Fishy parenting? Punishing offspring encourages cooperation
Study shows fish may use punishment to promote help from their offspring
2024-06-18
(Press-News.org)
Osaka, Japan — While there is an increasing consensus among humans that corporal discipline of children does more harm than good, fish may disagree.
Ryo Hidaka, Shumpei Sogawa, Masanori Kohda and Satoshi Awata from Osaka Metropolitan University have demonstrated that a fish species employs physical punishment to elicit helping efforts from their offspring, indicating advanced social and cognitive skills previously thought to be unique to higher vertebrates.
The results of their study were published online in Animal Behaviour on April 6.
For millennia, human societies have used punishment to promote cooperation and maintain social order. But humans are not the only species seeking better cooperative behavior. So how do other animals achieve this?
Seeking an answer, the research team from the Graduate School of Science at Osaka Metropolitan University took a look at a rather taciturn animal: fish, more specifically, Neolamprologus savoryi, a cooperatively breeding cichlid fish.
“Even though punishment in cooperatively breeding cichlid fish has been studied, there is limited evidence that they use punishment to encourage cooperative behavior,” said Satoshi Awata, a professor at Osaka Metropolitan University and lead author of the study.
N. savoryi subordinates, or helpers, assist dominant breeders in, for example, defending territory against intruders or maintaining the breeding shelter. By observing the behavior of N. savoryi in a controlled laboratory setting, the researchers were able to manipulate and measure the effects of punishment on helping behavior.
Their results showed that dominant breeders physically attacked idle helpers — including their own offspring — to promote the latter’s participation in cooperative activities. Indeed, those experiencing such aggression subsequently increased their efforts in helping behaviors. In contrast, helpers who engaged proactively in helping behaviors avoided aggression from dominant breeders.
“Our study demonstrated that nonhuman animals also use punishment to elicit cooperative behaviors in group members,” Awata said.
The study’s findings highlight that punishment is not exclusive to human societies but is also present in how other animals enforce cooperation and maintain social relationships. This research bridges a gap in understanding the evolution of cooperative behavior and the mechanisms animals use to sustain it.
“Our findings reveal that fish, like humans, employ advanced cognitive abilities to sustain their societies. This compels us to reconsider the notion of ‘intelligence’ not only in fish but across the animal kingdom,” Awata said.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-18
To get high scores at essay writing tests, learners of English as a foreign language need to focus on good arguments more than on complex grammar. The Kobe University finding challenges conventional approaches to test preparation and scoring rubrics.
Writing essays is a well-established tool for monitoring progress in learning English as a foreign language, as it provides a snapshot of a student’s mastery of grammar and vocabulary. Especially in Japan, where English language tests are often required for university admission and students closely follow advice on how to achieve high scores on these tests, a “good essay” is often seen as one that demonstrates ...
2024-06-18
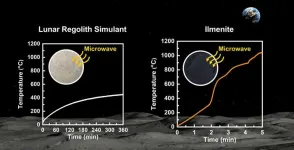
The United States’ NASA aims to construct a lunar base through the Artemis program, a manned lunar exploration initiative. However, the practical reality of what general public envision for the space base differs somewhat from well-known science fiction movies. To build a base on the Moon using abundant and diverse construction materials, significant transportation costs are involved. All these materials must be launched from Earth using rockets.
Because transporting construction materials from Earth to the ...
2024-06-18
Researchers from the Ontario Drug Policy Research Network (ODPRN) at St. Michael’s Hospital and Public Health Ontario analyzed health data from the Office of the Chief Coroner of Ontario and ICES, and found that there were 210 accidental opioid-related toxicity deaths within shelters between January 2018 to May 2022, with the number of deaths more than tripling during the study period (48 before the pandemic versus 162 during the pandemic).
Statistics Canada data shows that the annual number of emergency beds in Ontario grew by only 15% (6,764 to 7,767) between 2018 and 2022.
“People who use Ontario’s shelter system are not only facing housing instability, but ...
2024-06-18
With more working hours and lower average base pay, the well-being of U.S. teachers continues to be worse than that of similar working adults – a consistent pattern since 2021, according to a new RAND survey.
Managing student behavior, low salary and administrative work outside of teaching were the top-ranked sources of stress for teachers in 2024. Teachers reported working an average of 53 hours per week; 15 of these hours – or roughly one quarter of their working hours – were outside of their contracts. This compares to 44 hours per week for similar working adults. Only 36% of teachers said their base pay was adequate compared with 51% of similar ...
2024-06-18
An important chapter of the history of human occupation on the coast of Brazil is being rewritten by Brazilian researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo’s Museum of Archeology and Ethnology (MAE-USP) and supported by FAPESP.
In an article published in the journal PLOS ONE, the group, which also includes researchers in Santa Catarina state, South Brazil, and in other countries (the United States, Belgium and France), shows that the sambaqui builders of Galheta IV, an archeological ...
2024-06-18
Researchers from the University of Tokyo performed the first study to quantify highly processed food consumption and to investigate its association with diet quality among Japanese children and adolescents. Highly processed foods (HPFs) accounted for over one-fourth of the total energy intake amongst youths. Consumption was negatively associated with the intake of healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables and pulses, and positively associated with the consumption of confectioneries.
It's common knowledge that poor-quality diets are considered major risk factors for many health issues and even noncommunicable ...
2024-06-18
An international research team has discovered a new way to effectively treat cancer, by using nutrients to reactivate suppressed metabolic pathways in cancer cells.
The researchers used a common amino acid, tyrosine, packaged as a nanomedicine, to change the metabolism of melanoma, a deadly skin cancer, and prevent cancer growth.
Australia has the highest rate of skin cancer in the world. This new approach could be combined with current therapies to better treat melanoma. The technique also has the potential to treat other types of cancer.
The study, Nutrient-delivery and metabolism reactivation therapy for melanoma, was led by Professor Wenbo ...
2024-06-18
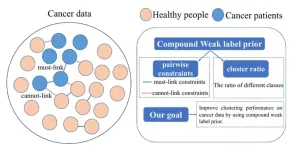
Clustering is widely exploited in data mining. It has been proved that embedding weak label prior into clustering is effective to promote its performance. Previous researches mainly focus on only one type of prior. However, in many real scenarios, two kinds of weak label prior information, e.g., pairwise constraints and cluster ratio, are easily obtained or already available. How to incorporate them to improve clustering performance is important but rarely studied.
To deal with this problem, a research team led by Chenping ...
2024-06-18
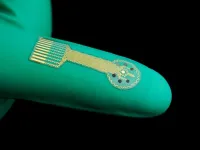
Chronic wounds, which include diabetic ulcers, surgical wounds, pressure injuries, and other problems, are deadlier than many people realize. Patients with chronic wounds have a five-year survival rate around 70%, worse than that of breast cancer, prostate cancer and other serious diseases. Treating wounds is also expensive, costing an estimated $28 billion each year in the U.S. alone.
A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) is developing a series of cutting-edge technologies to revolutionize wound care, including smart bandages that would automatically sense and ...
2024-06-18
A test that looks for genetic hallmarks of brain cancers in samples of cerebrospinal fluid can decrease the time to diagnosis and eliminate the need for invasive brain biopsies for some patients. Mass General Brigham experts in neurosurgery, cancer and pathology worked together to develop a rapid, genotyping test that can detect key mutations associated with brain cancers from samples taken during a lumbar puncture. The team evaluated the technique known as TetRS (Targeted Rapid Sequencing) among 70 patients admitted to Massachusetts General Hospital with new central nervous system ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fishy parenting? Punishing offspring encourages cooperation
Study shows fish may use punishment to promote help from their offspring