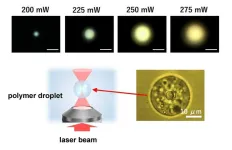
Novel application of optical tweezers: colorfully showing molecular energy transfer
Approach could have applications for microchemistry, quantum dots
2024-06-24
(Press-News.org)
A novel technique with potential applications for fields such as droplet chemistry and photochemistry has been demonstrated by an Osaka Metropolitan University-led research group.
Professor Yasuyuki Tsuboi of the Graduate School of Science and the team investigated Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), a phenomenon seen in photosynthesis and other natural processes where a donor molecule in an excited state transfers energy to an acceptor molecule.
Using dyes to mark the donor and acceptor molecules, the team set out to see if FRET could be controlled by the intensity of an optical force, in this case a laser beam. By focusing a laser beam on an isolated polymer droplet, the team showed that increased intensity accelerated the energy transfer, made visible by the polymer changing color due to the dyes mixing.
Fluorescence could also be controlled just by adjusting the laser intensity without touching the sample, offering a novel non-contact approach.
“Although this research is still at a basic stage, it may provide new options for a variety of future FRET research applications,” Professor Tsuboi explained. “We believe that extending this to quantum dots as well as new polymer systems and fluorescent molecules is the next challenge.”
The findings were published in Advanced Optical Materials.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-24
Background
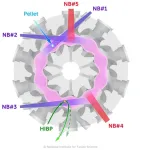
In the realm of fusion research, the control of plasma density, temperature, and heating is crucial for enhancing reactor performance. Effective confinement of plasma particles and heat, especially maintaining high density and temperature at the core where fusion occurs is essential. In the Large Helical Device (LHD)*1, challenges persist as the electron density profile often remains flat or even depressed at the center, complicating effort to sustain high central density.
Results
The LHD is equipped with five neutral beam (NB) injectors*3 for plasma ...
2024-06-24
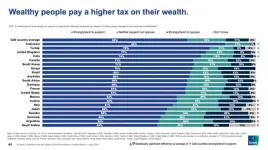
A new survey of adult citizens in 18 of the world’s largest economies has revealed majority support for tax reforms and broader political and economic reform. (Not all questions were asked in China, as indicated when findings reference 17 G20 countries.)
Around two-thirds (68%) of citizens across 17[1] G20 countries surveyed back a wealth tax on wealthy people as a means of funding major changes to our economy and lifestyle, with only 11% opposed, while 70% support higher rates of income tax on wealthy people, and 69% favour higher tax rates on large businesses, according to the survey conducted by Ipsos.
Support for a wealth tax on ...
2024-06-23
Key Findings:
Weight Loss: Women lost 9.6% of their body weight on average with semaglutide, compared with 7.2% in men, marking a significant difference.
Symptom Improvement: Both sexes saw notable improvements in HF symptoms, physical limitations, and exercise function.
Heart Failure Benefits Beyond Weight Loss: Despite greater weight loss in women, the improvement in HF symptoms was similar between sexes, suggesting semaglutide's heart failure benefits may be, in part, independent of weight loss.
WASHINGTON (June 23, 2024) – Semaglutide, a medication initially developed for ...
2024-06-22
Clarivate released the first Impact Factor (2023 IF) of Communications in Transportation Research (COMMTR) on June 20, 2024. COMMTR's 2023 IF is 12.5, ranking in Top 1 (1/57, Q1) among all journals in "TRANSPORTATION" category, and its 2023 CiteScore is 15.2 (top 5%) in Scopus database.
We would like to express our sincere appreciation for the authors, reviewers, readers, editorial board members for helping to make the journal a success. We welcome your continued readership and article ...
2024-06-21
The link between severe headache disorders headaches and the body’s circadian clock in pain timing and thresholds will be studied with a $2.4 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) to UTHealth Houston researchers.
The research is led by two faculty members of McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston: Mark Burish, MD, PhD, associate professor in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery, and Seung-Hee Yoo, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
The study builds on earlier research by Burish and Yoo, funded by the Will Erwin Headache Research Foundation and published ...
2024-06-21
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and international collaborators have led a worldwide, advanced study demonstrating the potential of tirzepatide, known to manage type 2 diabetes, as the first effective drug therapy for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a sleep-related disorder characterized by repeated episodes of irregular breathing due to complete or partial blockage of the upper airway.
The results, published in the June 21, 2024 online edition of New England Journal of Medicine, highlight the treatment’s potential to improve the quality of life for millions around the world affected by OSA.
“This study marks a significant ...
2024-06-21
Our bone marrow—the fatty, jelly-like substance inside our bones—is an unseen powerhouse quietly producing 500 billion new blood cells every day. That process is driven by hematopoietic stem cells that generate all of the various types of blood cells in our bodies and regenerating themselves to keep the entire assembly line of blood production operating smoothly.
As with any complex system, hematopoietic stem cells lose functionality as they age—and, in the process, contribute to the risk of serious diseases, including blood cancers. We know that the risk of developing aging-associated diseases is different among different individuals. ...
2024-06-21
DURHAM, N.C. -- Protected areas, like nature reserves, can conserve biodiversity without harming local economic growth, countering a common belief that conservation restricts development. A new study outlines what is needed for conservation to benefit both nature and people.
Conservation zones aim to preserve biodiversity, protect endangered species, and maintain natural habitats. “There’s long been uncertainty about the economic tradeoffs,” said Binbin Li, associate professor of environmental science at Duke Kunshan University, and lead author ...
2024-06-21
While seeking research internships last year, University of Washington graduate student Kate Glazko noticed recruiters posting online that they’d used OpenAI’s ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence tools to summarize resumes and rank candidates. Automated screening has been commonplace in hiring for decades. Yet Glazko, a doctoral student in the UW’s Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering, studies how generative AI can replicate and amplify real-world biases — such as those against disabled people. How might such a system, she wondered, rank resumes that implied someone had a disability?
In ...
2024-06-21
Fewer than one percent of people who get the flu every year get tested, in part because most tests require trained personnel and expensive equipment. Now researchers have developed a low-cost paper strip test that could allow more patients to find out which type of flu they have and get the right treatment.
The test, developed by a team from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Princeton University, and supported by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, uses CRISPR to distinguish between the two main types of seasonal flu, influenza A and B, as well as seasonal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Novel application of optical tweezers: colorfully showing molecular energy transfer
Approach could have applications for microchemistry, quantum dots