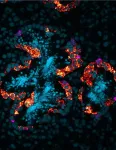
(Press-News.org) Worldwide, introduced non-native herbivores have the potential to threaten native ecosystems. For example, in western North America, uncontrolled numbers of feral horses and burros are threatening natural habitats and the native wildlife that rely on them. New research published in the wildlife research journal Wildlife Monographs documents the impact that non-native burros are having on plant and animal life in the Sonoran Desert of North America.
Investigators found that the presence of burros was associated with changes to long-lived plants important to the region. In areas with established burro herds, researchers documented lower ground cover, plant density, and foliage density, as well as smaller plant size in several species. Of particular concern was that some differences were observed among “nurse plants” that protect young plants of numerous other species from harsh conditions, and that the Sonoran Desert’s iconic saguaro cactus was observed to have lower recruitment (fewer new saguaros added to the population) in areas with burros. The study also found lower abundance in some native wildlife species.
“Our study has relevance to other ecosystems where large non-native herbivores have become established,” said corresponding author Esther Rubin, PhD, of the Arizona Game and Fish Department. “In the Sonoran Desert, the current management of this feral equid may not be adequate for maintaining the long-term viability of this arid and fragile ecosystem.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/wmon.1083
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Wildlife Monographs focuses on comprehensive syntheses of topics in wildlife science, management, and conservation. Research topics include wildlife biology and ecology, habitat use, demographics, genetics, behavior, quantitative analyses, and more areas relevant to wildlife management and conservation. Our emphasis is on aligning research with contemporary conservation and management issues and informing practitioners. We welcome extensive reviews, meta-analyses, interdisciplinary studies, and special topics. Wildlife Monographs is a journal by The Wildlife Society.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Why are scientists concerned about the effects of non-native horses and burros on natural ecosystems?
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New epidemiological tool provides warnings of heat and cold related mortality by sex and age in Europe
2024-06-26
Ambient temperatures are associated with over 5 million premature deaths worldwide every year, more than 300,000 of which in Western Europe alone. In a context of rapidly warming temperatures that successively broke previous records during the last two decades, it is essential to use epidemiological models to develop novel, impact-based early warning systems predicting the health effects of forecast temperatures.
This is precisely what the Adaptation group at the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has done: Forecaster.health is the first pan-European, open-access platform using sex- and age-specific epidemiological ...
The plants you need to keep bees on a healthy diet have been revealed
2024-06-26
As critical pollinators, bees keep our agricultural systems going — but human-caused changes to the planet heavily impact their foraging options. To help protect our food security, we need more information about bees’ own dietary requirements. Scientists writing in Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems studied the nutritional value of 57 types of pollen and found that bees need to forage from a variety of plants to balance their diet between fatty acids and essential amino acids.
“Despite public interest and a rise in pollinator plantings, little is known ...
"A hearty debate" concludes plant-based meat alternatives are healthier for your heart than meat
2024-06-26
Even though there is substantial variability in the contents and nutritional profiles of plant-based meat alternatives (PBMAs), the nutritional profiles tend to reflect a heart-healthy dietary pattern. A review article appearing in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, of the available studies directly comparing the impact of plant-based and animal-based meats consistently suggests that the plant-based alternatives improve cardiovascular risk factors.
PBMAs are highly processed plant-based food products that typically replace meat in the diet. ...
Convolutional optical neural networks herald a new era for AI imaging
2024-06-26
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), with its exceptional image recognition capabilities, have performed outstandingly in the field of AI and notably within platforms like ChatGPT. Recently, a team of Chinese researchers from University of Shanghai for Science and Technology have successfully introduced the concept of CNNs into the field of optics and realized convolutional all-optical neural network, bringing revolutionary progress to AI imaging technology.
Led by Prof. Min Gu and Prof. Qiming Zhang from School of Artificial Intelligence Science and Technology (SAIST) at the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology ...
Molecular mapping reveals tissue-specific gene regulation by diabetes-linked transcription factors
2024-06-26
SINGAPORE — Scientists have generated a comprehensive map of the gene targets regulated by the transcription factors HNF4A and HNF1A in human pancreatic beta cells and liver cells. Published in the journal Nature Communications, the study revealed common and tissue-specific molecular pathways regulated by HNF4A and HNF1A, two proteins that possess important functions governing the development and function of the pancreas and liver.
Notably, the scientists identified several novel gene targets in pancreatic beta cells, the cells responsible for insulin ...
Wildfires increasingly threaten oil and gas drill sites, compounding potential health risks, study says
2024-06-26
More than 100,000 oil and gas wells across the western U.S. are in areas burned by wildfires in recent decades, a new study has found, and some 3 million people live next to wells that in the future could be in the path of fires worsened by climate change.
Researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, said their analysis, which was published last week in the journal One Earth, is the first to examine historical and projected wildfire threats on oil and gas facilities in the U.S. While the public health effects of scorched and damaged drill sites are unclear, researchers said the study is a necessary step ...
Gender gaps in cardiovascular disease diagnosis and treatment persist; $28 billion opportunity found
2024-06-26
DALLAS, JUNE 25, 2024 — Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for women, and gaps in care and access persist between women and men. Addressing those gaps could lead to an increase of at least 1.6 million years of quality life and boost the U.S. economy by $28 billion annually by 2040, according to a new report published today by the American Heart Association and the McKinsey Health Institute (MHI). To help close these gaps and foster gender specific cardiovascular disease science into implementation, the Association, observing 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization ...
Researchers propose the next platform for brain-inspired computing
2024-06-26
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Computers have come so far in terms of their power and potential, rivaling and even eclipsing human brains in their ability to store and crunch data, make predictions and communicate. But there is one domain where human brains continue to dominate: energy efficiency.
“The most efficient computers are still approximately four orders of magnitude — that’s 10,000 times — higher in energy requirements compared to the human brain for specific tasks such as image processing and recognition, although they outperform the brain in tasks like mathematical calculations,” said UC Santa Barbara ...
Following the ‘BATT Signal:’ A new signaling pathway controlling planarian germ cells
2024-06-25
Biogenic monoamines — molecules like dopamine and serotonin — are famous for their role as the brain’s emissaries of mood, learning and memory, stress mechanisms, and fight-or-flight responses in the body.
But these neurotransmitters existed in nature long before brains popped up in the evolutionary tree. They’re prevalent in plants, bacteria, and single-cell organisms as well, but their functions there are far less understood.
Scientists at the Morgridge Institute for Research have added another task for ...
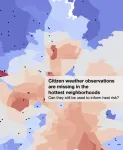
For many urban residents, it’s even hotter than their weather app says
2024-06-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- There’s a strong chance that last week’s scorching temperatures were even hotter than reported for those living in underserved urban areas.
It’s been well established that more impoverished areas within cities are typically hotter than their wealthier neighborhoods. Dubbed “urban heat islands,” these communities have more buildings, less vegetation and somewhat higher population density, which combine to produce the heating effect.
New research from environmental engineers at Duke University has shown that citizen science tools used to gauge heat in these ...