(Press-News.org) Small changes in our everyday actions can trigger significant, rapid societal shifts especially when it comes to climate action. A new IIASA-led study highlights the importance of analyzing these dynamics with a comprehensive framework to harness their full potential for reducing carbon emissions.
Making small changes in how we live day-to-day can quickly create significant changes in society, especially in ways that benefit the environment. This idea is captured in the term social tipping points.
According to the authors of a new paper just published in the journal One Earth, social tipping points are crucial for speeding up efforts to reduce carbon emissions. These points occur when social, political, economic, or technological systems rapidly shift to a new state due to positive feedback mechanisms. Understanding these tipping points requires analyzing the complexity of social systems, but current research lacks a practical framework that combines both theoretical and empirical aspects.
“Consider how one Swedish school student’s Friday protest has tipped millions into climate protest and activism that signal public support for climate action. Or how Norway’s electric vehicle policies have tipped the country's vehicle fleet away from combusting fossil fuels. Given the promise of social tipping it’s essential that scientific analysis is rigorous, not just in identifying and evidencing potential tipping points, but also in modeling their dynamics to understand how they unfold and what may block them. Explaining how to do this is what we do in this paper,” explains study coauthor Charlie Wilson, a senior researcher at IIASA and professor of Energy and Climate Change in the Environmental Change Institute at the University of Oxford, UK.
The study introduces a dynamic systems approach to studying social tipping points, which includes looking at interconnected feedback mechanisms and interactions across different systems and scales. The authors also emphasize the importance of gathering and analyzing data to provide solid evidence and monitor these tipping dynamics, using global modeling to predict future changes.
The approach builds on the findings of an expert workshop where the team identified key feedback mechanisms that drive tipping dynamics. The authors point out that it is also important to consider factors that can counteract these dynamics. For example, while spreading pro-environmental values is seen as a positive tipping point, societal polarization can hinder this spread.
“Our research shows that small actions can lead to significant changes that ripple through social and economic systems. This means that both policymakers and everyday people have a lot of power to influence big changes. However, it's crucial to carefully analyze which small actions can lead to these large impacts,” says study lead author Sibel Eker, a senior researcher at IIASA and Nijmegen School of Management at Radboud University in The Netherlands.
The comprehensive approach proposed and demonstrated in this study can support a better understanding of social tipping dynamics and strengthen the viability and effectiveness of climate policies. The authors however highlight that their approach could be enhanced further by identifying influential agents and considering differences between regions, like the Global North and South, through collaborative efforts to make the concept of social tipping even more robust and useful for policy and practice.
Reference
Eker, S., Wilson, C., Höhne, N., McCaffrey, M.S., Monasterolo, I., Niamir, L., Zimm, C. (2024). Harnessing social tipping dynamics: A systems approach for accelerating decarbonization. One Earth DOI: 10.1016/j.oneear.2024.05.012
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe. www.iiasa.ac.at
END
Supporting the right small changes can have big impacts
2024-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Grafted cucumbers get a boost: pumpkin's secret to withstanding salinity
2024-06-21
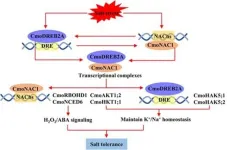
A pivotal study has discovered a genetic synergy between pumpkin and cucumber that fortifies the latter's resilience against salinity. The research illuminates the role of the CmoDREB2A transcription factor from pumpkin, which, when interacted with cucumber's CmoNAC1, forms a regulatory loop that enhances salt tolerance. This breakthrough could be key to developing crops that thrive in saline soils, safeguarding agricultural productivity.
Soil salinity, a silent blight on global agriculture, affects an estimated 10% of the world's arable land, leading to significant crop ...
Unlocking broccoli's genome: key to enhanced health benefits
2024-06-21
A detailed genomic study of broccoli has revealed the genetic foundations for the production of glucosinolates (GSLs), compounds celebrated for their health benefits, including anti-carcinogenic properties. By assembling a high-quality chromosome-level genome, researchers identified key genes involved in GSL biosynthesis. These findings offer critical insights for future genetic studies and the development of Brassica crops with enhanced nutritional value, paving the way for improved health benefits from these widely consumed vegetables.
Broccoli is renowned for its health benefits, primarily due to its rich glucosinolate (GSL) content, which has anti-carcinogenic ...
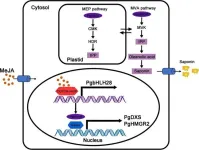
New insights into methyl jasmonate-induced saponin biosynthesis in balloon flower
2024-06-21
A cutting-edge study has pinpointed the PgbHLH28 gene as a crucial catalyst in the methyl jasmonate-induced (MeJA-induced) saponin biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus. This genetic insight could significantly bolster the production of saponins, which are beneficial in combating cerebrovascular diseases and COVID-19, offering a novel therapeutic avenue in medicinal plant cultivation.
Platycodon grandiflorus, commonly known as balloon flower, is renowned for its medicinal properties, primarily due to its rich saponin content. Saponins are known for ...
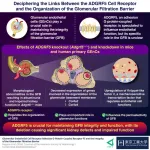
Unraveling the role of ADGRF5: Insights into kidney health and function
2024-06-21
Glomerulus, the fundamental filtering unit of the kidney, is an intricate network of capillaries — small blood vessels that regulate the movement of ions, water, and metabolites while maintaining impermeability to essential macromolecules such as proteins. The selectively permeable capillary wall, known as the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB), consists of three main components: glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs), the glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes. GEnCs line the inner surface of the capillary wall and are covered by a thin layer of glycoproteins and other carbohydrate-based moieties.
Adhesion G-protein-coupled ...
JMIR Dermatology accepted for MEDLINE indexing
2024-06-21
(Toronto, June 21, 2024) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Dermatology (JMIR Derm) has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE, which is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database.
JMIR Dermatology was previously already indexed in PubMed, but MEDLINE is a more selective subset of PubMed, consisting of the top 5200 biomedical journals, and indexing in MEDLINE also means that articles are now also indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) and other metadata.
Selection for MEDLINE is a result of a thorough review of the ...
Reduced infections seen in CLL and NHL patients undergoing immunoglobulin testing and replacement therapy
2024-06-21
(WASHINGTON, June 21, 2024) – Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) who received frequent tests for immunoglobulin G (IgG) were less likely to experience severe infections compared with those who didn’t, according to a study published in Blood Advances. Moreover, only half of patients undergo such testing.
Patients with blood cancers such as CLL and NHL are at elevated risk for potentially life-threatening infections due to low blood levels of immunoglobulins — proteins ...
Human activity: A double-edged sword in the face of drought
2024-06-21
Earth and environmental scientists reported that as human socio-economic activities increase, greenhouse gas emissions will rise, leading to more frequent extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. However, a research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has published a study suggesting that anthropogenic greenhouse gases might actually mitigate droughts, offering a new perspective on the impact of human activities on nature.
Professor Jonghun Kam from the Division of Environmental Science and Engineering at POSTECH ...
Portfolio performance in financial management: apraize, analyze, act.
2024-06-21
Co-authored by Pascal François (HEC Montreal) and Georges Hubner (University of Liège), both professors of finance, The Complete Guide to Portfolio Performance: Appraise, Analyse, Act, just published by Wiley, is a comprehensive guide to all aspects of financial portfolio performance. The book explores the essential topics of portfolio performance measurement in a realistic and rigorous way, with usable content clearly illustrated by practical examples that demonstrate the application of the concepts discussed.
Portfolio management is a complex field, requiring in-depth expertise ...
Landmark Nature Medicine study reports promising new treatment reduces suffering in Sanfilippo syndrome
2024-06-21
As a neurodegenerative disease characterized by childhood onset dementia, Sanfilippo syndrome causes immense suffering in many ways, including pain, loss of speech, extreme agitation, and distress, gastrointestinal symptoms, and profound sleep disturbance. With no approved treatment, clinical specialists have had few options to help alleviate this suffering until now. A groundbreaking clinical trial collaboration between study lead and principal investigator Lynda Polgreen, MD, MS, Investigator at The Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor-UCLA (TLI) and Associate ...
Membrane protein analogues could accelerate drug discovery
2024-06-21
Many drug and antibody discovery pathways focus on intricately folded cell membrane proteins: when molecules of a drug candidate bind to these proteins, like a key going into a lock, they trigger chemical cascades that alter cellular behavior. But because these proteins are embedded in the lipid-containing outer layer of cells, they are tricky to access and insoluble in water-based solutions (hydrophobic), making them difficult to study.
"We wanted to get these proteins out of the cell membrane, so we redesigned them as hyperstable, soluble analogues, which look like membrane proteins but are much ...