(Press-News.org) A new survey of adult citizens in 18 of the world’s largest economies has revealed majority support for tax reforms and broader political and economic reform. (Not all questions were asked in China, as indicated when findings reference 17 G20 countries.)
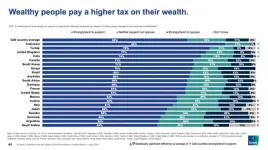
Around two-thirds (68%) of citizens across 17[1] G20 countries surveyed back a wealth tax on wealthy people as a means of funding major changes to our economy and lifestyle, with only 11% opposed, while 70% support higher rates of income tax on wealthy people, and 69% favour higher tax rates on large businesses, according to the survey conducted by Ipsos.
Support for a wealth tax on wealthy people is highest in Indonesia (86%), Turkey (78%), the UK (77%) and India (74%). Support is lowest in Saudi Arabia (54%), and Argentina (54%), but still over half the respondents surveyed. In the United States, France and Germany around two in three of those surveyed support a wealth tax on wealthy people (67%, 67% and 68% respectively).
Results also show that when thinking about climate change and protecting nature, 71% of citizens in 18 G20 countries surveyed believe the world needs to act immediately, within a decade to reduce carbon emissions from electricity, transport, food, industry and buildings. This rises to 91% of Mexicans, 83% of South Africans and 81% of Brazilians surveyed. This belief is lowest – but still over half of respondents – in Saudi Arabia (52%), Japan (53%), the United States (62%) and Italy (62%).
The findings come as finance ministers from G20 countries, including the United States, China, and India, prepare to meet in Brazil this July. For the first time, a wealth tax is on the agenda as these nations deliberate on strategies to address economic and environmental challenges.
The survey, commissioned by Earth4All and the Global Commons Alliance, explored support for economic and political transformation in 18 of the G20 nations.
The survey highlighted broad support for using additional tax revenues to fund policy proposals to changes to our economy and lifestyles. Key areas with strong support include green energy initiatives, universal healthcare and strengthening workers’ rights. Even less popular proposals, such as universal basic income and investment in citizens' assemblies to strengthen democracy, attract support from about half of respondents.
Owen Gaffney, co-lead of the Earth4All initiative, stated, “The message to politicians could not be clearer. The vast majority of people we surveyed in the world’s largest economies believe major immediate action is needed this decade to tackle climate change and protect nature. At the same time many feel the economy is not working for them and want political and economic reform. It’s possible this may well help explain the rise in populist leaders.”
“Our survey results provide a clear mandate from those across the G20 countries surveyed: redistribute wealth. Greater equality will build stronger democracies to drive a fair transformation for a more stable planet.”
Jane Madgwick, Executive Director at the Global Commons Alliance, echoed this urgency, saying, "Science demands a giant leap to address the planetary crisis, climate change and to protect nature. And 71% of citizens in 18 G20 countries surveyed support immediate action within the next decade to reduce carbon emissions.”
In 17[2] G20 countries surveyed, a majority of people believe economies should move beyond a singular focus on economic growth.
68% of those across 17[3] G20 countries surveyed agree that the way their country’s economy works should prioritise the health and wellbeing of people and nature rather than focusing solely on profit and increasing wealth. Furthermore, 62% agree that a country's economic success should be measured by the health and wellbeing of its citizens, not how fast the economy is growing.
Trust in government is low, with only 39% of people in 17 G20 countries surveyed believing their government can be trusted to make decisions for the benefit of the majority of people, and just 37% trusting their government to make long-term decisions that will benefit the majority of people 20 or 30 years from now.
There is a notable demand for reform of national and global political and economic systems. In the 17 G20 countries surveyed, 65% of respondents believe their national political system needs major changes (36%) or to be completely reformed (29%). A similar proportion (67%) feel the same about their country’s economic system (41% that it needs major changes and 27% that it needs to be completely reformed).
Sandrine Dixson-Declève, executive chair of Earth4All and co-president of the Club of Rome said, “This survey proves once again that the majority of citizens across G20 countries believe it is time for an economy that delivers greater wellbeing, more climate solutions and less inequality. But the results also show a lack of trust in government especially in Europe. With the recent European elections moving towards the radical right, we need to hold governments accountable to introduce an economy that services people and planet at the same time.”
The survey also asked whether people are optimistic or pessimistic about their future. On average, 62% of people in 18 G20 countries surveyed are optimistic about their own future. However, only 44% feel positive about their country’s future, while 38% are optimistic about the future of the world. Participants in emerging economies like Indonesia, Mexico, Brazil, and India, along with those in China and Saudi Arabia are the most optimistic while participants in Europe and those in Japan and South Korea tend to be less optimistic.
[1] Question not asked in China.
[2] Question not asked in China.
[3] Question not asked in China.
END
Tax the rich, say a majority of adults across 17 G20 countries surveyed
Across 17 G20 countries surveyed, a majority of adults (68% ) support the policy proposal where wealthy people pay a higher tax on their wealth, as a means of funding major changes to our economy and lifestyles
2024-06-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Semaglutide leads to greater weight loss in women than men with HF, improves HF symptoms in both sexes
2024-06-23
Key Findings:
Weight Loss: Women lost 9.6% of their body weight on average with semaglutide, compared with 7.2% in men, marking a significant difference.
Symptom Improvement: Both sexes saw notable improvements in HF symptoms, physical limitations, and exercise function.
Heart Failure Benefits Beyond Weight Loss: Despite greater weight loss in women, the improvement in HF symptoms was similar between sexes, suggesting semaglutide's heart failure benefits may be, in part, independent of weight loss.
WASHINGTON (June 23, 2024) – Semaglutide, a medication initially developed for ...
12.5, the 1st Impact Factor of COMMTR released!
2024-06-22
Clarivate released the first Impact Factor (2023 IF) of Communications in Transportation Research (COMMTR) on June 20, 2024. COMMTR's 2023 IF is 12.5, ranking in Top 1 (1/57, Q1) among all journals in "TRANSPORTATION" category, and its 2023 CiteScore is 15.2 (top 5%) in Scopus database.
We would like to express our sincere appreciation for the authors, reviewers, readers, editorial board members for helping to make the journal a success. We welcome your continued readership and article ...
Circadian clock impact on cluster headaches funded by $2.4M NIH grant for UTHealth Houston research
2024-06-21
The link between severe headache disorders headaches and the body’s circadian clock in pain timing and thresholds will be studied with a $2.4 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) to UTHealth Houston researchers.
The research is led by two faculty members of McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston: Mark Burish, MD, PhD, associate professor in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery, and Seung-Hee Yoo, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
The study builds on earlier research by Burish and Yoo, funded by the Will Erwin Headache Research Foundation and published ...
Study identifies first drug therapy for sleep apnea
2024-06-21
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and international collaborators have led a worldwide, advanced study demonstrating the potential of tirzepatide, known to manage type 2 diabetes, as the first effective drug therapy for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a sleep-related disorder characterized by repeated episodes of irregular breathing due to complete or partial blockage of the upper airway.
The results, published in the June 21, 2024 online edition of New England Journal of Medicine, highlight the treatment’s potential to improve the quality of life for millions around the world affected by OSA.
“This study marks a significant ...
How old is your bone marrow?
2024-06-21
Our bone marrow—the fatty, jelly-like substance inside our bones—is an unseen powerhouse quietly producing 500 billion new blood cells every day. That process is driven by hematopoietic stem cells that generate all of the various types of blood cells in our bodies and regenerating themselves to keep the entire assembly line of blood production operating smoothly.
As with any complex system, hematopoietic stem cells lose functionality as they age—and, in the process, contribute to the risk of serious diseases, including blood cancers. We know that the risk of developing aging-associated diseases is different among different individuals. ...
Boosting biodiversity without hurting local economies
2024-06-21
DURHAM, N.C. -- Protected areas, like nature reserves, can conserve biodiversity without harming local economic growth, countering a common belief that conservation restricts development. A new study outlines what is needed for conservation to benefit both nature and people.
Conservation zones aim to preserve biodiversity, protect endangered species, and maintain natural habitats. “There’s long been uncertainty about the economic tradeoffs,” said Binbin Li, associate professor of environmental science at Duke Kunshan University, and lead author ...
ChatGPT is biased against resumes with credentials that imply a disability — but it can improve
2024-06-21
While seeking research internships last year, University of Washington graduate student Kate Glazko noticed recruiters posting online that they’d used OpenAI’s ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence tools to summarize resumes and rank candidates. Automated screening has been commonplace in hiring for decades. Yet Glazko, a doctoral student in the UW’s Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering, studies how generative AI can replicate and amplify real-world biases — such as those against disabled people. How might such a system, she wondered, rank resumes that implied someone had a disability?
In ...
Simple test for flu could improve diagnosis and surveillance
2024-06-21
Fewer than one percent of people who get the flu every year get tested, in part because most tests require trained personnel and expensive equipment. Now researchers have developed a low-cost paper strip test that could allow more patients to find out which type of flu they have and get the right treatment.
The test, developed by a team from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Princeton University, and supported by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, uses CRISPR to distinguish between the two main types of seasonal flu, influenza A and B, as well as seasonal ...
UT Health San Antonio researcher awarded five-year, $2.53 million NIH grant to study alcohol-assisted liver disease
2024-06-21
SAN ANTONIO, June 21, 2024 – Liver transplants associated with alcohol-related disease are growing at a rapid pace, shifting research to address pathologies behind the ailments in light of a limited supply of organ donors.
At the forefront is Mengwei Zang, MD, PhD, an internationally recognized leader in chronic liver disease research at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) who was just awarded a groundbreaking five-year, $2.53 million grant from the National ...
Giving pre-med students hands-on clinical training
2024-06-21
A group of pre-medical students received valuable hands-on clinical training during a workshop in the new Smart Hospital at The University of Texas at Arlington.
The Clinical Experience Workshop allowed 10 pre-med students to participate in experiential activities and to interact one-on-one with “patients” portrayed by students from the UTA Department of Theatre Arts.
“This was a clinical opportunity for pre-med students with no clinical background to be immersed in clinical medicine, learn basic skills, and experience actual patient encounters with simulated patients ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
[Press-News.org] Tax the rich, say a majority of adults across 17 G20 countries surveyedAcross 17 G20 countries surveyed, a majority of adults (68% ) support the policy proposal where wealthy people pay a higher tax on their wealth, as a means of funding major changes to our economy and lifestyles