A call for renaming clinical research partnerships
2024-06-17
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA (June 17, 2024) - In a recently published opinion piece in BMJ Open, “Rhetoric of Research: A Call for Renaming the Clinical Research Partnership,” authors from Penn Nursing and Georgetown University School of Nursing, present a compelling argument for rethinking the language used to describe participants in clinical research. The opinion calls for a shift from the traditional term “patient participant” to “participant partner,” emphasizing the crucial role of participants in all facets of the research process.
The opinion piece traces the historical context of terms used to describe research participants. Initially referred to as “human subjects,” the terminology evolved to “patients” and then to “patient participants.” Despite these changes, the authors highlight that the existing terms suggest a power imbalance.
The authors, Anessa M. Foxwell, MSN, CRNP, ACHPN, doctoral student, and Connie M. Ulrich, PhD, RN, FAAN, Professor of Nursing and the Lillian S. Brunner Chair in Medical and Surgical Nursing, both from Penn Nursing; and Lillie LaRochelle, CNP, from Georgetown, argue this language does not properly reflect the value and contribution participants make to their studies. The term ‘’patient-participants’’ is seen as archaic because it sustains an authoritarian relationship in which researchers are regarded as holders of power while participants become dormant. The expression ‘’participant partners’’ is meant to emphasize the partnership between researchers and those taking part in research, thus creating a more inclusive environment.
The report describes different clinical trials that prove the advantages of involving participants as research partners. The ADAPTABLE aspirin study and the CONNECT-HF trial, for example, embedded patients in advisory capacities to enhance recruitment messages, understand patient perspectives, and improve other overall trial outcomes. These are but a few examples that show how a partnership model can improve clinical research quality and impact.
The article provides several basic principles for using “participant partner” terminology:
Dialogue and Discourse: Involve relevant stakeholders in talks on the new terminology as well as its effects.
Shared Values: Formulate an arrangement based upon such things as reciprocity, solidarity, advocacy, procedural justice, and transparency.
Inclusive Participation: Ensure that participants and their carers participate in various stages of the process.
Mutual Support: Have an interface through which patients can share opinions with researchers.
Transparent Processes: Establish clear mechanisms for addressing ethical and other concerns during research.
The authors conclude that changing the rhetoric around patient participation is a small but significant step towards recognizing the true partnership in clinical research. By adopting the term “participant partner,” the research community can take a meaningful step towards valuing those who contribute to scientific advancements.
# # #
About the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
The University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing is one of the world’s leading schools of nursing. For the ninth year in a row, it is ranked the #1 nursing school in the world by QS University. For the third year in a row, our Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program is ranked # 1 in the 2024 U.S. News & World Report’s Best Colleges rankings. Penn Nursing is also consistently ranked highly in the U.S. News & World Report annual list of best graduate schools and is ranked as one of the top schools of nursing in funding from the National Institutes of Health. Penn Nursing prepares nurse scientists and nurse leaders to meet the health needs of a global society through innovation in research, education, and practice. Follow Penn Nursing on: Facebook, X, LinkedIn, YouTube, & Instagram.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-17
SAN ANTONIO — June 17, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) today celebrated the groundbreaking of the Center for Accelerating Materials and Processes (CAMP), a new facility that will support research and development for tomorrow’s high-speed aerospace engines.
“This project will help ensure the U.S. is a leader in high-speed propulsion research and development,” said Dr. Barron Bichon, director of SwRI’s Materials Engineering Department. “SwRI is committed to advancing this vital technology on behalf of Texas and the nation.”
Market forces including growth in global defense, air travel, ...
2024-06-17
Since the very first instant after the Big Bang the Universe has been expanding. This means that the early Universe was considerably smaller and early-formed galaxies were more likely to interact and merge. Galaxy mergers fuel the formation of quasars — extremely luminous galactic cores where gas and dust falling into a central supermassive black hole emit enormous amounts of light. So when looking back at the early Universe astronomers would expect to find numerous pairs of quasars in close proximity to each other as their host galaxies undergo mergers. However, they have been surprised ...
2024-06-17
Roughly 50 families scattered across the world share ultra-rare variants in a particular gene. Silent for years, the inherited mutations make themselves known when patients reach the fourth decade of life. Changes in vision start a cascade of symptoms. Five to 20 years later, the illness is fatal.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have dedicated many years to understanding the rare condition known as retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy and systemic manifestations, or RVCL-S, with the aim of developing a treatment ...
2024-06-17
A new smartphone face-screening tool could help paramedics to identify stroke in seconds – much sooner and more accurately than is possible with current technologies.
Strokes, which affect millions of people globally, occur when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, which prevent brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. A few minutes of delay can result in permanent damage to the brain cells.
A team of biomedical engineers at RMIT University developed the AI capabilities behind the software technology and has published their results ...
2024-06-17
WASHINGTON, June 17, 2024 — L-DOPA is the best drug we have for Parkinson’s disease, but its molecular mirror image, D-DOPA, causes dangerous side effects. Making L-DOPA without also making D-DOPA is surprisingly hard and requires a specific kind of molecule to pull off. But that specific molecule must be made from a different and equally specific molecule. In this video, our host, George Zaidan, explains how one of the winners of the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry pulled it off, and why "chiral synthesis," as it's called, is really just turtles all the way down. https://youtu.be/_cb09XB07LQ?si=BuMEI5fOuHmuQlkZ
Reactions is a video series ...
2024-06-17
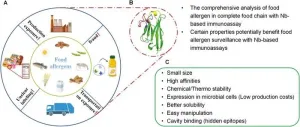
Recent advancements show nanobodies from camelid antibodies excel in food allergen detection with superior stability, specificity, and cost-effectiveness. This innovative approach aims to improve accuracy and efficiency, crucial for preventing severe allergic reactions. The study highlights nanobodies' potential in reliable immunoassays, addressing rising food allergies and enhancing safety measures.
Food allergies pose significant health risks, affecting millions worldwide, with the prevalence rising over the past decades. Traditional detection methods, such as monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, are often costly, labor-intensive, and prone to cross-reactions. The need for ...
2024-06-17
Researchers from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that among a cohort of 137,000 Medicare beneficiaries who experienced a nonfatal overdose in 2020, almost 24,000 (17.4%) experienced a subsequent nonfatal overdose, and about 1,300 (1%) died from overdose in the following year. Results were published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, identifying both effective interventions and significant gaps in care.
“People who have experienced ...
2024-06-17
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Mass General Brigham researchers analyzed 4,400 cognitively unimpaired adults with amyloid imaging, finding increased amyloid in those who reported that their mothers had symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Increased amyloid, a biomarker of AD, was also found in those with a history of the disease on both sides of their family and in those whose fathers had an early onset of symptoms.
The study suggests that a person’s maternal versus paternal family history could ...
2024-06-17
About The Study: More than 1 in 5 adults did not recover within 3 months of SARS-CoV-2 infection in this cohort study. Recovery within 3 months was less likely in women and those with preexisting cardiovascular disease and more likely in those with COVID-19 vaccination or infection during the Omicron variant wave.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Elizabeth C. Oelsner, M.D., M.P.H., email eco7@cumc.columbia.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.17440)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
2024-06-17
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial found that varenicline and nicotine-containing electronic cigarettes were both effective in helping individuals in quitting smoking conventional cigarettes for up to 6 months.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Anna Tuisku, Ph.D., email anna.tuisku@lapha.fi.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.1822)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A call for renaming clinical research partnerships