(Press-News.org) Studies have shown how inward foreign direct investment (FDI) increases the productivity or innovation of local firms in emerging markets, but little research has explored how local firms have to strategically cope with this competition. Upon exploring these connections, a new article in the Global Strategy Journal recommends that local firms adopt a balanced approach to contend with these competition challenges: Companies should adopt both market and nonmarket strategies to maximize benefits, as relying solely on political connections may not be the most effective option.
FDI refers to when a company purchases a business or sets up new operations in a country different from the one of its origin. Local firms do benefit from knowledge spillovers from foreign firms, but they also face the harm of the competition they bring to the local market, which they can address via two routes: Market strategies focus on being competitive within the marketplace, while nonmarket strategies aim to shape the market environment by way of — for example — regulation or public opinion.
Meitong Dong of The University of Hong Kong, Pengcheng Ma of Renmin University of China, and Lin Cui of Australian National University wanted to clarify the relationship between foreign firms, local firms, and the local government. The researchers drew from resource dependence theory to argue that, when there is a low to moderate level of inward FDI, its overall spillover benefits can alleviate local firms’ dependence on the government for some resources, which reduces the need for political connections. However, when inward FDI grows to a moderate to high level, the competitive threats it poses to local firms begin to outweigh the spillover benefits, which in turn motivates local firms to foster stronger connections with the government in an effort to neutralize foreign firms’ competitive advantages.
To test their theory, the team used China as its research setting because it both represents an emerging economy and is one of the largest recipients of foreign investment. The study used a sample of 1,463 Chinese listed firms from 2009 to 2017, along with data that measured FDI and the local firms’ political connections. They also used governmental R&D funding, institutional development, and market diversification to reflect the resource similarity offered by foreign firms and the local government.
The research team identified a U-shaped relationship between inward FDI and local firms’ political connections. The authors also argue that when the resources from foreign firms and the government are similar in type, local firms’ nonmarket strategies — their political connections — are more responsive to inward FDI. This occurs because the spillover benefits of inward FDI are more likely to be substitutable for government resources; at the same time, the competitive threats can be neutralized if local firms can secure matching resources from the government. Therefore, the U-shaped relationship is more pronounced when the resource similarity is high.
“For firms in emerging markets, relying solely on the government cannot be the perfect way to tackle the competition brought by inward FDI,” the authors say. “Local firms should consider market and nonmarket strategies in the face of inward FDI and how to combine the two strategies to optimize their benefits. Furthermore, local firms should try to understand the similarities between the resources provided by inward FDI and the government when implementing market and nonmarket strategies.”
To read the full context of the study and its methods, access the full paper available in the Global Strategy Journal.
About the Strategic Management Society
The Strategic Management Society (SMS) is the leading global member organization fostering and supporting rigorous and practice-engaged strategic management research. SMS enjoys the support of 3,000 members, representing more than 1,100 institutions and companies in more than 70 countries. SMS publishes three leading academic journals in partnership with Wiley: Strategic Management Journal, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, and Global Strategy Journal. These journals publish top-quality work applicable to researchers and practitioners with complementary access for all SMS Members. The SMS Explorer offers the latest insights and takeaways from the SMS Journals for business practitioners, consultants, and academics.
Click here to subscribe to the monthly SMS Explorer newsletter.
Click here to learn more about the programs and opportunities SMS has to offer.
END
New study explores how local firms should adopt market and nonmarket strategies in the face of foreign direct investment
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
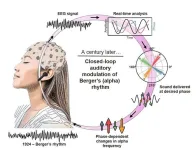
An auditory stimulation approach modulates brain alpha oscillations and interferes with sleep onset dynamics
2024-06-18
Alpha oscillations are electrophysiological features of the human brain linked to fundamental processes including memory and perception. This study introduces a closed-loop auditory stimulation approach to selectively modulate alpha oscillations in the human brain in a phase-dependent and spatially-specific manner.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002651
Article Title: A closed-loop auditory stimulation approach selectively modulates alpha oscillations and sleep onset dynamics in humans
Author Countries: United Kingdom
Funding: ...
Study finds air pollution can increase cardiovascular risk for cancer patients
2024-06-18
Modern therapies have extended the lives of many cancer patients; however, survivors often live with chronic health conditions, including cardiovascular disease. New research published in JACC: CardioOncology shows that air pollution plays a significant role in increasing cardiovascular disease and mortality in cancer patients and contributes to health disparities related to these conditions.
“The review underscores the critical need to consider environmental factors, especially air pollution, in cardio-oncology risk assessment and patient management,” said Xiaoquan Rao, MD, PhD, senior author of the study and a cardiologist ...
Sound stimulation with precise timings can help understand brain wave functions
2024-06-18
Using sound to stimulate certain brain waves has the potential to help those with dementia or cognitive decline sleep better, reveals a new study. Sleep disturbances are a common feature in dementia and may affect up to half of people living with the condition.
During the study, the research team from the University of Surrey and the UK Dementia Research Institute Centre for Care Research & Technology at Imperial College London, used sound stimulation to target alpha rhythms, a type of brainwave, at precise timings of the wave to investigate how the brain responds.
Alpha rhythms have been associated ...
Rutgers Health researchers find disparities in outcomes of hospice discharges
2024-06-18
Black patients who leave hospice care and patients with short stays in hospice care are at increased risks for being admitted to a hospital after being discharged from hospice, according to Rutgers Health researchers.
Their study, published in JAMA Network Open, examined patient outcomes after hospice care discharges to determine what factors contribute to transitions that lead to negative health implications.
“Hospice care teams may want to pay particular attention to the discharge planning needs of patients of racial and ethnic minority groups and patients with more complicated needs,” said Elizabeth Luth, the lead author of the study and ...
Mirror-image chemicals may revolutionize drug delivery
2024-06-18
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are complicated carbohydrates, a term that describes the natural, sugar-based, starchy material that makes up much of fruits, vegetables and grains.
Their unique chemical properties make them ideal for all sorts of uses, including air fresheners, medications and cosmetics. Scientists also are exploring their potential to treat cardiovascular diseases caused by atherosclerotic plaques.
Now, more than 130 years after CDs were first discovered and reported, a University of Texas at Arlington team of scientists has created chemical mirror images of these complex ...
What happens when neutron stars collide?
2024-06-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — When stars collapse, they can leave behind incredibly dense but relatively small and cold remnants called neutron stars. If two stars collapse in close proximity, the leftover binary neutron stars spiral in and eventually collide, and the interface where the two stars begin merging becomes incredibly hot. New simulations of these events show hot neutrinos — tiny, essentially massless particles that rarely interact with other matter — that are created during the collision can be briefly trapped at these interfaces and remain out of equilibrium with the cold cores of the merging stars for 2 to 3 milliseconds. ...
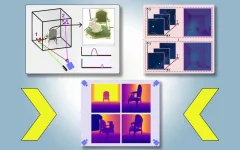
Researchers leverage shadows to model 3D scenes, including objects blocked from view
2024-06-18
Imagine driving through a tunnel in an autonomous vehicle, but unbeknownst to you, a crash has stopped traffic up ahead. Normally, you’d need to rely on the car in front of you to know you should start braking. But what if your vehicle could see around the car ahead and apply the brakes even sooner?
Researchers from MIT and Meta have developed a computer vision technique that could someday enable an autonomous vehicle to do just that.
They have introduced a method that creates physically accurate, 3D models of an entire scene, including areas blocked from view, ...
Is coffee good for you or bad for you?
2024-06-18
Coffee drinking is a heritable habit, and one that carries a certain amount of genetic baggage.
Caffeinated coffee is a psychoactive substance, notes Sandra Sanchez-Roige, Ph.D., an associate professor in the University of California San Diego School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry. She is one of an international group of researchers that compared coffee-consumption characteristics from a 23andMe database with an even larger set of records in the United Kingdom. She is the corresponding author of a study recently published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
Hayley ...
CWRU researcher, interdisciplinary team discover breakthrough on body’s adaptation to COVID-19
2024-06-18
CLEVELAND—Since 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic has presented significant challenges to global public health, infecting millions and claiming numerous lives. While widespread vaccination efforts have alleviated the immediate threat, lingering questions persist about the long-term effects of the virus on those infected.
An interdisciplinary team of scientists has made a significant breakthrough to understand how the body adapts to COVID-19 infection, potentially offering crucial insights into managing the complex disease. Led by Christopher Wilson, professor of medicine at Loma Linda University, the collaborative effort involved ...
New guidelines for radiation therapy for HPV-associated head and neck cancer
2024-06-18
Study Title: Radiation Therapy for HPV-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline
Publication: Practical Radiation Oncology
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Danielle Margalit, MD, MPH
Summary: A multi-disciplinary task force convened by the American Society for Radiation Oncology has issued new guidelines for radiation therapy for HPV-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC). The expert task force recommends optimal dosing regimens for radiation therapy when used alone or after surgery, incorporating the latest data on minimizing doses to areas that may affect patient quality of life such as swallowing. ...