(Press-News.org) The ecosystem that surrounds a tumor, also known as the tumor microenvironment, includes immune cells, tissues, blood vessels and other cells that interact with each other and with the tumor. Over time, the tumor shapes this ecosystem to its own benefit, monopolizing all of the nutrients and shielding it from immune attack. In working to understand the ecosystem’s role in cancer risk, development and treatment, researchers at The Jackson Laboratory have not only identified how two immune cells work together to fight cancer but also revealed the cascade of molecules that help coordinate this attack.
The work, led by JAX Assistant Professor Chih-Hao “Lucas” Chang, Ph.D., focuses on cytotoxic T-cells, a type of immune cell with many functions, including destroying cells infected with viruses and fighting bacterial infections and other pathogens. They also attack tumor cells. Our immune systems are able to eliminate most cancerous cells from our body before they can cause a problem. But once a tumor becomes established, cytotoxic T-cells become “exhausted” in the hostile tumor microenvironment and unable to effectively attack tumors. Chang and colleagues are investigating why these immune cells become exhausted, and potential ways to signal them back to targeting tumors.
“T-cells are excellent at identifying and attacking cells that become cancerous, but they can become exhausted in the tumor microenvironment; they can become overworked and overstimulated, while also being starved of glucose and other nutrients by tumor cells. Helping these cells to function better could improve cancer treatment strategies, particularly immunotherapies,” said Chang, whose work appears in Cancer Immunology Research.
Previous studies showed that when cytotoxic T-cells are activated, they release signaling molecules called cytokines. Chang and colleagues focused on one of these cytokines, interleukin-3 (IL-3), discovering that as a tumor grows, cytotoxic T-cells progressively lose the ability to produce IL-3 in the tumor microenvironment. Then, when Chang elevated IL-3 levels in mice bearing lymphoma or melanoma tumors, he observed strong antitumor effects.
Chang’s team further revealed that IL-3 works to mobilize basophils, a rare immune cell that can also play a role in allergies. In turn, these basophils produce another cytokine known as interleukin-4 (IL-4), which reenergizes cytotoxic T-cells, signaling them to resume detecting and destroying tumors. “Basophils have not previously been implicated in the signaling cascade for reinvigorating cytotoxic T-cells,” said Chang. “These findings are preliminary, but targeting tumor-associated basophils represents a promising avenue for enhancing antitumor immunity and improving patient outcomes.”
END
Reinvigorating exhausted immune cells reveals potential therapy target for cancer
Reenergizing exhausted T cells, with help from a rare immune cell known as a basophil, can kickstart the immune system into fighting cancer.
2024-06-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
After major traumatic brain injury, more blood transfusions could mean better outcomes
2024-06-13
Québec City, June 13, 2024–Increased use of blood transfusions after major traumatic brain injury could help people hospitalized in intensive care units regain greater functional independence and a better quality of life.
Six months after a major traumatic brain injury (TBI), patients who benefited from this approach regained more functional independence and had a better quality of life than those subjected to a more restrictive approach, even though the combined incidence of death and major ...
Low-dose glucocorticoids in SLE
2024-06-13
In a session on diagnosing and managing complex diseases at the 2024 EULAR congress in Vienna, two abstracts tackled this issue.
First, Filippo Vesentini presented on the risk of flare with glucocorticoid compared to low-dose maintenance – based on a retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data from people with SLE. Flare-free remission and predictors of such were evaluated respectively in remitted patients on and off glucocorticoids.
During follow-up, 484 patients achieved remission at least once during ...
Implementing physical activity recommendations
2024-06-13
An HPR abstract sessions at the 2024 EULAR congress looked specifically at harnessing the benefits of exercise in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMD) – and the challenges to their practical implementation.
Mohamed Saadi presented a systematic review examining barriers and facilitators affecting adherence to EULAR’s physical activity recommendations. Across 68 selected articles, 29 different themes were identified – 9 of which were social, 16 environmental, and 4 systemic. The five most frequently found themes were having supportive family and friends, a supportive health professional, followed by costs, and access or proximity to adapted and ...
Achieving drug-free remission in AXSPA
2024-06-13
Even though early therapeutic interventions have proven successful in inducing drug-free remission in other inflammatory rheumatic diseases, such studies remain difficult to conduct in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), which manifests itself by insidious onset inflammatory back pain. As a result it is often diagnosed late,5 and a consensus definition of early disease was only recently published.6
At the 2024 EULAR congress, Łukasik and colleagues shared data from their prospective study evaluating the efficacy of a ...
Unpicking the pathogenesis of RA
2024-06-13
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation and destruction.1 There is currently no cure – and although there are many treatments, their effectiveness varies from person to person, suggesting an undefined pathogenic diversity.1 Deep characterisation of myeloid cell subsets by single cell RNA sequencing across healthy and inflamed tissues in RA has led to the identification of new pathogenic cell states and subsets – with data coming from five large-scale studies.1-5 But subset overlap across studies and compartments – such as in blood versus synovial tissue – has not yet ...
Kids First DRC launches enhanced data portal to strengthen collaborative pediatric research
2024-06-13
The Gabriella Miller Kids First Data Resource Center (Kids First DRC) announces the release of an upgraded Kids First Data Resource Portal, designed to streamline big data search and data analysis. Accessible at portal.kidsfirstdrc.org, the new portal represents a significant advancement in data accessibility, user experience, and collaborative potential with researchers, families, and patients.
Elevated User Experience
Introducing several key enhancements, the new Kids First DRC Portal prioritizes user-centric ...
Neural balance in the brain is associated with brain maturity and better cognitive ability
2024-06-13
In a world where external and internal stimuli can throw our entire body system off balance, how does our brain prevent itself from becoming overly stimulated?
The answer lies in our brain’s ability to maintain the balance of neural excitation (E) and inhibition (I), known as the E/I ratio. By regulating the E/I ratio, the brain prevents over-stimulation and under-stimulation.
The E/I ratio of children decreases with healthy development. Children with a lower E/I ratio were observed to have better performance than their peers in cognitive tests such as memory and intelligence, according to studies by researchers from the Centre for Sleep and Cognition ...
Parliamentary members use simpler language on hot days
2024-06-13
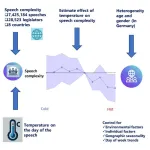
Climate change has many widespread and complicated effects on the well-being of people and the planet, and a new study in iScience on June 13 has now added a surprising one to the list. After analyzing the language used in seven million parliamentary speeches around the world, it shows that high temperatures lead to a significant and immediate reduction in politicians’ language complexity.
The results suggest that rising heat may come with impacts on our cognitive abilities with real and immediate consequences, the researchers say. The study also showcases ...
Food: Greater gender equality associated with men eating meat more frequently than women
2024-06-13
Men tend to eat meat more frequently than women and the extent of the differences in meat consumption frequency between both genders tend to be greater within countries with higher levels of gender equality and social and economic development, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The authors suggest that this could be due individuals within these countries having greater opportunities to express food preferences.
Christopher Hopwood and colleagues investigated differences in meat consumption between men and women across countries with differing levels of social ...
Antipsychotic medications don’t just stop working below the neck
2024-06-13
PITTSBURGH, June 13, 2024 – New University of Pittsburgh research points to a potential approach to reducing the risk of diabetes associated with widely prescribed antipsychotic medications.
The study presents early evidence in support of co-administering antipsychotic medications that block dopamine receptors in the brain alongside drugs that stop antipsychotics from blocking those same receptors in the pancreas. This approach, published today in Diabetes, could limit metabolic side effects, including impaired control over blood sugar, or dysglycemia.
This research may also explain why weight control medications, including new neuropeptide drugs Wegovy and Ozempic, may not ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Reinvigorating exhausted immune cells reveals potential therapy target for cancerReenergizing exhausted T cells, with help from a rare immune cell known as a basophil, can kickstart the immune system into fighting cancer.