(Press-News.org) Allison Lopatkin ’13, an assistant professor of chemical engineering, biomedical engineering, and microbiology and immunology at the University of Rochester, is one of 22 scientists selected to join the Pew Scholars Program in the Biomedical Sciences this year. The program provides early-career scientists four years of funding to explore some of the most pressing questions in human health and medicine.
The funding will help Lopatkin’s lab explore how changes in bacterial metabolism contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. She says that decades of antibiotic overuse—in both clinical and agricultural settings—have led to an alarming rise in bacterial strains that are resistant to antibiotics, contributing to a major public health concern.
“Currently, the study of antibiotic resistance mechanisms focuses mostly on a small handful of highly conserved intracellular targets that reduce antibiotic-target binding,” says Lopatkin. “However, as a postdoctoral fellow, I discovered that many bacteria can also escape the effects of these drugs by amassing widely diverse mutations that interfere with their metabolism.”
Using a suite of sophisticated tools integrating microbiology, biochemistry, and quantitative and computational biology techniques, Lopatkin’s lab will identify the drug-resistance mutations that arise in bacteria as they adapt to combinations of different antibiotics and metabolism-altering chemicals.
“These insights will allow us to determine how microbial metabolism contributes to the development of antibiotic resistance in real-world clinical contexts,” says Lopatkin. “This work will facilitate the development of improved diagnostic and prognostic tests for assessing antibiotic susceptibility, as well as novel classes of infection-fighting drugs.”
Lopatkin joins a community of more than 1,000 scientists who have received awards from Pew since 1985. She was chosen from 198 applicants nominated by leading academic institutions and researchers across the United States.
Prior to Lopatkin, the University’s most recent Pew Scholar in Biological Sciences were Edward Brown (2007), associate professor of biomedical engineering and neuroscience, and Laura Calvi (2005), the SKAWA Foundation’s Professor of Medicine in the Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism and Vice Chair for Basic & Translational Science for the Department of Medicine.
For a complete list of this year’s scholars, go to the Pew Charitable Trusts website.
END
Allison Lopatkin named 2024 Pew Scholar in Biomedical Sciences
Lopatkin is one of 22 early-career scientists selected nationwide to explore some of the most pressing questions in human health and medicine.
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
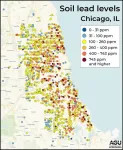
At least one in four US residential yards exceed new EPA lead soil level guideline
2024-06-18
American Geophysical Union
Press release 24-26
18 June 2024
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/millions-households-exceed-soil-lead-epa/
At least one in four US residential yards exceed new EPA lead soil level guideline
Nearly 40% of households will exceed safety recommendations where multiple lead sources may exist. Remediation with standard techniques at this scale could cost more than $1 trillion nationally
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, news@agu.org (UTC-4 hours)
Contact information ...
New study explores how local firms should adopt market and nonmarket strategies in the face of foreign direct investment
2024-06-18
Studies have shown how inward foreign direct investment (FDI) increases the productivity or innovation of local firms in emerging markets, but little research has explored how local firms have to strategically cope with this competition. Upon exploring these connections, a new article in the Global Strategy Journal recommends that local firms adopt a balanced approach to contend with these competition challenges: Companies should adopt both market and nonmarket strategies to maximize benefits, as relying solely on political connections may not be the most effective option.
FDI refers to when a company purchases a business or sets up new operations in a country different from the one of ...
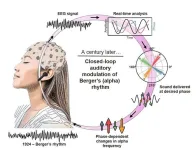
An auditory stimulation approach modulates brain alpha oscillations and interferes with sleep onset dynamics
2024-06-18
Alpha oscillations are electrophysiological features of the human brain linked to fundamental processes including memory and perception. This study introduces a closed-loop auditory stimulation approach to selectively modulate alpha oscillations in the human brain in a phase-dependent and spatially-specific manner.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002651
Article Title: A closed-loop auditory stimulation approach selectively modulates alpha oscillations and sleep onset dynamics in humans
Author Countries: United Kingdom
Funding: ...
Study finds air pollution can increase cardiovascular risk for cancer patients
2024-06-18
Modern therapies have extended the lives of many cancer patients; however, survivors often live with chronic health conditions, including cardiovascular disease. New research published in JACC: CardioOncology shows that air pollution plays a significant role in increasing cardiovascular disease and mortality in cancer patients and contributes to health disparities related to these conditions.
“The review underscores the critical need to consider environmental factors, especially air pollution, in cardio-oncology risk assessment and patient management,” said Xiaoquan Rao, MD, PhD, senior author of the study and a cardiologist ...
Sound stimulation with precise timings can help understand brain wave functions
2024-06-18
Using sound to stimulate certain brain waves has the potential to help those with dementia or cognitive decline sleep better, reveals a new study. Sleep disturbances are a common feature in dementia and may affect up to half of people living with the condition.
During the study, the research team from the University of Surrey and the UK Dementia Research Institute Centre for Care Research & Technology at Imperial College London, used sound stimulation to target alpha rhythms, a type of brainwave, at precise timings of the wave to investigate how the brain responds.
Alpha rhythms have been associated ...
Rutgers Health researchers find disparities in outcomes of hospice discharges
2024-06-18
Black patients who leave hospice care and patients with short stays in hospice care are at increased risks for being admitted to a hospital after being discharged from hospice, according to Rutgers Health researchers.
Their study, published in JAMA Network Open, examined patient outcomes after hospice care discharges to determine what factors contribute to transitions that lead to negative health implications.
“Hospice care teams may want to pay particular attention to the discharge planning needs of patients of racial and ethnic minority groups and patients with more complicated needs,” said Elizabeth Luth, the lead author of the study and ...
Mirror-image chemicals may revolutionize drug delivery
2024-06-18
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are complicated carbohydrates, a term that describes the natural, sugar-based, starchy material that makes up much of fruits, vegetables and grains.
Their unique chemical properties make them ideal for all sorts of uses, including air fresheners, medications and cosmetics. Scientists also are exploring their potential to treat cardiovascular diseases caused by atherosclerotic plaques.
Now, more than 130 years after CDs were first discovered and reported, a University of Texas at Arlington team of scientists has created chemical mirror images of these complex ...
What happens when neutron stars collide?
2024-06-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — When stars collapse, they can leave behind incredibly dense but relatively small and cold remnants called neutron stars. If two stars collapse in close proximity, the leftover binary neutron stars spiral in and eventually collide, and the interface where the two stars begin merging becomes incredibly hot. New simulations of these events show hot neutrinos — tiny, essentially massless particles that rarely interact with other matter — that are created during the collision can be briefly trapped at these interfaces and remain out of equilibrium with the cold cores of the merging stars for 2 to 3 milliseconds. ...
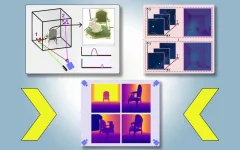
Researchers leverage shadows to model 3D scenes, including objects blocked from view
2024-06-18
Imagine driving through a tunnel in an autonomous vehicle, but unbeknownst to you, a crash has stopped traffic up ahead. Normally, you’d need to rely on the car in front of you to know you should start braking. But what if your vehicle could see around the car ahead and apply the brakes even sooner?
Researchers from MIT and Meta have developed a computer vision technique that could someday enable an autonomous vehicle to do just that.
They have introduced a method that creates physically accurate, 3D models of an entire scene, including areas blocked from view, ...
Is coffee good for you or bad for you?
2024-06-18
Coffee drinking is a heritable habit, and one that carries a certain amount of genetic baggage.
Caffeinated coffee is a psychoactive substance, notes Sandra Sanchez-Roige, Ph.D., an associate professor in the University of California San Diego School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry. She is one of an international group of researchers that compared coffee-consumption characteristics from a 23andMe database with an even larger set of records in the United Kingdom. She is the corresponding author of a study recently published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
Hayley ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Allison Lopatkin named 2024 Pew Scholar in Biomedical SciencesLopatkin is one of 22 early-career scientists selected nationwide to explore some of the most pressing questions in human health and medicine.