, it potentially offers a safe, and simple avenue on which to further improve CAR-T cell therapies in patients with poor responses,” said Wyss Founding Core Faculty member David Mooney, Ph.D., who led the study. “It also could have future potential to simplify the extremely arduous and expensive manufacturing of CAR-T cell by transferring part of the process into patients’ bodies.” Mooney is also the Robert P. Pinkas Family Professor of Bioengineering at SEAS.
A number of CAR-T cell-stimulating approaches have been developed that, besides introducing CAR receptors, made other genetic modifications to patients’ T cells to better maintain their therapeutic efficacies (cell-intrinsic) or that, inspired by vaccines, target other parts of the immune system to support CAR-T cells in their tumor cell attack (cell-extrinsic). However, most of them involve new challenges, including even more complex cell manipulations during CAR-T cell manufacturing and control of the resulting cells’ behavior in the case of cell-intrinsic methods, or unintended side-effects in the body in the case of cell-extrinsic methods.
Creating a pseudo-lymph node under the skin
“Previously, our team had designed biomaterial scaffolds that enabled the expansion of T-cells for immunotherapies in a culture dish by mimicking antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which normally reprogram T-cells in lymph nodes by presenting tumor antigens to them. We hypothesized that this basic concept could also be applied to potently stimulate CAR-T cells in the body – TES could essentially function as pseudo-lymph nodes,” said co-first author David Zhang, who obtained his Ph.D. working in Mooney’s group.
TES biomaterial scaffolds consist of tiny biodegradable mesoporous silica rods (MSRs) that self-assemble into a 3D, cell-permeable scaffold structures when injected under the skin, and connect themselves to the blood circulation via small blood vessels. TES are loaded with a soluble molecule known as interleukin-2 (IL-2), which is continuously released and stimulates the multiplication of T cells entering the TES from the blood circulation. In addition, the MSRs are coated with a double layer of lipids that mimics the outer cell membrane of an APC a T-cell would encounter in a lymph node. This lipid layer presents two antibody molecules, anti-CD3 and anti-CD28, to the T-cell receptor on the surface of T cells in a way similar to how APC-presented tumor antigens normally stimulate the receptors. This then induces the CAR-T cells to increase their numbers and differentiate into tumor-killing subtypes of T cells.
First, the researchers determined optimal anti-CD3:anti-CD28 antibody ratios and quantities in TES that helped recruit maximum numbers of cultured CAR-T cells and induce them to become “effector T-cells” with tumor cell-killing potential. When injected under the skin of mice, TES connected themselves with the animals’ vasculature and remained traceable as vascularized nodules for more than three weeks. More than 60% of the cells permeating their porous network were neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that acts as the immune system’s first line of defense, while a much smaller but significant proportion consisted of T cells that usually are part of delayed and much more target-specific tumor cell (or pathogen)-directed immune defenses.
The researchers think that “by causing some minor inflammation, TES scaffolds stimulate their vascularization and help attract certain classes of immune cells, which would add to the immune cells traveling passively through TES,” said co-first Joshua Brockman, Ph.D., who was a Postdoctoral Fellow on Mooney’s team and now is an Assistant Professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. “By removing the injected scaffolds again at different time points, culturing them with CAR-T cells, and measuring the cells’ activation level, we were able to conclude that TES could stimulate CAR-T cells for at least seven days following their injection.”
TESting in tumors
To test TES’ potential as therapy boosters, the team used a clinically-relevant mouse model of human Burkitt’s lymphoma, a blood cancer caused by B-cells becoming cancerous and impacting many organs. They first administered human lymphoma cells to the mice and then gave them a curative dose of CAR-T cells developed against this tumor before injecting TES under the skin of the animals. Importantly, TES that contained the full complement of IL-2, anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 factors, increased the numbers of circulating CAR-T cells more than five-fold over blank TES lacking the three factors, and more CAR-T cells had acquired a tumor cell-killing potential. When lower doses of CAR-T cells that were not sufficient to cure the cancer (subcurative doses) were used in otherwise the same settings, CAR-T cells multiplied even more.
“TES took up CAR-T cells into their porous structure, where they boosted their proliferation, activation, and differentiation, and eventually their exit into the blood stream to carry out their tumor-killing functions,” summarized Zhang. “And, importantly, while lymphoma-bearing animals that received subcurative doses of CAR-T cells and blank TES succumbed quickly to the spreading cancer, animals injected with CAR-T cells plus fully functional TES survived for much longer.”
Brockman added that “this aggressive lymphoma mouse model was an ideal tool to provide proof-of-concept. However, it corresponds to a cancer patient at late stages of the disease whose treatment requires a lot of cytotoxic T cell potential. In translating TES further toward human patients, even longer-lasting and more balanced approaches might be called for that also enhance the CAR-T cells’ memory of tumors.”
“This study by Dave Mooney’s group demonstrates the power of using engineering to mimic multicellular interactions that are central to our immune system's ability to fight off cancers. This technology could go a long way in changing the lives of many cancer patients receiving CAR-T therapies who are not yet benefitting from them,” said Wyss Founding Director Donald Ingber, M.D., Ph.D., who is also the Judah Folkman Professor of Vascular Biology at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, and the Hansjörg Wyss Professor of Bioinspired Engineering at SEAS.
Other authors on the study are Kwasi Adu-Berchie, Yutong Liu, Yoav Binenbaum, Irene de Lázaro, Miguel Sobral, and Rea Tresa. The study was funded by the Wyss Institute at Harvard University, Food and Drug Administration (under award# 5F01FD006589), and National Institutes of Health (under award# 1R01EB015498, #R01 CA276459, and U01CA214369).
PRESS CONTACTS
Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University
Benjamin Boettner, benjamin.boettner@wyss.harvard.edu
###
The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University (www.wyss.harvard.edu) is a research and development engine for disruptive innovation powered by biologically-inspired engineering with visionary people at its heart. Our mission is to transform healthcare and the environment by developing ground-breaking technologies that emulate the way Nature builds and accelerate their translation into commercial products through formation of startups and corporate partnerships to bring about positive near-term impact in the world. We accomplish this by breaking down the traditional silos of academia and barriers with industry, enabling our world-leading faculty to collaborate creatively across our focus areas of diagnostics, therapeutics, medtech, and sustainability. Our consortium partners encompass the leading academic institutions and hospitals in the Boston area and throughout the world, including Harvard’s Schools of Medicine, Engineering, Arts & Sciences and Design, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston Children’s Hospital, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital, Boston University, Tufts University, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, University of Zürich, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
The Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (http://seas.harvard.edu) serves as the connector and integrator of Harvard’s teaching and research efforts in engineering, applied sciences, and technology. Through collaboration with researchers from all parts of Harvard, other universities, and corporate and foundational partners, we bring discovery and innovation directly to bear on improving human life and society.
END