(Press-News.org) Thousands of years ago, people in ancient Syria likely ate mostly grains, grapes, olives and a small amount of dairy and meat — similar to today’s “Mediterranean diet,” according to a study published June 12 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Benjamin T. Fuller from the University of Leuven, Belgium, Simone Riehl from the University of Tübingen, Germany, and colleagues.
Tell Tweini, an archeological site located near the Syrian coastal city of Jableh, contains relics dating back to the early Bronze Age (around 2,600 BCE) and stretching all the way into the Iron Age, nearly 2,300 years later. For the new study, researchers used isotopic analyses of plant, animal and human remains from the site to map how nutrients flowed through the food chain and agricultural systems on this land over time.
Some of the most interesting results came from the Middle Bronze Age (between 2000 and 1600 BCE). Human remains from this period showed a relatively low level of δ15N — a nitrogen isotope — which indicates a diet mostly based on plants, such as grains and olives. But archaeologists have also found the remains of sheep, goats and cattle from Tell Tweini that suggest that these animals were occasionally eaten and used for milking, meaning the local residents were likely consuming some animal-based protein as well. This diet is similar to the modern day “Mediterranean diet” that highlights grains, fruits and vegetables with fewer animal products, often touted for its health benefits.
Other isotopic analyses from Tell Tweini may shed light on some of the climate and agricultural practices of the people who lived there. For example, all of the grapes found at Tell Tweini have relatively high levels of the Δ13 isotope of carbon, which suggests that the fruits received enough water and were well looked after throughout the site’s history.
The authors add: “Thanks to the interdisciplinary and technical progress of archaeological science, we can not only speculate on the existence of a long cultural tradition of the Mediterranean diet through taxonomic and typological determinations, but also extend these findings through additional analyses, e.g. of stable isotopes in human, animal and plant remains, and thus contribute to a better understanding of the emergence of cultural traditions in their anchoring in environmental and social dynamics.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301775
Citation: Fuller BT, Riehl S, Linseele V, Marinova E, De Cupere B, Bretschneider J, et al. (2024) Agropastoral and dietary practices of the northern Levant facing Late Holocene climate and environmental change: Isotopic analysis of plants, animals and humans from Bronze to Iron Age Tell Tweini. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0301775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0301775
Author Countries: Belgium, Germany, Canada
Funding: SR acknowledges that part of the stable carbon isotope measurements on barley was conducted with funds from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG; project RI 1193/6-2; www.dfg.de; Project website: https://gepris.dfg.de/gepris/OCTOPUS; Grant #163597005). We acknowledge support by Open Access Publishing Fund of University of Tübingen. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Ancient Syrian diets resembled the modern “Mediterranean diet”
Researchers analyzed chemistry of plant, animal, human remains to study historic food chains
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Greek Island was home to Bronze Age purple dye workshop
2024-06-12
The Greek island of Aegina was home to a Late Bronze Age purple dye workshop, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lydia Berger of Paris Lodron University of Salzburg, Austria and colleagues.
Colored dyes were a significant commodity in the Mediterranean region during the Late Bronze Age, and understanding the production of these dyes is valuable for interpretations of culture and trade at the time. In this study, Berger and colleagues describe the site of a purple dye workshop from the 16th century BC located at Aegina Kolonna in the Saronic Gulf.
The presence of a dye workshop at this site is inferred from three main lines of ...
Housing compatible shelter dogs together could reduce stress and might help them find homes sooner
2024-06-12
Housing compatible shelter dogs together could reduce stress and might help them find homes sooner
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301137
Article Title: Effects of single- or pair-housing on the welfare of shelter dogs: Behavioral and physiological indicators
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The current research was funded by a grant to ENF from the Waltham Foundation (grant number) www.waltham.com. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to ...
When the TV show Neighbours ended, surveyed fans experienced strong grief, loss, and sometimes a lack of closure - implying that strong "parasocial" relationships link TV viewers and favorite shows
2024-06-12
When the TV show Neighbours ended, surveyed fans experienced strong grief, loss, and sometimes a lack of closure - implying that strong "parasocial" relationships link TV viewers and favorite shows
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302160
Article Title: When TV neighbours become good friends: Understanding Neighbours fans’ feelings of grief and loss at the end of the series
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: The author received no ...
Some honeybees learn tasks better than others, and gene expression patterns in their brains may be associated with this difference in ability
2024-06-12
Some honeybees learn tasks better than others, and gene expression patterns in their brains may be associated with this difference in ability
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304563
Article Title: Behavioral and genetic correlates of heterogeneity in learning performance in individual honeybees, Apis mellifera
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Incorporating “touch” into social media interactions can increase feelings of support and approval
2024-06-12
Including “tactile emoticons” into social media communications can enhance communication, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alkistis Saramandi and Yee Ki Au from University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues.
Digital communications rely exclusively on visual and auditory cues (text, emoticons, videos, and music) to convey tone and emotion. Currently lacking from these platforms is touch, which can convey feelings of love and support, impact emotions, and influence behaviors. Technology companies are developing devices to incorporate touch into digital interactions, such as interactive kiss ...
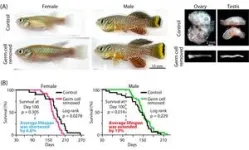
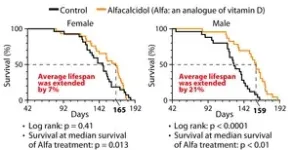
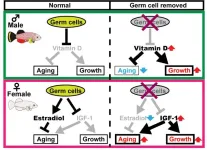
The gender gap in life expectancy: are eggs and sperm partly responsible?
2024-06-12
Osaka, Japan – Women live longer than men. This isn’t unique to humans, either; we see this trend in a wide range of other animals. Biologists have theorized that the discrepancy in life expectancy between sexes might be partly related to reproduction, but how?
In a study published in Science Advances, researchers from Osaka University have discovered for the first time that germ cells, the cells that develop into eggs in females and sperm in males, drive sex-dependent lifespan differences in vertebrate animals.
The researchers ...
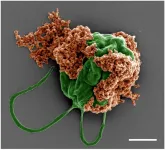
Swimming microrobots deliver cancer-fighting drugs to metastatic lung tumors in mice
2024-06-12
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed microscopic robots, known as microrobots, capable of swimming through the lungs to deliver cancer-fighting medication directly to metastatic tumors. This approach has shown promise in mice, where it inhibited the growth and spread of tumors that had metastasized to the lungs, thereby boosting survival rates compared to control treatments.
The findings are detailed in a paper published on June 12 in Science Advances.
The microrobots are an ingenious combination of biology ...
Ambivalence + polarized views can promote political violence
2024-06-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Feeling ambivalent about a political issue might seem to be a recipe for indecision and even inaction.
But a new study suggests, surprisingly, that ambivalence can actually lead some people –especially those with polarized views – to be more supportive of extreme actions, such as violence.
The reason? Researchers found that ambivalence creates discomfort in those with extreme views by making them feel weak or insecure about their beliefs – and that can lead them to compensate for that weakness by supporting extreme actions to signal strength.
“When people have ...
Unleashing the power of metamaterials to improve MRI imaging
2024-06-12
In recent years, the field of metamaterials has experienced substantial growth, revealing exciting potential, especially in advancing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology. Three new studies led by Dr. Xin Zhang, a BU College of Engineering Distinguished Professor and a professor at the BU Photonics Center, highlight the promising opportunities within this field. These studies, in collaboration with Dr. Stephan Anderson, a BU Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine professor of radiology, published in Advanced Science, Advanced Materials, and Science Advances, showcase innovative approaches to enhance the MRI experience for all patients. ...
USC EdTech Accelerator collaborates with Intel
2024-06-12
USC Rossier Education Technology Accelerator (USC EdTech Accelerator) announced a unique collaboration with Intel Corporation focused on supporting the use of technology for learning with a particular emphasis on supporting marginalized communities and AI.
The Partnership
The USC EdTech collaboration with Intel will provide free educational and technical assistance to learning-focused start-ups to increase the likelihood that they design viable, efficacious and scalable AI-enhanced solutions for learners. “We believe ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Ancient Syrian diets resembled the modern “Mediterranean diet”Researchers analyzed chemistry of plant, animal, human remains to study historic food chains