(Press-News.org) A popular and widely-promoted claim that dinosaur fossils inspired the legend of the griffin, the mythological creature with a raptorial bird head and wings on a lion body, has been challenged in a new study.
The specific link between dinosaur fossils and griffin mythology was proposed over 30 years ago in a series of papers and books written by folklorist Adrienne Mayor. These started with the 1989 Cryptozoology paper entitled ‘Paleocryptozoology: a call for collaboration between classicists and cryptozoologists’, and was cemented in the seminal 2000 book ‘The First Fossil Hunters. The idea became a staple of books, documentaries and museum exhibits.
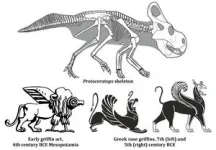
It suggests that an early horned dinosaur of Mongolia and China, Protoceratops, was discovered by ancient nomads prospecting for gold in Central Asia. Tales of Protoceratops bones then travelled southwest on trade routes to inspire, or at least influence, stories and art of the griffin.
Griffins are some of the oldest mythological creatures, first appearing in Egyptian and Middle Eastern art during the 4th millennium BC, before becoming popular in ancient Greece during the 8th century BC.
Protoceratops was a small (around 2 metres long) dinosaur that lived in Mongolia and northern China during the Cretaceous period (75-71 million years ago). They belong to the horned dinosaur group, making it a relative of Triceratops, although they actually lack facial horns. Like griffins, Protoceratops stood on four legs, had beaks, and had frill-like extensions of their skulls that, it’s been argued, could be interpreted as wings.
In the first detailed assessment of the claims, study authors Dr Mark Witton and Richard Hing, palaeontologists at the University of Portsmouth, re-evaluated historical fossil records, the distribution and nature of Protoceratops fossils, and classical sources linking the griffin with the Protoceratops, consulting with historians and archeologists to fully understand the conventional, non-fossil based view of griffin origins. Ultimately, they found that none of the arguments withstood scrutiny.
Ideas that Protoceratops would be discovered by nomads prospecting for gold, for instance, are unlikely when Protoceratops fossils occur hundreds of kilometres away from ancient gold sites. In the century since Protoceratops was discovered, no gold has been reported alongside them. It also seems doubtful that nomads would have seen much of Protoceratops skeletons, even if they prospected for gold where their fossils occur.
“There is an assumption that dinosaur skeletons are discovered half-exposed, lying around almost like the remains of recently-deceased animals,” said Dr Witton. “But generally speaking, just a fraction of an eroding dinosaur skeleton will be visible to the naked eye, unnoticed to all except for sharp-eyed fossil hunters.
“That’s almost certainly how ancient peoples wandering around Mongolia encountered Protoceratops. If they wanted to see more, as they’d need to if they were forming myths about these animals, they’d have to extract the fossil from the surrounding rock. That is no small task, even with modern tools, glues, protective wrapping and preparatory techniques. It seems more probable that Protoceratops remains, by and large, went unnoticed — if the gold prospectors were even there to see them.”
Similarly, the geographic spread of griffin art through history does not align with the scenario of griffin lore beginning with Central Asian fossils and then spreading west. There are also no unambiguous references to Protoceratops fossils in ancient literature.
Protoceratops is only griffin-like in being a four-limbed animal with a beak. There are no details in griffin art suggesting that their fossils were referenced but, conversely, many griffins were clearly composed from features of living cats and birds.
Dr Witton added: “Everything about griffin origins is consistent with their traditional interpretation as imaginary beasts, just as their appearance is entirely explained by them being chimaras of big cats and raptorial birds. Invoking a role for dinosaurs in griffin lore, especially species from distant lands like Protoceratops, not only introduces unnecessary complexity and inconsistencies to their origins, but also relies on interpretations and proposals that don’t withstand scrutiny.”
The authors are keen to stress that there is excellent evidence of fossils being culturally important throughout human history, and innumerable instances of fossils inspiring folklore around the world, referred to as ‘geomyths’.
Richard Hing said: “It is important to distinguish between fossil folklore with a factual basis — that is, connections between fossils and myth evidenced by archaeological discoveries or compelling references in literature and artwork — and speculated connections based on intuition.
“There is nothing inherently wrong with the idea that ancient peoples found dinosaur bones and incorporated them into their mythology, but we need to root such proposals in realities of history, geography and palaeontology. Otherwise, they are just speculation.”
Dr Witton added: “Not all mythological creatures demand explanations through fossils. Some of the most popular geomyths — Protoceratops and griffins, fossil elephants and cyclopes, and dragons and dinosaurs — have no evidential basis and are entirely speculative. We promote these stories because they’re exciting and seem intuitively plausible, but doing so ignores our growing knowledge of fossil geomyths grounded in fact and evidence. These are just as interesting as their conjectural counterparts, and probably deserve more attention than entirely speculated geomythological scenarios.”
The study is published in Interdisciplinary Science Reviews.
END
New study finds dinosaur fossils did not inspire the mythological griffin
2024-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA astronaut Woody Hoburg to deliver keynote address at ISSRDC focused on developing a space workforce
2024-06-20
BOSTON (MA), June 20, 2024 – NASA astronaut Warren “Woody” Hoburg will deliver a keynote address at the International Space Station Research and Development Conference (ISSRDC) in Boston on Thursday, August 1, 2024. Hoburg has close ties to Boston as a graduate and former assistant professor of aeronautics and astronautics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
Hoburg’s address will focus on his six-month science expedition on the space station and the importance of shaping the future workforce ...
Study: Fatigue-management training improved sleep, safety, well-being for Seattle police
2024-06-20
Policing is a profession that features shift work and long hours, both of which can lead to insufficient sleep and fatigue. Because of the unique demands of the job, fatigue raises risks related to decision making, impulse control, driving, and other aspects of work. In a new study, researchers tested the effect of a fatigue-management program on the sleep, mental health, well-being, and safety of police employees in Seattle. The training improved sleep duration as well as various aspects of employees’ safety and well-being.
The study, by researchers at Washington State University (WSU) and the Seattle Police Department, ...
Guiding humanity beyond the moon: OHIO’s Nate Szewczyk and students coauthor papers published in “Nature” journals that revolutionize human space biology
2024-06-20
What actually happens to the human body in space? While scientists and researchers have heavily researched how various factors impact the human body here on Earth, the amount of information available about changes that occur in the body in space is not as well-known. Scientists, including OHIO’s Nate Szewczyk and several of his trainees, have been studying for years how the body, specifically on the molecular side, changes in space. Recently, a new package of papers has been published in “Nature” journals depicting how the modern tools of molecular biology and precision medicine can help guide humanity into more challenging missions beyond where we’ve already been.
The ...
Grant supports research to identify barriers to health care for Black women
2024-06-20
A $1.58 million grant will support work by a health communication scholar at the University of Tennessee (UT) Health Science Center’s College of Nursing and a medical oncologist at West Cancer Center and Research Institute (WCCRI) to identify sociocultural and structural factors that are root causes of cancer health disparities for Black women in the Mid-South.
Assistant Professor Janeane Anderson, PhD, MPH, is a social scientist and health communication scholar at the College of Nursing whose research focuses on how interpersonal factors affect ...
Scientists at uOttawa develop innovative method to validate quantum photonics circuits performance
2024-06-20
A team of researchers from the University of Ottawa’s Nexus for Quantum Technologies Institute (NexQT), led by Dr. Francesco Di Colandreanorth_eastexternal link, under the supervision of Professor Ebrahim Karimi, associate professor of physics, has developed an innovative technique for evaluating the performance of quantum circuits. This significant advancement, recently published in the prestigious journal npj Quantum Information, represents a substantial leap forward in the field of quantum computing.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of quantum technologies, ...
New report on community-centered approach to providing vaccine education and resources to persons experiencing homelessness during COVID-19
2024-06-20
(Boston)— A community-support model for providing health resources and education is a way to continuously engage unhoused people and other underserved groups who are particularly vulnerable during health emergencies like the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Having a stable system for bringing health information to unhoused people and connecting them to providers at Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program (BHCHP), is a pathway for addressing a number of health issues they experience,” said Kareem King, Jr., research program manager at Boston University’s Clinical & Translational Science ...
Government updates race and ethnicity data collection standards: implications and insights
2024-06-20
New Rochelle, NY, June 20, 2024–The latest issue of the peer-reviewed journal Health Equity features a pivotal roundtable discussion titled “Implications and Insights on Federal Revisions to Race and Ethnicity Collection.” This roundtable assembles leading experts to explore newly revised race and ethnicity data collection standards from the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), highlighting the significant impact these changes have on policy and practice. The expanded standards now capture historically marginalized communities, ...
Dr. Vivek S. Kavadi named CEO of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO)
2024-06-20
ARLINGTON, Va., June 20, 2024 — The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) announced today that following a nationwide search, Vivek S. Kavadi, MD, MBA, FASTRO will become CEO of the Society effective November 1, 2024. Dr. Kavadi will succeed Laura Thevenot, who previously announced her intent to retire after leading the organization since 2002.
Dr. Kavadi, a radiation oncologist and ASTRO member since 1994, ascends to the role from his current position as Chief Radiation Oncology Officer for The ...
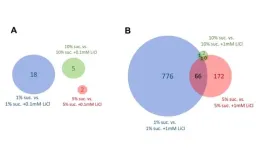
Dietary sucrose determines activity of lithium on gene expression and lifespan in drosophila melanogaster
2024-06-20
“[...] we found that, in female D. melanogaster, the life-prolonging effect of dietary lithium is dependent on the actual sucrose content of the medium.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 19, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Dietary sucrose determines the regulatory activity of lithium on gene expression and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster.”
The amount of dietary sugars and the administration of lithium both impact the lifespan of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. It is noteworthy that lithium ...
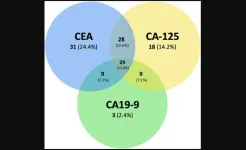
Assessment of CEA, CA-125, and CA19-9 as adjuncts in non-small cell lung cancer management
2024-06-20
“[...] these inexpensive, widely available tests with rapid turnaround times and relatively short half-lives (CEA, CA-125, and CA19-9) are perfectly situated to serve as adjunctive clinical tools in the management of NSCLC.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 20, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 13, 2024, entitled, “Assessment of serum tumor markers CEA, CA-125, and CA19-9 as adjuncts in non-small cell lung cancer management.”
Conventional tumor markers may serve as adjuncts in non-small cell lung cancer ...