(Press-News.org) The Argonne in Chicago South Side STEM Opportunity Landscape Project was awarded the Societal Impact Award by the Chicago Council on Science and Technology (C2ST) for its commitment to advancing equity and opportunity in STEM education and careers across underserved communities.
C2ST is a nonprofit that works to inspire and engage all segments of society about science and technology and their contributions to society. The South Side STEM Opportunity Landscape Project is part of Argonne in Chicago, which is focused on driving inclusive innovation to advance economic and societal impacts for underserved and underrepresented communities. The idea for the STEM landscape project began with a collaborative effort between the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory and Northwestern University's Digital Youth Network. Together, they mapped existing STEM resources and opportunities across nine South Side of Chicago communities — Douglas, Grand Boulevard, Greater Grand Crossing, Hyde Park, Kenwood, Oakland, South Shore, Washington Park and Woodlawn. The program aims to establish effective STEM pathways within the nine communities by addressing disparities in educational and workforce development opportunities within the emerging STEM economy.
At the helm of the STEM initiative are Meridith Bruozas, Argonne’s institutional partnerships director, and Jessica Burgess, Argonne's STEM education partnerships and outreach manager. With extensive backgrounds in education and STEM programing, Bruozas and Burgess have convened a diverse group of South Side education leaders and community partners to work together on advancing equitable STEM access and literacy.
"We are honored to receive this award from such an influential organization as C2ST,” Bruozas said. “This recognition is a testament to the power of collaboration and collective impact. It reaffirms our commitment to equity and inclusion in STEM, ensuring that every individual has the opportunity to thrive and succeed."
The culmination of these efforts is a website that provides free access to interactive maps and visuals of STEM programming and organizations, offering insights into workforce development, internship opportunities and STEM education within the nine communities.
"By highlighting existing resources and fostering partnerships, we're laying the groundwork for a more equitable and accessible STEM ecosystem," Burgess said. "This award helps fuel our determination to continue making a tangible difference in the lives of those we serve."
The Societal Impact Award was presented to Argonne at C2ST’s Matrix of Metropolis Annual Science in the City Gala, where C2ST also honored other award recipients. All the awards for the evening honored outstanding organizations and individuals who have had a great impact in the Chicagoland STEM ecosystem in the last few years.
“We look forward to the next chapter of this project and remain committed to working with our community and education partners to expand its impact,” said Bruozas.
END
Argonne’s South Side STEM Opportunity Landscape Project dedicated to STEM equity wins Societal Impact Award
Program focuses on advancing equity and opportunity in STEM in Chicago South Side communities
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wildfire resilience initiative launches with $3.7 million in seed funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation
2024-06-18
The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation has awarded $3.7 million to kickstart the Western Fire & Forest Resilience Collaborative, led by Winslow Hansen, a forest ecologist at Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. Funds are enabling the formation of an interdisciplinary collaborative that will advance science-based management solutions to the growing wildfire crisis.
In the Western US, climate change and a legacy of fire suppression have led to larger, more severe, and more frequent fires — with devastating consequences for people, natural resources, and the climate. By dramatically speeding ...
New NOvA results add to mystery of neutrinos
2024-06-18
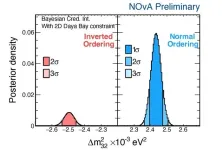
The international NOvA collaboration presented new results at the Neutrino 2024 conference in Milan, Italy, on June 17. The collaboration doubled their neutrino data since their previous release four years ago, including adding a new low-energy sample of electron neutrinos. The new results are consistent with previous NOvA results, but with improved precision. The data favor the “normal” ordering of neutrino masses more strongly than before, but ambiguity remains around the neutrino’s oscillation properties.
The latest NOvA data provide a very precise measurement ...
Gastroenterologists generally trust and accept use of AI medical tools in clinics and hospitals, finds NTU Singapore study
2024-06-18
Artificial intelligence (AI) has permeated many aspects of medicine, with promises of accurate diagnoses, better management decisions, and improved outcomes for both patients and the healthcare system. However, to successfully implement AI technology in clinical practice, trust and acceptance among healthcare providers to use such tools is crucial.
Now, using the treatment of digestive diseases as a case study, an international study led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has found that doctors in the gastroenterology practice generally trust and accept AI medical tools.
Through ...
State cannabis legalization and trends in cannabis-related disorders in older adults
2024-06-18
About The Study: Rates of cannabis-related disorder encounters increased from 2017 through 2022 among Medicare-insured older adults. This study observed the highest rates in states or territories that legalized adult and medical use of cannabis. The results also suggest higher average annual increases in states or territories that legalized medical cannabis.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Silvia Perez-Vilar, Ph.D., Pharm.D., email silvia.perezvilar@fda.hhs.gov
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Availability of medications for opioid use disorder in community mental health facilities
2024-06-18
About The Study: In this study of 450 community outpatient mental health treatment facilities in 20 high-burden states, approximately one-third offered medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). These results suggest that further study is needed to report MOUD uptake, either through increased prescribing at all clinics or through effective referral models.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Jonathan Cantor, Ph.D., email jcantor@rand.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Variation in postoperative outcomes across federally designated hospital star ratings
2024-06-18
About The Study: Although Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) hospital star rating was associated with postoperative mortality, serious complications, and readmissions, there was wide variation in surgical outcomes within each star rating group. These findings highlight the limitations of the CMS hospital star rating system as a measure of surgical quality and should be a call for continued improvement of publicly reported hospital grade measures.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Adrian Diaz, M.D., M.P.H., email adrian.diaz@osumc.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
Sepsis patients could get the right treatment faster, based on their genes
2024-06-18
Sepsis patients could be treated based on their immune system’s response to infection, not their symptoms.
New research uncovers how different people respond to sepsis based on their genetic makeup, which could help identify who would benefit from certain treatments and lead to the development of targeted therapies.
The team, from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Oxford, and collaborators, built on their previous work that identified different subgroups of patients with sepsis. They aimed to understand more about why sepsis response varies between patients and the different underlying immune response pathways.
The new study, published today (18 June) in Cell Genomics, ...
Odors are encoded in rings in the brain of migratory locusts
2024-06-18
The migratory locust Locusta migratoria is an economically important crop pest that is said to have come to Egypt in the Old Testament as the eighth of the ten biblical plagues, "to devour all that plants that grow". The migratory locust is rarely found in Europe, but in Africa and Asia it not only causes millions of dollars’ worth of damage but also has a deadly impact on local people, threatening their food and their very existence. The locusts occur in two phases: as solitary animals and in swarms. The insects are most feared when they ...
New global research aims to improve survival rates for pancreatic cancer patients
2024-06-18
A new study published today in JAMA Network Open by an international cohort of researchers provides the latest data on the effectiveness of treating pancreatic cancer patients with chemotherapy (with or without radiation therapy) before surgery to remove a tumor. The study focuses specifically on pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients.
The research found that after treatment and surgery, nearly five percent of patients had no detectable cancer cells left in the area where the tumor was, achieving a pathological complete response (pCR).
“PCR means that the cancer has responded extremely well to the treatment, leaving no ...
Medication treatment for opioid use disorder offered at only a third of outpatient mental health facilities
2024-06-18
Only a third of outpatient community mental health treatment facilities in 20 states with the highest opioid related overdose deaths report offering medication treatment for opioid use disorders, suggesting efforts may be needed to strengthen such services, according to a new RAND study.
Among the 450 clinics surveyed, factors that increased the likelihood that clinics would provide medication for opioid use disorders included being a certified behavioral health clinic and providing integrated mental and substance use disorder treatment.
Researchers found that most clinics that did not offer medication treatment said they referred patients to other clinics for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
[Press-News.org] Argonne’s South Side STEM Opportunity Landscape Project dedicated to STEM equity wins Societal Impact AwardProgram focuses on advancing equity and opportunity in STEM in Chicago South Side communities