(Press-News.org) Scientists at the University of Cambridge have discovered that a type of white blood cell - called a regulatory T cell - exists as a single large population of cells that constantly move throughout the body looking for, and repairing, damaged tissue.
This overturns the traditional thinking that regulatory T cells exist as multiple specialist populations that are restricted to specific parts of the body. The finding has implications for the treatment of many different diseases – because almost all diseases and injuries trigger the body’s immune system.
Current anti-inflammatory drugs treat the whole body, rather than just the part needing treatment. The researchers say their findings mean it could be possible to shut down the body’s immune response and repair damage in any specific part of the body, without affecting the rest of it. This means that higher, more targeted doses of drugs could be used to treat disease – potentially with rapid results.
“We’ve uncovered new rules of the immune system. This ‘unified healer army’ can do everything - repair injured muscle, make your fat cells respond better to insulin, regrow hair follicles. To think that we could use it in such an enormous range of diseases is fantastic: it’s got the potential to be used for almost everything,” said Professor Adrian Liston in the University of Cambridge’s Department of Pathology, senior author of the paper.
To reach this discovery, the researchers analysed the regulatory T cells present in 48 different tissues in the bodies of mice. This revealed that the cells are not specialised or static, but move through the body to where they’re needed. The results are published today in the journal Immunity.
“It's difficult to think of a disease, injury or infection that doesn’t involve some kind of immune response, and our finding really changes the way we could control this response,” said Liston.
He added: “Now that we know these regulatory T cells are present everywhere in the body, in principle we can start to make immune suppression and tissue regeneration treatments that are targeted against a single organ – a vast improvement on current treatments that are like hitting the body with a sledgehammer.”
Using a drug they have already designed, the researchers have shown - in mice - that it’s possible to attract regulatory T cells to a specific part of the body, increase their number, and activate them to turn off the immune response and promote healing in just one organ or tissue.
“By boosting the number of regulatory T cells in targeted areas of the body, we can help the body do a better job of repairing itself, or managing immune responses,” said Liston.
He added: “There are so many different diseases where we’d like to shut down an immune response and start a repair response, for example autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, and even many infectious diseases.”
Most symptoms of infections such as COVID are not from the virus itself, but from the body’s immune system attacking the virus. Once the virus is past its peak, regulatory T cells should switch off the body’s immune response, but in some people the process isn’t very efficient and can result in ongoing problems. The new finding means it could be possible to use a drug to shut down the immune response in the patient’s lungs, while letting the immune system in the rest of the body continue to function normally.
In another example, people who receive organ transplants must take immuno-suppressant drugs for the rest of their lives to prevent organ rejection, because the body mounts a severe immune response against the transplanted organ. But this makes them highly vulnerable to infections. The new finding helps the design of new drugs to shut down the body’s immune response against only the transplanted organ but keep the rest of the body working normally, enabling the patient to lead a normal life.
Most white blood cells attack infections in the body by triggering an immune response. In contrast, regulatory T cells act like a ‘unified healer army’ whose purpose is to shut down this immune response once it has done its job - and repair the tissue damage caused by it.
The researchers are now fundraising to set up a spin-out company, with the aim of running clinical trials to test their findings in humans within the next few years.
END
Discovery of ‘new rules of the immune system’ could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases, say scientists.
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
5 Pew-Stewart Scholars chosen to advance innovative cancer research
2024-06-18
PHILADEPHIA—The Pew Charitable Trusts and the Alexander and Margaret Stewart Trust announced today the 2024 class of the Pew-Stewart Scholars for Cancer Research, five early-career scientists who will each receive four-year grants to explore new avenues in cancer development, diagnosis, and treatment. This is the 11th year the Alexander and Margaret Stewart Trust has partnered with Pew to cultivate a legacy of cutting-edge cancer research.
“Despite decades of groundbreaking research and innovative breakthroughs, millions of Americans are still all too familiar with the devastation and uncertainty of a cancer diagnosis,” ...
Pew funds 10 Latin American scientists conducting biomedical research
2024-06-18
PHILADELPHIA—The Pew Charitable Trusts today announced the 2024 class of the Pew Latin American Fellows Program in the Biomedical Sciences.
The 10 postdoctoral fellows from six Latin American countries—Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Cuba, Mexico, and Peru—will receive two years of funding to conduct research in laboratories across the United States. They will work under the mentorship of prominent biomedical scientists, including alumni from the Latin American fellows program and the Pew Scholars Program in the Biomedical Sciences.
“The grave threats to human health over the past few years—from COVID-19 to growing rates of cancer in younger adults—underscore ...
Accelerating drug discovery with the CCDC, AWS, and Intel
2024-06-18
Thanks to the combined computing power of Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Intel, the CCDC announces that a potentially significant advancement in drug discovery has been achieved. A curated data set of protein structures from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) with predicted hydrogen positions is now available for download. This project was supported by an Intel RISE Technology Initiative contribution.
Historically, collaborations with the pharmaceutical industry have enabled the development of reliable methods for interpreting interactions within protein binding sites using proprietary information not publicly available. Repeating these studies ...
Updates from the 2022 WHO classification of kidney epithelial tumors
2024-06-18
Renal tumor pathology has evolved considerably, expanding from two main types of renal malignant tumors to over 20 distinct types. Diagnostic criteria have advanced from purely morphological features to include histochemistry, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and molecular genetics. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Society of Urologic Pathology (ISUP) have been instrumental in updating these criteria, resulting in a comprehensive framework essential for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved patient outcomes.
The field of renal tumor pathology has undergone ...
Interdisciplinary team at MUSC Hollings Cancer Center maps role of P. gingivalis in drug resistance
2024-06-18
A new paper from an interdisciplinary team at MUSC Hollings Cancer Center describes how the bacteria Porphyromonas gingivalis interferes with chemotherapy-induced mitophagy, allowing oral cancer tumors to become resistant to the drug’s effects.
Besim Ogretmen, Ph.D., SmartState Endowed Chair in Lipidomics and Drug Discovery in the College of Medicine, and Ӧzlem Yilmaz, D.D.S., Ph.D., a professor, clinician-scientist and microbiologist in the College of Dental Medicine, worked with graduate ...
Astronomers see a massive black hole awaken in real time
2024-06-18
In late 2019 the previously unremarkable galaxy SDSS1335+0728 suddenly started shining brighter than ever before. To understand why, astronomers have used data from several space and ground-based observatories, including the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT), to track how the galaxy’s brightness has varied. In a study out today, they conclude that they are witnessing changes never seen before in a galaxy — likely the result of the sudden awakening of the massive black hole at its core.
“Imagine you’ve been observing a distant galaxy for years, and it always seemed calm and inactive,” ...
A review and update on therapy of gastrointestinal tract tumors: from the bench to clinical practice
2024-06-18
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, encompassing esophageal, gastric, small bowel, and colorectal carcinomas, represent a significant global health burden due to their high incidence and mortality rates. This review by M. Jesús Fernández-Aceñero et al. provides an in-depth analysis of the molecular characteristics, prognosis, and current therapeutic strategies for these malignancies, highlighting the latest advancements and challenges in the field.
Esophageal carcinoma is among the ten most prevalent tumors globally, with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) being the most common subtype. ...
Study suggests hepatitis E may be a sexually transmitted infection
2024-06-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Discovering that hepatitis E virus is associated with sperm in pigs suggests the virus may be both sexually transmitted and linked to male infertility, according to a new study.
Hepatitis E (HEV) is the leading cause of the acute viral liver infection in humans worldwide, mostly in developing regions where sanitation is poor. The virus is also endemic in pigs in the United States – though it is present mostly in organs rather than muscle, and is killed when the meat is cooked.
Because HEV has been linked to fatal pregnancy complications and reports of male infertility ...
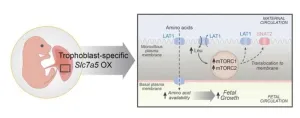
Investigating the causes of fetal growth disorders
2024-06-18
Common complications of pregnancy affecting fetal size may be caused by irregularities in the transport of amino acids across the placenta—a finding with therapeutic implications. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and fetal overgrowth affect 15-20% of pregnancies worldwide. Abnormal fetal growth is strongly linked to the development of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease in later life. Placental transport of essential amino acids is decreased in human IUGR and increased in fetal overgrowth, but whether this was a cause or consequence was unclear. Fredrick Rosario-Joseph and colleagues created a line of mice ...
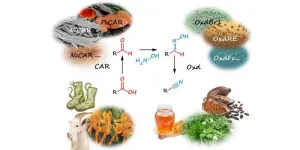
Enzymes instead of cyanide: Researchers develop biocatalytic process for nitrile production
2024-06-18
If the household cleaner emits a lemon-like odour, this may be due to a nitrile called citronellyl nitrile. These versatile chemical nitrile groups are also used in the manufacture of active pharmaceutical ingredients, superglue and chemical-resistant gloves. The prevalent production process used so far has required a chemical reaction of certain molecules with highly toxic cyanide. Margit Winkler from the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology at TU Graz, together with Ludmila Martínková from the Institute of Microbiology at the Czech Academy of Sciences, ...