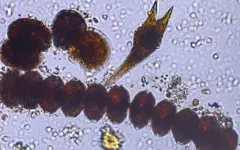
(Press-News.org) Comprising the base of the food web, plankton are extremely important to marine ecosystems. However, there is still much to be discovered about these organisms, and that’s especially true for mixoplankton.
Plankton are typically divided into two groups. Similar to plants, phytoplankton contain chlorophyll and derive energy from photosynthesis. Zooplankton, on the other hand, consume other organisms for their energy. However, there is also a third group, mixoplankton, that is a combination of the two. And, despite accounting for, at times, more than half of all plankton in the ocean, they remain poorly classified from a scientific perspective.
This is why a group of researchers is calling upon their community to better understand these diverse and fascinating creatures. In a journal article published in Frontiers of Marine Science, the scientists propose eight research questions with accompanying methodologies to help propel mixoplankton to the forefront of aquatic ecology. The paper is a follow-up to a 2023 publication that broadly outlined a series of important mixoplankton research topics.
“It’s impossible to overemphasize the impact of expanding this field. Everything that happens at the base of the food web will eventually cascade into other parts of the ecosystem, impacting species many people rely upon for nourishment or income,” said lead author Nicole Millette, assistant professor at William & Mary’s Virginia Institute of Marine Science (VIMS). “While there is a small but dedicated group of researchers studying these creatures, mixoplankton are routinely overlooked in scientific studies due to limitations of current methodologies. Until mixoplankton are routinely included in plankton research, we will only have part of the picture of what is occurring at the base of the marine ecosystem.”
The questions posed in the paper are centered around four mixotrophy research topics: evolution, observable traits and their accompanying tradeoffs, ecological biogeography and biogeochemistry and trophic transfer. The interdisciplinary methods proposed to answer these questions combine empirical data with modeling approaches, utilizing techniques such as flow cytometry, omics and molecular methods, isotopes, analysis of historical data and mathematical modeling to help unravel the complexities of mixoplankton.
The implications of answering these questions are not limited to the small organisms at the center of the research.
“If we want to understand how climate change will impact ocean ecosystems, we must understand how they are currently operating to determine what changes might occur in the future.” said Millette. “Our lack of understanding of mixoplankton’s role in the food web and biogeochemical cycling severely limits our ability to accurately predict how the ocean ecosystem may shift under climate change.”
Ultimately, the authors hope to inspire others to consider how they might contribute to the field, emphasizing the potential to shift our foundational understanding of plankton ecology.
“My goal is that, within my career, it becomes normal when I teach biological oceanography to talk about mixoplankton as one of the three main plankton groups, instead of occasionally acknowledging their existence,” said Millette. “Progress has been made, but there is so much more to be discovered.”
END
Plankton researchers urge their colleagues to mix it up
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Leading-edge model predicts impact of river plants on flood level
2024-06-26
River plants provide ecological and environmental benefits, but they raise flood risk by blocking the flow during heavy rain. Removing woody riparian vegetation patches is a primary flood prevention method, but it threatens stream's biodiversity. The research team at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim, Byung-Suk) has developed a technology for quantifying the effect of river vegetation patches on flood level changes to aid in better decision-making of river management for balancing ecological benefits and flood mitigation.
Rivers ...
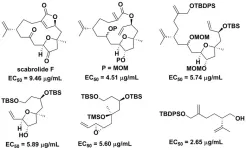
Towards non-toxic antifouling agents: A novel method for total synthesis of scabrolide F
2024-06-26
Marine organisms produce many organic compounds with diverse chemical structures and biological activities. These natural marine products are regarded as potential starting points for the discovery and development of new drugs. Among these are norcembranolide diterpenes isolated from the soft corals of the genus Sinularia. These compounds exhibit diverse biological activities, and many of them have anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. Consequently, many studies have investigated the properties of norcembranolide diterpenes and their synthesis methods. Given their potential in drug discovery, developing a synthetic ...
Researchers identify vascular changes in the brain linked to Alzheimer's disease
2024-06-26
JACKSONVILLE, Florida — The blood-brain barrier — a network of blood vessels and tissues that nurtures and protects the brain from harmful substances circulating in the blood — is disrupted in Alzheimer's disease. Now, researchers at Mayo Clinic and collaborators have uncovered unique molecular signatures of blood-brain barrier dysfunction that could point to new ways to diagnose and treat the disease. Their findings are published in Nature Communications.
"These signatures have high potential to become novel biomarkers that capture brain changes in Alzheimer's ...
New global study unveils city-region networks, highlights role of intermediate cities
2024-06-26
Rome - Rural livelihoods are quite intertwined with urban centers, with mid-sized cities playing an extraordinary role in providing required services, including for food security, agricultural livelihoods and viable rural development, according to a new study by researchers at the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and other institutions.
Some two-thirds of the world’s population, or more than 5 billion people, live within one hour of travel time – using locally available means of ...
Scientists discover high-risk form of endometrial cancer — and how to test for it — using AI
2024-06-26
A discovery by researchers at the University of British Columbia promises to improve care for patients with endometrial cancer, the most common gynecologic malignancy.
Using artificial intelligence (AI) to spot patterns across thousands of cancer cell images, the researchers have pinpointed a distinct subset of endometrial cancer that puts patients at much greater risk of recurrence and death, but would otherwise go unrecognized by traditional pathology and molecular diagnostics.
The findings, published today in Nature Communications, will help doctors identify patients with high-risk disease ...
COSPAR welcomes launch of International Space Innovation Centre, Nicosia, Cyprus
2024-06-26
The COSPAR Panel on Innovative Solutions (PoIS) charter aims to bring state-of-the-art technology to address the hardest problems facing COSPAR researchers. PoIS first focused on predicting adverse events from solar activity and applying innovative technologies and sophisticated tools to atmospheric modelling of Mars, Earth, and Venus. This effort led to the creation of the Cyprus Space Research and Innovation Center (C-SpaRC), co-funded by the European Union (EU) in December 2023 as a new infrastructure with related research, with the cooperation of COSPAR. C-SpaRC is now under the auspices of COSPAR, and is designated the COSPAR International ...
Potential long-term volcanic activity on Iceland's Reykjanes Peninsula
2024-06-26
Given the volcanic activity on Iceland over the last three years, researchers from six universities anticipate recurring, moderately sized eruptions of similar style in the coming years to decades. They therefore stress the need for preparedness in view of the risks posed to local populations and critical infrastructure. Their study was recently published in the scientific journal Terra Nova.
“The study uses information from local earthquakes and geochemical data on the erupted magma through time to reveal the geological processes behind these recent Icelandic eruptions. A comparison of these eruptions with historical events provides strong evidence that Iceland will ...
Study finds innovative cuffless blood pressure device streamlines and enhances hypertension management
2024-06-26
A study led by a Brigham investigator evaluated a novel device that automatically measures blood pressure at the wrist, generating hundreds of readings within days that may help clinicians determine cardiovascular risk and improve hypertension care
High blood pressure, the leading risk factor for death worldwide, is present in one in every two adults. Only one-quarter of individuals with hypertension have their blood pressure under control, highlighting the need for innovative strategies for blood pressure management. A study led by an investigator from Brigham and Women’s ...
Iceland’s volcano eruptions may last decades, researchers find
2024-06-26
Iceland’s ongoing volcanic eruptions may continue on and off for years to decades, threatening the country’s most densely populated region and vital infrastructure, researchers predict from local earthquake and geochemical data.
The eruptions on the Reykjanes Peninsula have forced authorities to declare a state of emergency, with a series of eight eruptions having occurred since 2021. This southwestern region is home to 70 percent of the country’s population, its only international airport, and several geothermal power plants that supply ...
Research shows children and adolescents may be motivated to rectify gender and ethnicity biases in the classroom
2024-06-26
A new Child Development study by researchers at the University of Maryland, Furman University, Education Northwest and University of Hawaiʻi at Manoa in the United States, examined whether children think it’s unfair for a teacher to select students from only one gender or ethnic group for leadership duties.
Researchers learned that children and adolescents are not only aware of these situations, but they are also motivated to rectify these types of inequalities in the classroom. Understanding ...