(Press-News.org) As the deadly disease that came to be known as COVID-19 started spreading in late 2019, scientists rushed to answer a critical question: Who is most at risk?
They quickly recognized that a handful of characteristics — including age, smoking history, high body mass index (BMI) and the presence of other diseases such as diabetes — made people infected with the virus much more likely to become seriously ill and even die. But one suggested risk factor remains unconfirmed more than four years later: cannabis use. Evidence has emerged over time indicating both protective and harmful effects.
Now, a new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis points decisively to the latter: Cannabis is linked to an increased risk of serious illness for those with COVID-19.
The study, published June 21 in JAMA Network Open, analyzed the health records of 72,501 people seen for COVID-19 at health centers in a major Midwestern health-care system during the first two years of the pandemic. The researchers found that people who reported using any form of cannabis at least once in the year before developing COVID-19 were significantly more likely to need hospitalization and intensive care than were people with no such history. This elevated risk of severe illness was on par with that from smoking.
“There’s this sense among the public that cannabis is safe to use, that it’s not as bad for your health as smoking or drinking, that it may even be good for you,” said senior author Li-Shiun Chen, MD, DSc, a professor of psychiatry. “I think that’s because there hasn’t been as much research on the health effects of cannabis as compared to tobacco or alcohol. What we found is that cannabis use is not harmless in the context of COVID-19. People who reported yes to current cannabis use, at any frequency, were more likely to require hospitalization and intensive care than those who did not use cannabis.”
Cannabis use was different than tobacco smoking in one key outcome measure: survival. While smokers were significantly more likely to die of COVID-19 than nonsmokers — a finding that fits with numerous other studies — the same was not true of cannabis users, the study showed.
“The independent effect of cannabis is similar to the independent effect of tobacco regarding the risk of hospitalization and intensive care,” Chen said. “For the risk of death, tobacco risk is clear but more evidence is needed for cannabis.”
The study analyzed deidentified electronic health records of people who were seen for COVID-19 at BJC HealthCare hospitals and clinics in Missouri and Illinois between Feb. 1, 2020, and Jan. 31, 2022. The records contained data on demographic characteristics such as sex, age and race; other medical conditions such as diabetes and heart disease; use of substances including tobacco, alcohol, cannabis and vaping; and outcomes of the illness — specifically, hospitalization, intensive-care unit (ICU) admittance and survival.
COVID-19 patients who reported that they had used cannabis in the previous year were 80% more likely to be hospitalized and 27% more likely to be admitted to the ICU than patients who had not used cannabis, after taking into account tobacco smoking, vaccination, other health conditions, date of diagnosis, and demographic factors. For comparison, tobacco smokers with COVID-19 were 72% more likely to be hospitalized and 22% more likely to require intensive care than were nonsmokers, after adjusting for other factors.
These results contradict some other research suggesting that cannabis may help the body fight off viral diseases such as COVID-19.
“Most of the evidence suggesting that cannabis is good for you comes from studies in cells or animals,” Chen said. “The advantage of our study is that it is in people and uses real-world health-care data collected across multiple sites over an extended time period. All the outcomes were verified: hospitalization, ICU stay, death. Using this data set, we were able to confirm the well-established effects of smoking, which suggests that the data are reliable.”
The study was not designed to answer the question of why cannabis use might make COVID-19 worse. One possibility is that inhaling marijuana smoke injures delicate lung tissue and makes it more vulnerable to infection, in much the same way that tobacco smoke causes lung damage that puts people at risk of pneumonia, the researchers said. That isn’t to say that taking edibles would be safer than smoking joints. It is also possible that cannabis, which is known to suppress the immune system, undermines the body’s ability to fight off viral infections no matter how it is consumed, the researchers noted.
“We just don’t know whether edibles are safer,” said first author Nicholas Griffith, MD, a medical resident at Washington University. Griffith was a medical student at Washington University when he led the study. “People were asked a yes-or-no question: ‘Have you used cannabis in the past year?’ That gave us enough information to establish that if you use cannabis, your health-care journey will be different, but we can’t know how much cannabis you have to use, or whether it makes a difference whether you smoke it or eat edibles. Those are questions we’d really like the answers to. I hope this study opens the door to more research on the health effects of cannabis.”
END
Cannabis use tied to increased risk of severe COVID-19
Similar to smokers, cannabis users nearly twice as likely to need hospitalization, intensive care when infected with the virus
2024-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to make ageing a ‘fairer game’ for all wormkind
2024-06-21
Why do some people live for longer than others? The genes in our DNA sequence are important, helping avoid disease or maintain general health, but differences in our genome sequence alone explain less than 30% of the natural variance of human life expectancy.
Exploring how ageing is influenced at the molecular level could shed light on lifespan variation, but generating data at the speed, scale and quality necessary to study this in humans is unfeasible. Instead, researchers turn to worms (Caenorhabditis elegans). Humans share a lot of biology with these small creatures, who also have a large, natural variation in lifespan.
Researchers ...
Supporting the right small changes can have big impacts
2024-06-21
Small changes in our everyday actions can trigger significant, rapid societal shifts especially when it comes to climate action. A new IIASA-led study highlights the importance of analyzing these dynamics with a comprehensive framework to harness their full potential for reducing carbon emissions.
Making small changes in how we live day-to-day can quickly create significant changes in society, especially in ways that benefit the environment. This idea is captured in the term social tipping points.
According to the authors of a new paper just published in the journal One Earth, social tipping points are crucial for speeding up efforts to reduce carbon emissions. These points occur when ...
Grafted cucumbers get a boost: pumpkin's secret to withstanding salinity
2024-06-21
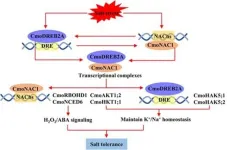
A pivotal study has discovered a genetic synergy between pumpkin and cucumber that fortifies the latter's resilience against salinity. The research illuminates the role of the CmoDREB2A transcription factor from pumpkin, which, when interacted with cucumber's CmoNAC1, forms a regulatory loop that enhances salt tolerance. This breakthrough could be key to developing crops that thrive in saline soils, safeguarding agricultural productivity.
Soil salinity, a silent blight on global agriculture, affects an estimated 10% of the world's arable land, leading to significant crop ...
Unlocking broccoli's genome: key to enhanced health benefits
2024-06-21
A detailed genomic study of broccoli has revealed the genetic foundations for the production of glucosinolates (GSLs), compounds celebrated for their health benefits, including anti-carcinogenic properties. By assembling a high-quality chromosome-level genome, researchers identified key genes involved in GSL biosynthesis. These findings offer critical insights for future genetic studies and the development of Brassica crops with enhanced nutritional value, paving the way for improved health benefits from these widely consumed vegetables.
Broccoli is renowned for its health benefits, primarily due to its rich glucosinolate (GSL) content, which has anti-carcinogenic ...
New insights into methyl jasmonate-induced saponin biosynthesis in balloon flower
2024-06-21
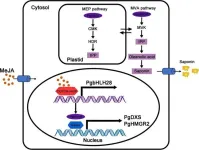
A cutting-edge study has pinpointed the PgbHLH28 gene as a crucial catalyst in the methyl jasmonate-induced (MeJA-induced) saponin biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus. This genetic insight could significantly bolster the production of saponins, which are beneficial in combating cerebrovascular diseases and COVID-19, offering a novel therapeutic avenue in medicinal plant cultivation.
Platycodon grandiflorus, commonly known as balloon flower, is renowned for its medicinal properties, primarily due to its rich saponin content. Saponins are known for ...
Unraveling the role of ADGRF5: Insights into kidney health and function
2024-06-21
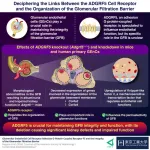
Glomerulus, the fundamental filtering unit of the kidney, is an intricate network of capillaries — small blood vessels that regulate the movement of ions, water, and metabolites while maintaining impermeability to essential macromolecules such as proteins. The selectively permeable capillary wall, known as the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB), consists of three main components: glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs), the glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes. GEnCs line the inner surface of the capillary wall and are covered by a thin layer of glycoproteins and other carbohydrate-based moieties.
Adhesion G-protein-coupled ...
JMIR Dermatology accepted for MEDLINE indexing
2024-06-21
(Toronto, June 21, 2024) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Dermatology (JMIR Derm) has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE, which is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database.
JMIR Dermatology was previously already indexed in PubMed, but MEDLINE is a more selective subset of PubMed, consisting of the top 5200 biomedical journals, and indexing in MEDLINE also means that articles are now also indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) and other metadata.
Selection for MEDLINE is a result of a thorough review of the ...
Reduced infections seen in CLL and NHL patients undergoing immunoglobulin testing and replacement therapy
2024-06-21
(WASHINGTON, June 21, 2024) – Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) who received frequent tests for immunoglobulin G (IgG) were less likely to experience severe infections compared with those who didn’t, according to a study published in Blood Advances. Moreover, only half of patients undergo such testing.
Patients with blood cancers such as CLL and NHL are at elevated risk for potentially life-threatening infections due to low blood levels of immunoglobulins — proteins ...
Human activity: A double-edged sword in the face of drought
2024-06-21
Earth and environmental scientists reported that as human socio-economic activities increase, greenhouse gas emissions will rise, leading to more frequent extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. However, a research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has published a study suggesting that anthropogenic greenhouse gases might actually mitigate droughts, offering a new perspective on the impact of human activities on nature.
Professor Jonghun Kam from the Division of Environmental Science and Engineering at POSTECH ...
Portfolio performance in financial management: apraize, analyze, act.
2024-06-21
Co-authored by Pascal François (HEC Montreal) and Georges Hubner (University of Liège), both professors of finance, The Complete Guide to Portfolio Performance: Appraise, Analyse, Act, just published by Wiley, is a comprehensive guide to all aspects of financial portfolio performance. The book explores the essential topics of portfolio performance measurement in a realistic and rigorous way, with usable content clearly illustrated by practical examples that demonstrate the application of the concepts discussed.
Portfolio management is a complex field, requiring in-depth expertise ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
[Press-News.org] Cannabis use tied to increased risk of severe COVID-19Similar to smokers, cannabis users nearly twice as likely to need hospitalization, intensive care when infected with the virus