Creation of a power-generating, gel electret-based device
Technology may be used to develop soft, lightweight wearable motion sensors for healthcare purposes
2024-06-20
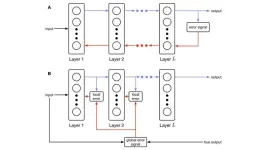
(Press-News.org) 1. A team of researchers from NIMS, Hokkaido University and Meiji Pharmaceutical University has developed a gel electret capable of stably retaining a large electrostatic charge. The team then combined this gel with highly flexible electrodes to create a sensor capable of perceiving low-frequency vibrations (e.g., vibrations generated by human motion) and converting them into output voltage signals. This device may potentially be used as a wearable healthcare sensor.
2. Interest in the development of soft, lightweight, power-generating materials has been growing in recent years for use in soft electronics designed for various purposes, such as healthcare and robotics. Electret materials capable of stably retaining electrostatic charge may be used to develop vibration-powered devices without external power sources. NIMS has been leading efforts to develop a low-volatility, room-temperature alkyl–π liquid composed of a π-conjugated dye moiety and flexible yet branched alkyl chains (a type of hydrocarbon compound). The alkyl–π liquids exhibit excellent charge retention properties, can be applied to other materials (e.g., through painting and impregnation) and are easily formable. However, when these liquids have been combined with electrodes to create flexible devices, they have proven difficult to immobilize and seal, resulting in leakage issues. Moreover, the electrostatic charge retention capacities of alkyl–π liquids needed to be increased in order to improve their power generation capabilities.
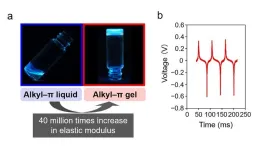
3. The research team recently succeeded in creating an alkyl–π gel by adding a trace amount of a low-molecular-weight gelator to an alkyl–π liquid. The elastic storage modulus of this gel was found to be 40 million times that of its liquid counterpart, and it could be simplified fixation and sealed. Moreover, the gel-electret obtained by charging this gel achieved a 24% increase in charge retention compared to the base material (i.e., the alkyl–π liquid), thanks to the improved confinement of electrostatic charges within the gel. The team then combined flexible electrodes with the gel-electret to create a vibration sensor. This sensor was able to perceive vibrations with frequencies as low as 17 Hz and convert them into an output voltage of 600 mV—83% higher than the voltage generated by an alkyl–π liquid electret-based sensor.
4. In future research, the team aims to develop wearable sensors capable of responding to subtle vibrations and various strain deformations by further improving the charging electret characteristics (i.e., charge capacity and charge life) and strength of the alkyl–π gel. Additionally, since this gel is recyclable and reusable as a vibration sensor material, its use is expected to help promote a circular economy.
***
5. This project was carried out by a research team led by Akito Tateyama (Trainee, Frontier Molecules Group (FMG), Research Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (MANA), NIMS; also Student, Hokkaido University-NIMS Joint Graduate School), Kazuhiko Nagura (Researcher, FMG, MANA, NIMS), Takashi Nakanishi (Group Leader, FMG, MANA, NIMS) and Masamichi Yamanaka (Professor, Meiji Pharmaceutical University).
6. This research was published in the online version of Angewandte Chemie International Edition on April 11, 2024.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-20
When E. coli detects damage to its genetic material, it sends out an SOS signal that alters activity inside the cells.
“The bacteria go into full emergency mode,” says PhD candidate Olaug Elisabeth Torheim Bergum at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
Imagine that you have a very sore throat. You're sick, your throat hurts, and a visit to the doctor confirms that the pain is due to a bacterial infection. You get a prescription for antibiotics, which quickly sorts out your sore throat. You are pleased that the treatment ...
2024-06-20
DETROIT (June 20, 2024)— Mental health experts from across the globe will gather to share insights, best practices, and innovations for preventing suicide during the 5th Zero Suicide International Summit June 24-25 in Liverpool, England.
Named for the innovative, evidence-based suicide intervention model developed at Henry Ford Health, the Zero Suicide International Summit is presented by the Detroit-based healthcare system in partnership with Zero Suicide Alliance (ZSA) and The Kevin and Margaret Hines Foundation.
The Zero Suicide model was developed at Henry Ford Health in 2001. Within a year of implementing the ...
2024-06-20
It reads. It talks. It collates mountains of data and recommends business decisions. Today’s artificial intelligence might seem more human than ever. However, AI still has several critical shortcomings.
“As impressive as ChatGPT and all these current AI technologies are, in terms of interacting with the physical world, they’re still very limited. Even in things they do, like solve math problems and write essays, they take billions and billions of training examples before they can do them well, " explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) NeuroAI Scholar Kyle Daruwalla.
Daruwalla ...
2024-06-20
Changing climate will make home feel like somewhere else
Interactive app shows how climate change will make places around the world feel like they are closer to the equator
FROSTBURG, MD (June 20, 2024)—The impacts of climate change are being felt all over the world, but how will it impact how your hometown feels? An interactive web application from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science allows users to search 40,581 places and 5,323 metro areas around the globe to match the expected future climate in each city with the current climate of another location, ...
2024-06-20
What do you get when you cross Norse mythology with a 78-million-year-old ancestor to the Triceratops? Answer: Lokiceratops rangiformis, a plant-eating dinosaur with a very fancy set of horns.
The new dinosaur was identified and named by Colorado State University affiliate faculty member Joseph Sertich and University of Utah Professor Mark Loewen. The dinosaur’s name, announced today in the scientific journal PeerJ, translates roughly to “Loki’s horned face that looks like a caribou.”
Loewen and Sertich, co-lead authors of the PeerJ study, dubbed the new species Lokiceratops (lo-Kee-sare-a-tops) ...
2024-06-20
In democracies where civilian control is followed, the power to make crucial decisions, like those of national security, is mainly exercised by elected officials, allowing the citizens who elect them to influence such decisions indirectly. This role can give people a sense of participation in matters of national importance, potentially associated with their political trust. The military, in such cases, advises and helps these elected leaders in serving the nation, rather than assuming leadership itself. A balance between civilians and military organizations is, therefore, crucial for any democracy to thrive, and it is pointed out that civilian control is a requisite of democracy.
Existing ...
2024-06-20
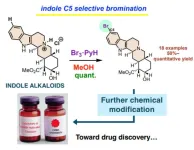
Indolo[2,3-a]quinolizidine is a common structural motif in various natural products. Its molecular structure contains the indole ring, a functional group in tryptophan. Tryptophan, an essential amino acid, is required for the production and maintenance of our body’s proteins, muscles, enzymes, and neurotransmitters. Many natural products are derived from it. Over 3,000 monoterpene indole alkaloids (MTIAs), which are natural products consisting of indole rings, have been found in plants, and some of them have been used as medicines. For example, vinblastine has been used as an anticancer drug, and reserpine is used to treat high blood pressure.
The ...
2024-06-20
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – June 20, 2024 – Women who have their ovaries removed before menopause, particularly before the age of 40, have reduced white matter integrity in multiple regions of the brain later in life. White matter refers to the nerve fibers that connect neurons in different areas of the brain.
The findings appear online today in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
“We know that having both ovaries removed before natural menopause causes abrupt endocrine dysfunction, which increases ...
2024-06-20
The composition of the intestinal flora can predict the chances of developing serious infections such as pneumonia. Researchers from Amsterdam UMC and the University of Turku, Finland, followed more than 10,000 people for 6 years. More than 600 people who had less healthy intestinal flora developed a serious infection, with this leading in some cases to death. The results of the study are published today in The Lancet Microbe.
The 602 people who were hospitalised due to an infection showed at the start of the study that they had fewer butyrate-producing ...
2024-06-20
PULLMAN, Wash. -- A wearable health monitor developed by Washington State University researchers can reliably measure levels of important biochemicals in sweat during physical exercise.
The 3D-printed monitor could someday provide a simple and non-invasive way to track health conditions and diagnose common diseases, such as diabetes, gout, kidney disease or heart disease.
Reporting in the journal, ACS Sensors, the researchers were able to accurately monitor the levels of volunteers’ glucose, lactate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Creation of a power-generating, gel electret-based device
Technology may be used to develop soft, lightweight wearable motion sensors for healthcare purposes