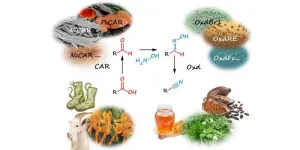
(Press-News.org) If the household cleaner emits a lemon-like odour, this may be due to a nitrile called citronellyl nitrile. These versatile chemical nitrile groups are also used in the manufacture of active pharmaceutical ingredients, superglue and chemical-resistant gloves. The prevalent production process used so far has required a chemical reaction of certain molecules with highly toxic cyanide. Margit Winkler from the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology at TU Graz, together with Ludmila Martínková from the Institute of Microbiology at the Czech Academy of Sciences, has now developed a biocatalytic process that does not require cyanide, works at room temperature and therefore requires less energy and produces less harmful waste. The project was funded by the Austrian Science Fund FWF and the Czech Science Foundation (GACR).
Two enzyme-guided steps
To replace the cyanide, the research group uses enzymes and combines three individual reactions into a cascade. The starting materials are carboxylic acids, such as fatty acids from plant oils or lignin, which is a by-product of wood processing. In the first step, the carboxylic acid is converted to an aldehyde by adding sugar, oxygen and the enzyme carboxylate reductase contained in living bacterial cells. However, this aldehyde is highly reactive and therefore unstable, and in many cases also volatile. To capture this substance, the aldehyde is allowed to react with hydroxylamine, which converts it into oxime, which is stable.
Oxime is a ‘watered’ form of nitrile, which is why the enzyme aldoxime dehydratase is used in the final step. This enzyme is also confined in bacterial cells and is responsible for water abstraction from the oxime. Once this has been done, the cascade has achieved its objective and the desired nitrile has been produced.
This method can now be used for the preparation of small nitrile quantities. This is already a promising technology for very potent fragrances, for example, of which only a small amount is needed to achieve an effect. Optimisation work is still required for the production of larger quantities of nitrile in order to be able to use the biocatalytic process at reasonable costs. Currently, highly diluted solutions are used in the first process step and a large reactor would be required to produce large quantities, which is not economic yet. Margit Winkler is therefore already conducting research on how to make the first step more efficient. Dehydration of the oxime alone, on the other hand, is extremely efficient and already reached technical maturity for production today.
A bio-based process
“I’ve been interested in cyanide chemistry ever since I wrote my master thesis, and as we know from Agatha Christie’s novels, cyanide is highly toxic,” says Margit Winkler. “It was therefore important for us to find a way to avoid this hazardous substance in production. The fatty acids we use come from vegetable oils. So, we really do have a bio-based production method here. We would now like to improve it even further so that it can be used widely.”
This research area is anchored in the Field of Expertise “Human & Biotechnology“, one of the five strategic research areas of TU Graz.
END
Enzymes instead of cyanide: Researchers develop biocatalytic process for nitrile production
A research team from Graz University of Technology and the Czech Academy of Sciences has used two enzymes to eliminate the need for highly toxic cyanide in the production of nitriles.
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
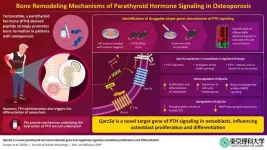
New study reveals promising drug target for treating osteoporosis
2024-06-18
Osteoporosis is a skeletal condition that leads to the weakening of bones, making them porous, fragile, and prone to breakage. A whopping 8.9 million fractures are caused by osteoporosis annually, with one fracture occurring every three seconds! The aging population is the most vulnerable to primary osteoporosis, given, their frailty, and often, requires long-term therapy and support. Advances in healthcare and the corresponding rise in the aging population have put a strain on available resources, underscoring the need for effective therapies against osteoporosis.
Induction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) signaling using the PTH-derived ...
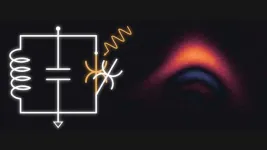
Breakthrough may clear major hurdle for quantum computers
2024-06-18
The potential of quantum computers is currently thwarted by a trade-off problem. Quantum systems that can carry out complex operations are less tolerant to errors and noise, while systems that are more protected against noise are harder and slower to compute with. Now a research team from Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, has created a unique system that combats the dilemma, thus paving the way for longer computation time and more robust quantum computers.
For the impact of quantum computers to be realised in society, quantum researchers first need to deal with some major obstacles. So far, errors and noise stemming from, for example, ...
Authority's physical proximity means greater obedience. New look at results of famous experiment
2024-06-18
Who should be spared pain, hurt or disappointment, and who should be harmed? This internal dilemma accompanied the participants of the Milgram experiment, say experts from SWPS University. They have revisited the causes of obedience in that famous study and showed that the experimenter's physical proximity promote subjects' obedience, while the learner's physical proximity decreases it.
American social psychologist Stanley Milgram's demonstration of the human tendency to show extreme obedience to authority was one of the most ...
Large wildfires create weather that favors more fire
2024-06-18
A new UC Riverside study shows soot from large wildfires in California traps sunlight, making days warmer and drier than they ought to be.
Many studies look at the effect of climate change on wildfires. However, this study sought to understand the reverse — whether large fires are also changing the climate.
“I wanted to learn how the weather is affected by aerosols emitted by wildfires as they’re burning,” said lead study author and UCR doctoral candidate James Gomez.
To find his answers, Gomez analyzed peak fire days and ...
Election administration performance linked to counties’ economic, racial makeup
2024-06-18
PULLMAN, Wash. – Voters who are neither wealthy nor white are more likely to live in counties with fewer resources available to make sure ballots are counted on time, a new election index revealed.
Researchers developed the County Election Administration index, detailed in the Election Law Journal, to evaluate election performance by county rather than just by state. Election administration encompasses the policies and processes that ensure election access, integrity and accuracy. Despite voter fraud claims in the last presidential election, researchers found that overall election performance ...
Blood markers detect rare forms of dementia as well as the neurological diseases ALS and PSP
2024-06-18
In a study with 991 adults, scientists at DZNE show that the most common forms of frontotemporal dementia (FTD) as well as the neurological diseases amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) can be recognised by blood testing. Their procedure is not yet ready for routine medical use, but in the long term it could facilitate disease diagnosis and advance the development of new therapies already now. The findings published in the journal “Nature Medicine” are based ...
Restored rat-free islands could support hundreds of thousands more breeding seabirds
2024-06-18
Hundreds of thousands more breeding pairs of seabirds could return to remote island archipelagos if invasive rats were removed and native vegetation restored – a new paper finds.
In a first of its kind study, researchers also calculated that there are enough fish in the seas surrounding the remote tropical islands that were the focus of the research within hunting range of seabirds to support these restored populations.
This is an important factor that has not been considered in previous island restoration studies and could become ...
University of the Witwatersrand chooses Figshare to support its open data goals
2024-06-18
Figshare, a leading provider of institutional repository infrastructure that supports open research, is pleased to announce that the University of the Witwatersrand Library has chosen Figshare to support its research community with archiving, publishing, sharing and promoting their datasets.
The University of the Witwatersrand (Wits) – a leading research institution in South Africa based in Johannesburg, ranked as the second best university in Africa 2024 (jointly with Stellenbosch University) – will ...
Cancer survivors are at increased risk of disease throughout life
2024-06-18
Swedish researchers have surveyed all people under the age of 25 who have had cancer since 1958. The study, led by researchers at Linköping University and Region Östergötland, shows that cancer survivors are at greater risk for cardiovascular diseases, other cancers and other diagnoses later in life. In addition, the researchers saw that socioeconomic factors played a role in survival.
Since 1958, Sweden has registered all cancer patients in the National Cancer Register. Swedish researchers have now used this register to study all cancer survivors who had cancer as a child, adolescent or adult to examine outcomes in later life. The results have been published ...
Fishy parenting? Punishing offspring encourages cooperation
2024-06-18
Osaka, Japan — While there is an increasing consensus among humans that corporal discipline of children does more harm than good, fish may disagree.
Ryo Hidaka, Shumpei Sogawa, Masanori Kohda and Satoshi Awata from Osaka Metropolitan University have demonstrated that a fish species employs physical punishment to elicit helping efforts from their offspring, indicating advanced social and cognitive skills previously thought to be unique to higher vertebrates.
The results of their study were published online in Animal Behaviour on April 6.
For millennia, human societies have used punishment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Enzymes instead of cyanide: Researchers develop biocatalytic process for nitrile productionA research team from Graz University of Technology and the Czech Academy of Sciences has used two enzymes to eliminate the need for highly toxic cyanide in the production of nitriles.