Innovative electrospinning techniques revolutionize precise medicine through advanced medical devices
2024-06-26
(Press-News.org)
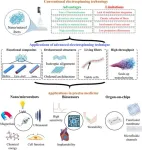
In a groundbreaking advancement that could reshape the landscape of precise medicine, researchers from the Beijing Institute of Technology and Rutgers University have unveiled a series of innovative electrospinning techniques capable of significantly enhancing the functionality and effectiveness of medical devices. This pioneering study, recently published in the Cyborg Bionic Systems journal, promises to revolutionize the creation and implementation of nano/microrobots, wearable/implantable biosensors, and organ-on-chip systems.
Precise medicine, aimed at tailoring healthcare to individual patients by considering their genetic, environmental, and lifestyle differences, has long sought more effective ways to integrate advanced technology in medical applications. The research led by Dr. Jinhua Li and Dr. Ge Gao focuses on overcoming the limitations of traditional electrospinning methods, which include issues like limited material compatibility, uncontrollable fiber orientation, and low production scalability.
The team’s work introduces modified electrospinning processes that allow for the manufacturing of highly specialized and functional composites, living constructs, and orchestrated structures, thereby expanding the potential applications in medicine significantly. These advanced techniques facilitate the integration of delicate biological components such as cells and enzymes, improving the structural and functional diversity of the produced materials.
One of the significant breakthroughs reported involves the development of core-sheath fibers, which enable the encapsulation of sensitive molecules and living cells within biocompatible materials, protecting them from mechanical stress and increasing their functional viability when implanted or applied externally on patients. This technique is especially promising for developing next-generation biosensors that can monitor physiological signals with unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity.
Furthermore, the research highlights the utilization of electrospinning in creating microfabricated environments that mimic human tissues, offering a more sophisticated approach to organ-on-chip applications. These devices can replicate human organ functions and interactions more accurately, which is crucial for drug testing and disease modeling.
Dr. Li emphasized the potential impact of their findings, stating, “Our work not only pushes the boundaries of nanotechnology in medicine but also paves the way for creating more personalized and precise treatments. The ability to craft custom-tailored biomedical products that can integrate seamlessly with the patient's body will significantly enhance the efficacy of medical treatments and interventions.”
As the demand for more effective and less invasive medical technologies grows, the innovations presented by Dr. Li, Dr. Gao, and their team could represent a major step forward in the field of precise medicine. By advancing the capabilities of electrospinning techniques, this research supports the ongoing shift towards more individualized treatment options, marking a pivotal moment in the evolution of healthcare technology.
The paper, "Recent Advances in Electrospinning Techniques for Precise Medicine," was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on May 22, 2024, at DOI: https://doi.org/10.34133/cbsystems.0101
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-26
SAN FRANCISCO —The Public Library of Science (PLOS) is pleased to announce a consortium agreement with Consorcio Colombia / Consortia facilitated by Accucoms, that allows joining member institutions to participate in PLOS’ three innovative publishing models across all 14 PLOS titles. The agreement provides researchers from affiliated institutions unlimited publishing privileges in PLOS journals without incurring fees. Eight Colombian institutions have joined the agreement in 2024 [1], and more institutions are expected to join in the following years.
“Consorcio ...
2024-06-26
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [June 26, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—a nonprofit alliance of leading cancer centers—is publishing new results for its latest survey on cancer drug shortages in the United States. This follows data published one year ago, and six months ago, illustrating how up to 93% of centers surveyed were experiencing shortages of the crucial chemotherapy carboplatin at its peak. In June 2023, 70% of centers surveyed were also lacking adequate supply for cisplatin. In the latest survey, only 11% of surveyed centers reported a shortage of carboplatin and 7% for cisplatin; but new concerns have emerged.
“Critical ...
2024-06-26
Highlights:
Bovine mastitis is a potentially fatal condition with myriad known causes, including bacteria.
Biting flies may help cause mastitis, but the mechanisms are not well elucidated.
Researchers characterized microbial diversity in biting flies and manure to look for connections.
The flies carried relevant bacterial strains, also found in the manure, associated with mastitis.
The research may point to new strategies for protecting cows from disease-causing pathogens.
Washington, D.C.—Bovine mastitis, which affects cows, leads to reduced milk production and can be fatal if left untreated. The USDA National Animal Health Monitoring ...
2024-06-26
Balance can be impacted by various factors, including diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, acute and chronic injuries to the nervous system, and the natural aging process. Accurately assessing balance in patients is important to identify and manage conditions that affect coordination and stability. Balance assessments also play a key role in preventing falls, understanding movement disorders, and designing appropriate therapeutic interventions across age groups and medical conditions.
However, traditional methods used to assess balance often suffer from subjectivity, are not comprehensive enough and cannot be administered remotely. Moreover, these assessments rely on expensive, ...
2024-06-26
Stars blinking code in Netflix’s “3 Body Problem” might be science fiction, but by deciphering neutron stars’ erratic flickers, a new study has revealed the twisted origin of these dead stars’ mysterious “heartbeats.”
When neutron stars—ultra-dense remnants of massive stars that exploded in supernovae—were first discovered in 1967, astronomers thought their strange periodic pulses could be signals from an alien civilization. Although we now know these “heartbeats” ...
2024-06-26
Many municipal landfills “burp” gas from decomposing organic matter rather than letting it build up. And burps from buried waste containing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) can release these “forever chemicals” into the air, say researchers in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters. Their study reports unexpectedly high levels of airborne PFAS at three landfills and demonstrates that vented gases and liquid by-products called leachates could transport similar amounts of these contaminants to the environment.
Some consumer products and commercial waste, such as children’s clothing, cosmetics and wastewater treatment sludge solids, contain ...
2024-06-26
Clean, safe water is a limited resource and access to it depends on local bodies of water. But even dry regions have some water vapor in the air. To harvest small amounts of humidity, researchers in ACS Energy Letters have developed a compact device with absorbent-coated fins that first trap moisture and then generate potable water when heated. They say the prototype could help meet growing demands for water, especially in arid locations.
Earth’s atmosphere holds trillions of liters of fresh water as vapor, but it’s challenging to collect this colorless, transparent and dilute gas. Previously, researchers developed systems that trap ...
2024-06-26
Comprising the base of the food web, plankton are extremely important to marine ecosystems. However, there is still much to be discovered about these organisms, and that’s especially true for mixoplankton.
Plankton are typically divided into two groups. Similar to plants, phytoplankton contain chlorophyll and derive energy from photosynthesis. Zooplankton, on the other hand, consume other organisms for their energy. However, there is also a third group, mixoplankton, that is a combination of the two. And, despite accounting for, at times, more than half of all plankton in the ocean, they remain ...
2024-06-26
River plants provide ecological and environmental benefits, but they raise flood risk by blocking the flow during heavy rain. Removing woody riparian vegetation patches is a primary flood prevention method, but it threatens stream's biodiversity. The research team at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim, Byung-Suk) has developed a technology for quantifying the effect of river vegetation patches on flood level changes to aid in better decision-making of river management for balancing ecological benefits and flood mitigation.
Rivers ...
2024-06-26
Marine organisms produce many organic compounds with diverse chemical structures and biological activities. These natural marine products are regarded as potential starting points for the discovery and development of new drugs. Among these are norcembranolide diterpenes isolated from the soft corals of the genus Sinularia. These compounds exhibit diverse biological activities, and many of them have anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. Consequently, many studies have investigated the properties of norcembranolide diterpenes and their synthesis methods. Given their potential in drug discovery, developing a synthetic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Innovative electrospinning techniques revolutionize precise medicine through advanced medical devices