(Press-News.org) Artificial intelligence continues to squirm its way into many aspects of our lives. But what about biology, the study of life itself? AI can sift through hundreds of thousands of genome data points to identify potential new therapeutic targets. While these genomic insights may appear helpful, scientists aren’t sure how today’s AI models come to their conclusions in the first place. Now, a new system named SQUID arrives on the scene armed to pry open AI’s black box of murky internal logic.
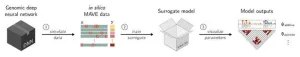
SQUID, short for Surrogate Quantitative Interpretability for Deepnets, is a computational tool created by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) scientists. It’s designed to help interpret how AI models analyze the genome. Compared with other analysis tools, SQUID is more consistent, reduces background noise, and can lead to more accurate predictions about the effects of genetic mutations.
How does it work so much better? The key, CSHL Assistant Professor Peter Koo says, lies in SQUID’s specialized training.
“The tools that people use to try to understand these models have been largely coming from other fields like computer vision or natural language processing. While they can be useful, they’re not optimal for genomics. What we did with SQUID was leverage decades of quantitative genetics knowledge to help us understand what these deep neural networks are learning," explains Koo.
SQUID works by first generating a library of over 100,000 variant DNA sequences. It then analyzes the library of mutations and their effects using a program called MAVE-NN (Multiplex Assays of Variant Effects Neural Network). This tool allows scientists to perform thousands of virtual experiments simultaneously. In effect, they can “fish out” the algorithms behind a given AI’s most accurate predictions. Their computational “catch” could set the stage for experiments that are more grounded in reality.
“In silico [virtual] experiments are no replacement for actual laboratory experiments. Nevertheless, they can be very informative. They can help scientists form hypotheses for how a particular region of the genome works or how a mutation might have a clinically relevant effect," explains CSHL Associate Professor Justin Kinney, a co-author of the study.
There are tons of AI models in the sea. More enter the waters each day. Koo, Kinney, and colleagues hope that SQUID will help scientists grab hold of those that best meet their specialized needs.
Though mapped, the human genome remains an incredibly challenging terrain. SQUID could help biologists navigate the field more effectively, bringing them closer to their findings’ true medical implications.
END
SQUID pries open AI black box
2024-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Resiliency shaped by activity in the gut microbiome and brain
2024-06-21
A new UCLA Health study has found that resilient people exhibit neural activity in the brain regions associated with improved cognition and regulating of emotions, and were more mindful and better at describing their feelings. The same group also exhibited gut microbiome activity linked to a healthy gut, with reduced inflammation and gut barrier.
For the study, rather than examine microbiome activity and composition linked to disease conditions-- like anxiety and depression -- the researchers wanted to flip the script and study the gut microbiome and brain in healthy, resilient people who effectively cope with different types of stress, including discrimination ...
Inspired by nature: synthetic nightshade molecule effective against leukemia cells
2024-06-21
Nightshade plants produce a diverse array of compounds with therapeutic potential. Researchers at CeMM have now identified an artificial variant inspired by the Withanolides group that acts highly specifically against leukemia cells. Using state-of-the-art chemical and genetic high-throughput analyses, the team led by Georg Winter not only confirmed its effectiveness but also elucidated its mechanism of action: the molecule disrupts the cholesterol metabolism of tumor cells. The study's findings ...
Promise green hydrogen may not always be fulfilled
2024-06-21
Green hydrogen often, but certainly not always, leads to CO2 gains. This claim is based on research published in Nature Energy by Kiane de Kleijne from Radboud University and Eindhoven University of Technology. “If you calculate the entire life cycle of green hydrogen production and transport, CO2 gains may be disappointing. However, if green hydrogen is produced from very clean electricity and locally, it can really help reduce emissions.”
It is thought that green hydrogen can make ...
Unifying behavioral analysis through animal foundation models
2024-06-21
Although there is the saying, “straight from the horse’s mouth”, it's impossible to get a horse to tell you if it's in pain or experiencing joy. Yet, its body will express the answer in its movements. To a trained eye, pain will manifest as a change in gait, or in the case of joy, the facial expressions of the animal could change. But what if we can automate this with AI? And what about AI models for cows, dogs, cats, or even mice? Automating animal behavior not only removes observer bias, but it helps humans more efficiently get to the right answer.
Today ...
Up to 30 percent more time: Climate change makes it harder for women to collect water
2024-06-21
Climate change could increase the amount of time women spend collecting water by up to 30 percent globally by 2050, according to a new study published in Nature Climate Change. In regions of South America and Southeast Asia, the time spent collecting water could double due to higher temperatures and less rainfall. A team of scientists from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) estimates the large welfare losses that could result from climate impacts and highlights how women are particularly vulnerable to changing future climate conditions. Worldwide, two billion people currently lack access to safe drinking water. The ...
Heart failure in space: scientists calculate potential health threats facing future space tourists in microgravity
2024-06-21
[The following is a guest editorial written by Dr Lex van Loon, an assistant professor at the Australian National University and the University of Twente in the Netherlands. He is co-author of a new Frontiers in Physiology article.]
Space exploration has always captivated our imagination, offering the promise of discovering new worlds and pushing the boundaries of human capability. As commercial space travel becomes more accessible, individuals with various underlying health conditions—including heart failure—may soon be among those venturing beyond Earth’s atmosphere. This raises critical questions about the impact of space travel ...
Experts offer guidance on talking with children about racism at pediatrician's office
2024-06-21
Extensive research shows the link between exposure to racism during childhood and adolescence and increased risks of depression and metabolic health issues, such as obesity, diabetes and heart disease. Conversely, racial socialization, described as behaviors and practices that teach children about race and ethnic identity, has shown potential in mitigating these negative effects, and discussions like these could be effective in pediatric clinics, according to the first expert consensus guidance on this topic published in Pediatrics.
“Over the years, numerous calls to action have been made to address racism in medicine. ...
Drugs for HIV and AIDS trialed as brain tumor treatment for first time
2024-06-21
Drugs developed to combat HIV and AIDS are being trialled for the first time in patients with multiple brain tumours.
Scientists at the Brain Tumour Research Centre of Excellence at the University of Plymouth are conducting a clinical trial to see whether using anti-retroviral medications, Ritonavir and Lopinavir, could help people with Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2).
The rare inherited genetic condition causes tumours such as schwannoma (which include acoustic neuroma), ependymoma and meningioma which develop ...
Breakthrough in nanoscale force measurement opens doors to unprecedented biological insights
2024-06-21
Groundbreaking research has revealed a new way to measure incredibly minute forces at the nanoscale in water, pushing the boundaries of what scientists know about the microscopic world.
The significant nanotechnology advance was achieved by researchers from Beihang University in China with RMIT University and other leading institutions including the Australian National University and University of Technology Sydney.
The new technique, involving a super-resolved photonic force microscope (SRPFM), is capable of detecting forces in water as small as 108.2 attonewtons—a scale so minute that it compares to measuring the weight of a virus.
Lead ...
Scientists discover new behavior of membranes that could lead to unprecedented separations
2024-06-21
Imagine a close basketball game that comes down to the final shot. The probability of the ball going through the hoop might be fairly low, but it would dramatically increase if the player were afforded the opportunity to shoot it over and over.
A similar idea is at play in the scientific field of membrane separations, a key process central to industries that include everything from biotechnology to petrochemicals to water treatment to food and beverage.
“Separations lie at the heart of so many of the products we use in our everyday lives,” said Seth Darling, head of the Advanced Materials for Energy Water Systems (AMEWS) Center at the U.S. Department of ...