(Press-News.org) Coffee drinking is a heritable habit, and one that carries a certain amount of genetic baggage.
Caffeinated coffee is a psychoactive substance, notes Sandra Sanchez-Roige, Ph.D., an associate professor in the University of California San Diego School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry. She is one of an international group of researchers that compared coffee-consumption characteristics from a 23andMe database with an even larger set of records in the United Kingdom. She is the corresponding author of a study recently published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
Hayley H. A. Thorpe, Ph.D., is the lead author on the paper. Thorpe, of the Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry at Western University in Ontario, explained that the team collected genetic data as well as self-reported coffee-consumption numbers to assemble a genome-wide association study (GWAS). The idea was to make connections between the genes that were known to be associated with coffee consumption and the traits or conditions related to health.
“We used this data to identify regions on the genome associated with whether somebody is more or less likely to consume coffee,” Thorpe explained. “And then identify the genes and biology that could underlie coffee intake.”
Abraham Palmer, Ph.D., is also a lead researcher on the paper and a professor in the UC San Diego School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry. He said that most people are surprised that there is a genetic influence on coffee consumption. “We had good reason to suspect from earlier papers that there were genes that influence how much coffee someone consumes,” he said. “And so, we weren't surprised to find that in both of the cohorts we examined there was statistical evidence that this is a heritable trait. In other words, the particular gene variants that you inherit from your parents influence how much coffee you're likely to consume.”
Sanchez-Roige said the genetic influence on coffee consumption was the first of two questions the researchers wanted to address.
“The second is something that coffee lovers are really keen on learning,” Sanchez-Roige said. “Is drinking coffee good or bad? Is it associated with positive health outcomes or not?”
The answer is not definitive. The group’s genome-wide association study of 130,153 U.S.-based 23andMe research participants was compared with a similar UK Biobank database of 334,649 Britons, revealing consistent positive genetic associations between coffee and harmful health outcomes such as obesity and substance use. A positive genetic association is a connection between a specific gene variant (the genotype) and a specific condition (the phenotype). Conversely, a negative genetic association is an apparent protective quality discouraging the development of a condition. The findings get more complicated when it comes to psychiatric conditions.
“Look at the genetics of anxiety, for instance, or bipolar and depression: In the 23andMe data set, they tend to be positively genetically correlated with coffee intake genetics,” Thorpe said. “But then, in the UK Biobank, you see the opposite pattern, where they're negatively genetically correlated. This is not what we expected.”
She said there were other instances in which the 23andMe set didn’t align with the UK Biobank, but the greatest disagreement was in psychiatric conditions.
“It’s common to combine similar datasets in this field to increase study power. This information paints a fairly clear picture that combining these two datasets was really not a wise idea. And we didn't end up doing that,” Thorpe said. She explained that melding the databases might mask effects, leading researchers toward incorrect conclusions — or even cancelling each other out.
Sanchez-Roige says the researchers have some ideas about how the differences in results arose. To begin with, there was an apples-and-oranges aspect to the surveys. For instance, the 23andMe survey asked, “How many 5-ounce (cup-sized) servings of caffeinated coffee do you consume each day?” Compare it to the UK Biobank’s “How many cups of coffee do you drink each day? (Include decaffeinated coffee)”
Beyond serving size and the caffeinated/decaf divide, the surveys made no accommodation for the various ways coffee is served. “We know that in the U.K., they have generally higher preference for instant coffee, whereas ground coffee is more preferred in the U.S.,” Thorpe said.
“And then there’s the frappuccinos,” Sanchez-Roige added, citing the American trend of taking coffee loaded with sugary additives. Palmer mentioned other caffeinated drinks and especially in the context of the UK Biobank, tea, none of which were included in the GWAS, which addressed only coffee. Palmer added that the GWAS demonstrates the relationship between genotype and phenotype is more different than the relationship between coffee and tea.
“Genetics influences lots of things. For instance, it influences how tall you might be,” he said. “And those kinds of things probably would play out very similarly, whether you lived in the U.S. or the U.K. But coffee is a decision that people make.”
Sanchez-Roige pointed out that coffee comes in a variety of forms, from instant to frappuccino, and is consumed amid cultural norms that differ from place to place. A person with a given genotype might end up having quite a different phenotype living in the U.K. versus the U.S.
“And that's really what the data are telling us,” she said. “Because unlike height, where your behavior doesn't really have much to do with it, your behavior and the choices you're making in your environment play out in various ways. So the interaction between genotype and environment complicates the picture.”
The collaborators stressed the need for more investigation to unravel the relationships between genetics and the environment, focusing not only on coffee/caffeine intake but also other substance-use issues.
In addition to the researchers noted above, co-authors on the paper from UC San Diego are: Benjamin K. Pham, John J. Meredith, Mariela V. Jennings, Natasia S. Courchesne-Krak and Sevim B. Bianchi, all of the Department of Psychiatry. Other co-authors are Pierre Fontanillas, of 23andMe, Inc.; Laura Vilar-Ribó, of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Spain; Julian Mutz, of King's College London, U.K.; Sarah L. Elson and Jibran Y. Khokhar, of the University of Guelph, Canada; Abdel Abdellaoui, of the University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Lea K. Davis, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center; and the 23andMe Research Team.
Mariela V. Jennings, Sevim B. Bianchi and Sandra Sanchez-Roige are supported by funds from the California Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program (TRDRP; Grant Number T29KT0526 and T32IR5226). Sevim B. Bianchi and Abraham Palmer were also supported by P50DA037844. BKP, Julian Mutz, and Sandra Sanchez-Roige are supported by NIH/NIDA DP1DA054394. Hayley H. A .Thorpe is funded through a Natural Science and Engineering Research Council PGS-D scholarship and Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Fellowship. Jibran Y. Khokhar is supported by a CIHR Canada Research Chair in Translational Neuropsychopharmacology. Lea K. Davis is supported by R01 MH113362. Natasia S. Courchesne-Krak is funded through an Interdisciplinary Research Fellowship in NeuroAIDs (Grant Number R25MH081482). Julian Mutz is funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London.
The datasets used for the PheWAS and LabWAS analyses described were obtained from Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s BioVU which is supported by numerous sources: institutional funding, private agencies, and federal grants. These include the NIH funded Shared Instrumentation Grant S10RR025141; and CTSA grants UL1TR002243, UL1TR000445, and UL1RR024975. Genomic data are also supported by investigator-led projects that include U01HG004798, R01NS032830, RC2GM092618, P50GM115305, U01HG006378, U19HL065962, R01HD074711; and additional funding sources listed at https://victr.vumc.org/biovu-funding/. PheWAS and LabWAS analyses used CTSA (SD, Vanderbilt Resources). This project was supported by the National Center for Research Resources, Grant UL1 RR024975-01, and is now at the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, Grant 2 UL1 TR000445-06.
# # #
END
Is coffee good for you or bad for you?
When it comes to your genetics, the answer is complicated
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CWRU researcher, interdisciplinary team discover breakthrough on body’s adaptation to COVID-19
2024-06-18
CLEVELAND—Since 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic has presented significant challenges to global public health, infecting millions and claiming numerous lives. While widespread vaccination efforts have alleviated the immediate threat, lingering questions persist about the long-term effects of the virus on those infected.
An interdisciplinary team of scientists has made a significant breakthrough to understand how the body adapts to COVID-19 infection, potentially offering crucial insights into managing the complex disease. Led by Christopher Wilson, professor of medicine at Loma Linda University, the collaborative effort involved ...
New guidelines for radiation therapy for HPV-associated head and neck cancer
2024-06-18
Study Title: Radiation Therapy for HPV-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline
Publication: Practical Radiation Oncology
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Danielle Margalit, MD, MPH
Summary: A multi-disciplinary task force convened by the American Society for Radiation Oncology has issued new guidelines for radiation therapy for HPV-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC). The expert task force recommends optimal dosing regimens for radiation therapy when used alone or after surgery, incorporating the latest data on minimizing doses to areas that may affect patient quality of life such as swallowing. ...
Argonne’s South Side STEM Opportunity Landscape Project dedicated to STEM equity wins Societal Impact Award
2024-06-18
The Argonne in Chicago South Side STEM Opportunity Landscape Project was awarded the Societal Impact Award by the Chicago Council on Science and Technology (C2ST) for its commitment to advancing equity and opportunity in STEM education and careers across underserved communities.
C2ST is a nonprofit that works to inspire and engage all segments of society about science and technology and their contributions to society. The South Side STEM Opportunity Landscape Project is part of Argonne in Chicago, which is focused on driving inclusive innovation to advance economic and societal impacts for underserved and underrepresented communities. The ...
Wildfire resilience initiative launches with $3.7 million in seed funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation
2024-06-18
The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation has awarded $3.7 million to kickstart the Western Fire & Forest Resilience Collaborative, led by Winslow Hansen, a forest ecologist at Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. Funds are enabling the formation of an interdisciplinary collaborative that will advance science-based management solutions to the growing wildfire crisis.
In the Western US, climate change and a legacy of fire suppression have led to larger, more severe, and more frequent fires — with devastating consequences for people, natural resources, and the climate. By dramatically speeding ...
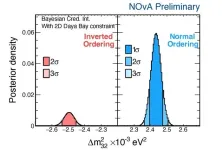
New NOvA results add to mystery of neutrinos
2024-06-18
The international NOvA collaboration presented new results at the Neutrino 2024 conference in Milan, Italy, on June 17. The collaboration doubled their neutrino data since their previous release four years ago, including adding a new low-energy sample of electron neutrinos. The new results are consistent with previous NOvA results, but with improved precision. The data favor the “normal” ordering of neutrino masses more strongly than before, but ambiguity remains around the neutrino’s oscillation properties.
The latest NOvA data provide a very precise measurement ...
Gastroenterologists generally trust and accept use of AI medical tools in clinics and hospitals, finds NTU Singapore study
2024-06-18
Artificial intelligence (AI) has permeated many aspects of medicine, with promises of accurate diagnoses, better management decisions, and improved outcomes for both patients and the healthcare system. However, to successfully implement AI technology in clinical practice, trust and acceptance among healthcare providers to use such tools is crucial.
Now, using the treatment of digestive diseases as a case study, an international study led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has found that doctors in the gastroenterology practice generally trust and accept AI medical tools.
Through ...
State cannabis legalization and trends in cannabis-related disorders in older adults
2024-06-18
About The Study: Rates of cannabis-related disorder encounters increased from 2017 through 2022 among Medicare-insured older adults. This study observed the highest rates in states or territories that legalized adult and medical use of cannabis. The results also suggest higher average annual increases in states or territories that legalized medical cannabis.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Silvia Perez-Vilar, Ph.D., Pharm.D., email silvia.perezvilar@fda.hhs.gov
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Availability of medications for opioid use disorder in community mental health facilities
2024-06-18
About The Study: In this study of 450 community outpatient mental health treatment facilities in 20 high-burden states, approximately one-third offered medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). These results suggest that further study is needed to report MOUD uptake, either through increased prescribing at all clinics or through effective referral models.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Jonathan Cantor, Ph.D., email jcantor@rand.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Variation in postoperative outcomes across federally designated hospital star ratings
2024-06-18
About The Study: Although Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) hospital star rating was associated with postoperative mortality, serious complications, and readmissions, there was wide variation in surgical outcomes within each star rating group. These findings highlight the limitations of the CMS hospital star rating system as a measure of surgical quality and should be a call for continued improvement of publicly reported hospital grade measures.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Adrian Diaz, M.D., M.P.H., email adrian.diaz@osumc.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
Sepsis patients could get the right treatment faster, based on their genes
2024-06-18
Sepsis patients could be treated based on their immune system’s response to infection, not their symptoms.
New research uncovers how different people respond to sepsis based on their genetic makeup, which could help identify who would benefit from certain treatments and lead to the development of targeted therapies.
The team, from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Oxford, and collaborators, built on their previous work that identified different subgroups of patients with sepsis. They aimed to understand more about why sepsis response varies between patients and the different underlying immune response pathways.
The new study, published today (18 June) in Cell Genomics, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Is coffee good for you or bad for you?When it comes to your genetics, the answer is complicated