(Press-News.org) A class of drugs already on the market to lower blood pressure appears to reduce adults’ risk of developing epilepsy, Stanford Medicine researchers and their colleagues have discovered. The finding comes out of an analysis of the medical records of more than 2 million Americans taking blood pressure medications.
The study, published June 17 in JAMA Neurology, suggests that the drugs, called angiotensin receptor blockers, could prevent epilepsy in people at highest risk of the disease, including older adults who have had strokes.
“This is incredibly exciting because we don’t currently have any medicines that prevent epilepsy,” said Kimford Meador, MD, a professor of neurology and the neurosciences and the senior author of the paper. “I hope these initial findings lead to randomized clinical trials.”
Preventing seizures after stroke
While epilepsy is often diagnosed during childhood, more than 1% of people over age 65 are diagnosed with the recurring seizures that characterize the disorder. These seizures can temporarily disrupt the brain’s function and cause a range of symptoms.
In older adults, the most common risk factor for developing epilepsy is stroke; about 10% of stroke survivors experience seizures within five years. Vascular disease and chronic high blood pressure, even in the absence of stroke, also boost epilepsy risk.
“This can be a very debilitating disorder, and it’s much more common in older adults than people realize,” said Meador, a member of the Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute.
Although anti-seizure medications can be used to control epilepsy after diagnosis, no drugs are approved to prevent epilepsy in people at high risk of developing the disorder.
During the past decade, however, studies have suggested that one type of blood pressure medication might help quell seizures because of their ability to tamp down inflammation. This aspect would be particularly apt for preventing seizures that follow stroke or traumatic brain injuries, as both cause brain inflammation that can trigger epilepsy.
In 2022, a study of more than 160,000 people in Germany found that people taking angiotensin receptor blockers — one of multiple classes of drugs prescribed to treat high blood pressure — had a diminished risk of developing epilepsy. The drugs block certain hormone receptors, leading to lower blood pressure and decreased inflammation in blood vessels and other organs — including the brain.
“Those results out of Germany echoed what had been found in animal studies and seemed very promising, but I felt that it was important to reproduce that analysis using data on people in the U.S.,” Meador said.
A bigger, broader data set
For the new study, Meador and colleagues at the University of Rhode Island turned to a national database that includes information on health care claims from more than 20 million Americans enrolled in either commercial health insurance plans or Medicare — a group more racially diverse than that in the German study. They focused their analysis on 2.2 million adults who had been diagnosed with high blood pressure, were prescribed at least one high blood pressure medication and did not already have epilepsy.
Overall, people taking angiotensin receptor blockers had a 20% to 30% lower risk of developing epilepsy between 2010 and 2017 compared with people taking other blood pressure drugs. This difference held true even when patients with strokes were removed from the analysis, suggesting that the lower rates of epilepsy were not a result solely of a decreased risk of stroke.
“What we’ve done is replicate what was found in Germany but in a larger and completely different population,” Meador said. “That really increases the strength of the signal and tells us that there’s something real going on here.”
The data also indicated that one particular angiotensin receptor blocker — losartan — had the most powerful effect on lowering epilepsy risk, but the researchers said more work is needed to confirm that.
Toward clinical trials
All blood pressure medications likely have an impact on decreasing epilepsy risk because high blood pressure is a contributing factor to epilepsy. Keeping blood pressure under control through any combination of antihypertensive drugs and lifestyle factors can therefore lower a person’s chance of developing epilepsy, Meador said.
However, the new research suggests that angiotensin receptor blockers might be more beneficial than other antihypertensives for patients to reduce the risk of epilepsy. In the new study, about 14% of people taking a blood pressure drug took angiotensin receptor blockers, while most took other classes of drugs to control their blood pressure, including beta blockers, calcium channel blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
“This could be a new chapter in the story of preventive medicine,” Meador said. “There are so many people with stroke or high blood pressure; knowing that this class of drug not only lowers blood pressure but also helps lower their epilepsy risk could change how we treat them.”
However, Meador added, randomized clinical trials are needed to prove the association between angiotensin receptor blockers and reduce epilepsy risk before treatment guidelines change.
Researchers from Brown University were also involved in the research.
The researchers have no outside funding sources or conflicts of interest to disclose.
END
Existing high blood pressure drugs may prevent epilepsy, Stanford Medicine-led study finds
Blood pressure drug may prevent epilepsy
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ACM recognizes innovators who solve real world problems
2024-06-18
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, today announced the recipients of four prestigious technical awards. These four awards in diverse categories celebrate the hard work and creativity which underpin many of today’s most important technologies.
Prateek Mittal, Princeton University, is the recipient of the 2023 ACM Grace Murray Hopper Award for foundational contributions to safeguarding Internet privacy and security using a cross-layer approach.
The unifying theme in Mittal’s ...
Wooden surfaces may have natural antiviral properties
2024-06-18
Viruses, including the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, can get passed from person to person via contaminated surfaces. But can some surfaces reduce the risk of this type of transmission without the help of household disinfectants? As reported in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, wood has natural antiviral properties that can reduce the time viruses persist on its surface — and some species of wood are more effective than others at reducing infectivity.
Enveloped viruses, like the coronavirus, can live up to five days on surfaces; nonenveloped viruses, including enteroviruses linked to the common cold, can live for weeks, in some cases even if the ...
For sustainable livestock farming bordering the Amazon Rainforest, look to the women
2024-06-18
When trees and livestock compete for land, the trees usually lose. It doesn’t have to be this way. But centrally designed plans to implement tree-livestock coexistence in deforested areas don’t always work on faraway farmland.
The ineffectiveness can be due to trying to accomplish too much too quickly. Transforming hundreds of thousands of hectares of treeless or degraded pastures into sustainable landscapes for livestock, nature and people should be a gradual, low-disruption process. And it should start ...
Dr. Felice J. Levine to step down as AERA Executive Director in June 2025
2024-06-18
AERA President Janelle T. Scott and Executive Director Felice J. Levine issued the following joint letter on June 18, 2024.
Dear AERA Members, Colleagues in the Field, and Leaders in Research and Education:
We are writing this joint letter to announce that Felice has decided to step down as Executive Director (ED) effective June 15, 2025. As she entered her fifth consecutive term, she signaled that she wished to move to an Emerita status next June and would not seek a further term of office. We both want to communicate this news now to provide sufficient lead time to conduct a search and ensure a smooth transition.
As ...
Treatment for autoimmune disorder acts on balance of immune cell types
2024-06-18
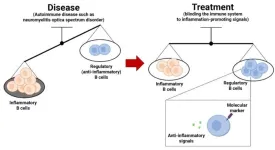
Autoimmune diseases cannot currently be cured, only treated, and this is also true for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, which affects the central nervous system. A Kobe University study of how the treatment acts on the immune system shows that it shifts the balance of types of immune cells. This finding may represent a step toward the development of personalized medicine for autoimmune diseases.
An autoimmune disease is the body’s immune system turning against parts of the body itself. Neuromyelitis optica disorder spectrum, or NMOSD, is one of them and it causes inflammation of the central nervous system, leading to vision and sensory loss, weakness ...
Anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib could reduce risk of colon cancer recurrence for a subset of patients
2024-06-18
Boston – An analysis of data from a randomized clinical trial for patients with stage 3 colon cancer found that those with PIK3CA mutations who took celecoxib, an anti-inflammatory drug, after surgery lived significantly longer and had longer disease-free survival compared to those without the mutation. The study, highlighting a potential breakthrough in personalized cancer treatment, was led by clinical investigators at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
These findings are ...
Social inequalities widen after a breast cancer
2024-06-18
When it comes to health, inequalities can be seen at every level for women with breast cancer: prevention, screening, diagnosis, treatment, and survival. But what about their quality of life? A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Inserm, and Gustave Roussy has tracked nearly 6,000 women diagnosed with breast cancer over a 2-year period, showing that socioeconomic status has a major and lasting impact on their quality of life, despite identical medical treatment. These results from the UNICANCER-sponsored CANTO study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, call ...
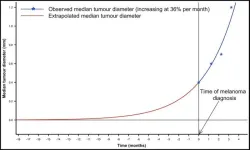
When does a melanoma metastasize? Implications for management
2024-06-18
“[...] immunotherapy is more likely to be effective at eliminating metastatic disease if the tumor burden is low, making it more logical to treat patients with high-risk melanomas at the earliest possible time [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- June 18, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 13, 2024, entitled, “When does a melanoma metastasize? Implications for management.”
In this new perspective, researchers John F. Thompson and Gabrielle J. Williams from The University of Sydney, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, and the University ...
Allison Lopatkin named 2024 Pew Scholar in Biomedical Sciences
2024-06-18
Allison Lopatkin ’13, an assistant professor of chemical engineering, biomedical engineering, and microbiology and immunology at the University of Rochester, is one of 22 scientists selected to join the Pew Scholars Program in the Biomedical Sciences this year. The program provides early-career scientists four years of funding to explore some of the most pressing questions in human health and medicine.
The funding will help Lopatkin’s lab explore how changes in bacterial metabolism contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. She says that decades of antibiotic overuse—in both clinical and agricultural ...
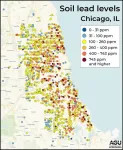
At least one in four US residential yards exceed new EPA lead soil level guideline
2024-06-18
American Geophysical Union
Press release 24-26
18 June 2024
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/millions-households-exceed-soil-lead-epa/
At least one in four US residential yards exceed new EPA lead soil level guideline
Nearly 40% of households will exceed safety recommendations where multiple lead sources may exist. Remediation with standard techniques at this scale could cost more than $1 trillion nationally
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, news@agu.org (UTC-4 hours)
Contact information ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
[Press-News.org] Existing high blood pressure drugs may prevent epilepsy, Stanford Medicine-led study findsBlood pressure drug may prevent epilepsy