New approach to identifying altermagnetic materials
Theoretical simulations and synchrotron experiments reveal the hidden fingerprint of new magnets
2024-06-14
(Press-News.org)
Magnetic materials have traditionally been classified as either ferromagnetic, like the decorative magnets on iron refrigerator doors that are seemingly always magnetic, or antiferromagnetic, like two bar magnets placed end-to-end with opposite poles facing each other, canceling each other out so that the material has no net magnetism. However, there appears to be a third class of magnetic materials exhibiting what in 2022 was dubbed altermagnetism.
Microscopically, magnetism arises from a collection of tiny magnets associated with electrons, called spin. In ferromagnetic materials, all the electron spins point in the same direction, while in antiferromagnetic materials, the electron spins are aligned in opposite directions, half pointing one way and half the other, canceling out the net magnetism. Altermagnetic materials are proposed in theory to possess properties combining those of both antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic materials. One potential application of altermagnetic materials is in spintronics technology, which aims to utilize the spin of electrons effectively in electronic devices such as next-generation magnetic memories. However, identifying altermagnets has been a challenge.
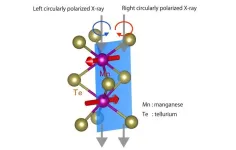
An international research group led by Associate Professor Atsushi Hariki from the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University pioneered a new method to identify altermagnets, using manganese telluride (α-MnTe) as a testbed.
With the aid of a supercomputer, the researchers theoretically predicted a fingerprint of altermagnetism in X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), which measures the absorption difference between left- and right-circularly polarized light. Then, using the Diamond Light Source synchrotron in England, they experimentally demonstrated the XMCD spectrum for altermagnetic α-MnTe for the first time in the world.
“Our results show that XMCD is an effective method for the simple identification of altermagnetic materials,” Professor Hariki said. “Also, it can be expected to further accelerate the application of altermagnets in spintronics.”
The findings were published in Physical Review Letters.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-14
Magnesium compounds are a common ingredient of many remedies designed to help people wind down and escape the stresses of modern life.
However, a new study has shown it is not only humans that are using forms of the chemical as a way to help them survive challenging conditions.
In tests conducted on beaches in Cornwall, and in the laboratory at the University of Plymouth, scientists confirmed the findings of previous studies which showed large sandhoppers (Talitrus saltator) increase the levels of magnesium ions in their bodies as temperatures fall. This slows them down so they are less active than they would be during the warmer months.
However, the new study has shown for the first time ...
2024-06-14
Report highlights trajectory challenges for women in elite football
A new report commissioned by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) and Fédération Internationale des Associations de Footballeurs Professionnels (FIFPRO), undertaken by Edith Cowan University (ECU), surveyed footballers across 12 countries in six confederations. More than 700 players participated in the survey, with 71.5% classifying themselves as professional, with a further ...
2024-06-14
Men are often urged to talk about their mental health with friends, but what does that involve?
This week, researchers from the Men’s Health Research Program at UBC introduced In Good Company, a website and podcast series aimed at answering precisely that question. The website provides practical advice for men seeking to make new connections, strengthen existing relationships and provide mutual support. The podcast series interviews men’s health experts and psychologists to explore the nuances and benefits of authentic male connection. Both ...
2024-06-14
Excess sodium intake and a lack of potassium are major contributing factors towards high blood pressure in Indonesia, prompting calls for low-sodium potassium-rich salt substitutes (LSSS) to be readily available to improve health and curb health costs.
New Griffith University research has looked at the impact of switching out current table salt (100 per cent sodium chloride) with a low-sodium alternative in Indonesia.
Lead author Dr Leopold Aminde from the School of Medicine and Dentistry said the World Health Organisation has recommended a population-wide reduction in sodium consumption to tackle the burden of high blood pressure and ...
2024-06-14
Background
High-temperature fusion plasma experiments conducted in the Large Helical Device (LHD) of the National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS), have renewed the world record for an acquired data amount, 0.92 terabytes (TB) per experiment, in February 2022, by using a full range of state-of-the-art plasma diagnostic devices*1. The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), which is currently under construction in France through the international collaboration of seven parties, is expected to generate ...
2024-06-14
EMBARGOED for release until 1pm U.S. Central Time (2pm Eastern) on June 13, 2024
HOUSTON – (June 13, 2024) – Solar power is not only the fastest growing energy technology in recent history but also one of the cheapest energy sources and the most impactful in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
A Rice University study featured on the cover of today’s issue of Science describes a way to synthesize formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3) ⎯ the type of crystal currently used to make the highest-efficiency perovskite solar cells ⎯ into ultrastable, high-quality photovoltaic films. The overall efficiency of the resulting ...
2024-06-14
A group of researchers from the University of Tartu and international scientists discovered new mechanisms of how stroke occurs by studying changes in mouse and human cells. The study lays the foundation for new, more precise treatment methods and better diagnostics, which could improve cardiovascular health in the future.
One of the authors of the study, a PhD student of Faculty of Medicine of University of Tartu Katyayani Sukhavasi said that affecting people of all ages, every fifth minute, someone suffers a stroke resulting in brain bleeding or ischemia. „Consequently, many people die ...
2024-06-14
Long term thinking and stable, consistent policies are key to improving our nation’s financial prosperity and wellbeing, say experts on The BMJ Commission on the Future of the NHS as they set out their manifesto for a healthier UK.
The BMJ Commission brings together leading experts from medicine and healthcare to identify the key challenges and priorities and make recommendations aimed at ensuring that the vision of the NHS is realised.
Their key pledges of what they would do if they were in government are:
Reaffirming ...
2024-06-14
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- An international team led by researchers at the University of California, Riverside, has made a significant breakthrough in how to enable and exploit ultra-fast spin behavior in ferromagnets. The research, published in Physical Review Letters and highlighted as an editors’ suggestion, paves the way for ultra-high frequency applications.
Today’s smartphones and computers operate at gigahertz frequencies, a measure of how fast they operate, with scientists working to make them even faster. The new research has found a way to achieve terahertz frequencies using conventional ferromagnets, which ...
2024-06-14
A new report offers lessons for post-pandemic transit policy and planning. Notably, it calls for planners to downplay the role of offices in transit station areas and increase the opportunity for people to live in them. Researchers Arthur C. Nelson and Robert Hibberd published "Transit Station Area Development and Demographic Outcomes (PDF)," updating their longitudinal analysis of the impacts of development near transit stations.
The new report includes a foreword by U.S. Congressman Earl Blumenauer. An excerpt reads:
"In this report, Arthur ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New approach to identifying altermagnetic materials
Theoretical simulations and synchrotron experiments reveal the hidden fingerprint of new magnets