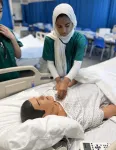
(Press-News.org) A group of pre-medical students received valuable hands-on clinical training during a workshop in the new Smart Hospital at The University of Texas at Arlington.
The Clinical Experience Workshop allowed 10 pre-med students to participate in experiential activities and to interact one-on-one with “patients” portrayed by students from the UTA Department of Theatre Arts.
“This was a clinical opportunity for pre-med students with no clinical background to be immersed in clinical medicine, learn basic skills, and experience actual patient encounters with simulated patients who were actually trained UTA theater students,” said Steve Gellman, College of Science pre-med consultant and co-director of the minor in medical humanities and bioethics program.
Students learned how to check vital signs, start an intravenous line, and deliver a baby by using lifelike manikins in the state-of-the-art Smart Hospital. They also received instruction on various medical procedures and participated in virtual-reality exercises in the Smart Hospital’s simulation lab.
During the live patient portion of the workshop, each theater student portrayed a patient with specific symptoms that the pre-med students had to diagnose.
“The workshop was so much fun—for the students and staff. There was universal agreement that this was a valuable and memorable experience that will have a lasting impact on the participants,” Gellman said. “Experiential learning is an excellent path toward meaningful and lasting education, especially for teaching the important humanities aspect of patient care.”
The workshop, which was made possible by funds from the UTA Libraries Department of Experiential Learning and the College of Science, is just one of the many ways UTA and the College of Science help prepare students for medical and other health professions schools.
UTA’s Office of Health Professions offers test prep classes, a pre-med preceptorship program, career information events featuring professionals from various fields, an annual Health Professions Fair, a graduate school advisory program, and more. It also oversees the Joint Admission Medical Program (JAMP), which was created by the Texas legislature to help highly qualified economically disadvantaged students pursue a medical education.
Another popular program the office offers is an emergency medical technician (EMT) class that allows students to earn an EMT certification via a hybrid online and in-person class. The class is offered in partnership with UT Dallas and University Emergency Medical Response.
END
Giving pre-med students hands-on clinical training
Smart Hospital workshop provides basic skills and virtual-reality exercises
2024-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CAMH research suggests potential targets for prevention and early identification of psychotic disorders
2024-06-21
A new study by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH), entitled Mental Health Service Use Before First Diagnosis of a Psychotic Disorder and published in JAMA Psychiatry, found that nearly 75 per cent of young Ontarians with a psychotic disorder had at least one mental health service visit within the three years prior to their first diagnosis of the disorder.
The retrospective cohort study—one of the largest of its kind—suggests that youth with a psychotic disorder are nearly four times as likely to have a previous mental health-related hospital ...
Mapping the heart to prevent damage caused by a heart attack
2024-06-21
Scientists at the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute in Australia have produced a first of its kind integrated map of heart cells which unlocks the process of cardiac fibrosis – a major cause of heart failure.
The discovery opens new avenues to develop targeted drugs to prevent scarring damage caused after a heart attack.
During and after a heart attack, the heart’s muscles are damaged leading to the formation of scar tissue which lacks the elasticity and contractility of healthy heart muscle. This damage is permanent and can affect ...
Study challenges popular idea that Easter islanders committed ‘ecocide’
2024-06-21
Some 1,000 years ago, a small band of Polynesians sailed thousands of miles across the Pacific to settle one of the world’s most isolated places—a small, previously uninhabited island they named Rapa Nui. There, they erected hundreds of “moai,” or gigantic stone statues that now famously stand as emblems of a vanished civilization. Eventually, their numbers ballooned to unsustainable levels; they chopped down all the trees, killed off the seabirds, exhausted the soils and in the end, ruined their environment. Their population and civilization collapsed, with just a few thousand people remaining when ...
Chilling discovery: Study reveals evolution of human cold and menthol sensing protein, offering hope for future non-addictive pain therapies.
2024-06-21
Chronic pain affects millions worldwide, and current treatments often rely on opioids, which carry risks of addiction and overdose.
Non-addictive alternatives could revolutionize pain management, and new research targeting the human protein which regulates cold sensations, brings scientists closer to developing pain medications that don't affect body temperature and don't carry the risks of addiction.
Research published in Science Advances on June 21, led by Wade Van Horn, professor in Arizona State University’s School of Molecular Sciences and Biodesign ...
Elena Beccalli, new rector of Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, takes office on 1st July
2024-06-21
Elena Beccalli will be rector of the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore on 1st July for the four-year term 2024–2028. After being appointed by the University's Board of Directors, which convened today, Thursday 20 June 2024, Professor Beccalli succeeds Professor Franco Anelli. She is the first woman appointed to this role in the history of our university.
The decision of the Board of Directors follows the appointment of Professor Elena Beccalli, Dean of the School of Banking, Finance, and Insurance ...
Pacific Northwest Research Institute uncovers hidden DNA mechanisms of rare genetic diseases
2024-06-21
Seattle, WA — June 21, 2024 — Researchers at the Pacific Northwest Research Institute (PNRI) and collaborating institutions have made a groundbreaking discovery that could significantly advance our understanding of genomic disorders. Their latest study, funded by the National Institutes of Health[1] and published in the journal Cell Genomics, reveals how specific DNA rearrangements called inverted triplications contribute to the development of various genetic diseases.
Understanding the Study
Genomic disorders occur when there are changes or mutations in DNA that disrupt normal biological functions. These can lead ...
Empowering older adults: Wearable tech made easier with personalized support
2024-06-21
(Toronto, June 20, 2024) A new review in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, published by JMIR Publications, found that community-dwelling older adults are more likely to continue using wearable monitoring devices (WMDs), like trackers, pedometers, and smartwatches, if they receive support from health care professionals or peers.
The research team from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, led by Dr. Arkers Kwan Ching Wong, reviewed data from 3 randomized controlled trials involving over 150 older adults. The evaluation showed that the interventions that focused on increasing awareness of being monitored and used collaborative goal-setting and feedback tools, such as the SystemCHANGE ...
Pennington Biomedical researchers partner on award-winning Long Covid study
2024-06-21
Dr. John Kirwan, Executive Director of Pennington Biomedical Research Center, is serving as a co-principal investigator on the Pathobiology in RECOVER of Metabolic and Immune Systems, or PROMIS, study. The study has been awarded more than $802,000 by the National Institutes of Health to identify potential causes of Long COVID.
“The PROMIS study will help us better understand what is driving Long COVID,” Dr. Kirwan said. “In the early days of the pandemic, Pennington Biomedical directed its resources to address the urgent health needs of our population. Now with estimates that more than 25 percent of people in the U.S. who had COVID have experienced ...
Cooling ‘blood oranges’ could make them even healthier – a bonus for consumers
2024-06-21
An orange teeming with antioxidants and other health benefits may be a shot in the arm for consumers and citrus growers, if the fruit is stored at cool temperatures, a new University of Florida study shows.
But it’s too soon to know if the so-called “blood oranges” are a viable crop for the Florida citrus industry, says Ali Sarkhosh, a UF/IFAS associate professor of horticultural sciences. Sarkhosh’s post-doctoral associate Fariborz Habibi explains further.
“Although blood oranges typically command higher prices than other common varieties, such as navel or ...
Body image and overall health found important to the sexual health of older gay men, according to new studies
2024-06-21
According to a National Poll on Healthy Aging, 93% of people in the U.S. between 50-80 years old report experiencing at least one form of ageism from other people. Internalized ageism is when a person believes ageist ideas about themselves, such as thinking they had a “senior moment” or thinking they are too old to learn new technology. Internalizing ageist stereotypes can impact older people’s mental and physical health, including sexual health. Various aspects of older adults’ sexual ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Giving pre-med students hands-on clinical trainingSmart Hospital workshop provides basic skills and virtual-reality exercises