(Press-News.org) About The Study: Multivitamin use was not associated with a mortality benefit in this cohort study of U.S. adults. Still, many adults report using multivitamins to maintain or improve health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Erikka Loftfield, Ph.D., M.P.H., email erikka.loftfield@nih.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.18729)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.18729?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=062624
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Multivitamin use and mortality risk in 3 prospective US cohorts
JAMA Network Open
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
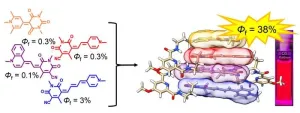
Solar technology: Innovative light-harvesting system works very efficiently
2024-06-26
In order to convert sunlight into electricity or other forms of energy as efficiently as possible, the very first step is an efficient light-harvesting system. Ideally, this should be panchromatic, i.e. absorb the entire spectrum of visible light.
The light-collecting antennae of plants and bacteria are a model for this. They capture a broad spectrum of light for photosynthesis, but are very complex in structure and require many different dyes to transmit the energy of the absorbed light and focus it on a central point.
The light-harvesting systems developed by humans to date also have disadvantages:
Although ...
Brain’s ‘escape switch’ controlled by threat sensitivity dial
2024-06-26
Neuroscientists have discovered how the brain bidirectionally controls sensitivity to threats to initiate and complete escape behaviour in mice. These findings could help unlock new directions for discovering therapies for anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The study, published today in Current Biology, outlines how researchers at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre at UCL studied a region of the brain called the periaqueductal gray (PAG), which is known to be hyperactive in people with anxiety and PTSD. Their ...
Improving prostate cancer screening for transgender women
2024-06-26
Transgender women are still at risk for prostate cancer. A new study led by Cedars-Sinai Cancer investigators, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the American Medical Association, concludes that current screening guidelines could miss early-stage prostate cancer in transgender women on hormone therapy.
The prostate, a small gland that helps make semen, also produces a protein called prostate-specific antigen, or PSA. Blood levels of PSA tend to be elevated in people who have prostate cancer, and the PSA test, which measures those levels, is a common prostate ...
For healthy adults, taking multivitamins daily is not associated with a lower risk of death
2024-06-26
What: A large analysis of data from nearly 400,000 healthy U.S. adults followed for more than 20 years has found no association between regular multivitamin use and lower risk of death. The study, led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute, was published June 26, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
Many adults in the United States take multivitamins with the hope of improving their health. However, the benefits and harms of regular multivitamin use remain unclear. ...
From takeoff to flight, the wiring of a fly's nervous system is mapped
2024-06-26
Work is underway on a wiring diagram of the motor circuits in the central nervous system that control muscles in fruit flies. This connectome, as the wiring diagram is called, is already providing detailed information on how the nerve coordination of leg movements differs from that controlling the wings.
Although fruit flies seem like simple creatures, the researchers said that their motor system contains “an unexpected level of complexity.”
“A typical fly motor neuron receives thousands of synapses from hundreds ...
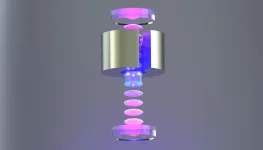
A chip-scale Titanium-sapphire laser
2024-06-26
As lasers go, those made of Titanium-sapphire (Ti:sapphire) are considered to have “unmatched” performance. They are indispensable in many fields, including cutting-edge quantum optics, spectroscopy, and neuroscience. But that performance comes at a steep price. Ti:sapphire lasers are big, on the order of cubic feet in volume. They are expensive, costing hundreds of thousands of dollars each. And they require other high-powered lasers, themselves costing $30,000 each, to supply them with enough energy to function.
As a result, Ti:sapphire lasers ...
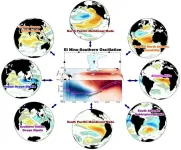
El Niño forecasts extended to 18 months with innovative physics-based model
2024-06-26
Across Asia, the Pacific Ocean, and the Americas, El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) brings variations in winds, weather, and ocean temperature that can cause droughts, floods, crop failures, and food shortages. Recently, the world has experienced a major El Niño event in 2023-2024, dramatically impacting weather, climate, ecosystems, and economies globally. By developing an innovative modeling approach, researchers from the School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) at the University ...
Scientists discover genetic ‘off switch’ in legume plants that limits biological ability to source nutrients
2024-06-26
A genetic “off switch” that shuts down the process in which legume plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into nutrients has been identified for the first time by a team of international scientists.
Legumes like beans, peas and lentils are unique among crops for their ability to interact with soil bacteria to convert or “fix” nitrogen into a usable form of nutrients. However, this energy-intensive biological process is reduced when nitrogen is already abundant in the soil either through natural processes or through the application of synthetic ...
The Frontiers Planet Prize announces 2024 International Champions
2024-06-26
The Frontiers Planet Prize today (26 June) announced its 2024 International Champions. The Prize recognizes and rewards scientists whose groundbreaking research accelerates solutions to help humanity remain safely within the nine planetary boundaries. The three winning scientists, Dr Pedro Jaureguiberry, Instituto Multidisciplinario de Biología Vegetal (Argentina), Prof Dr Peter Haase, Senckenberg Society for Nature Research (Germany), and Prof Jason Rohr, University of Notre Dame (USA), were each awarded 1.1 million (USD) / 1 million (CHF) to support their research.
The International Champions award-winning research ...
Precision instrument bolsters efforts to find elusive dark energy
2024-06-26
Dark energy — a mysterious force pushing the universe apart at an ever-increasing rate — was discovered 26 years ago, and ever since, scientists have been searching for a new and exotic particle causing the expansion.
Pushing the boundaries of this search, University of California, Berkeley physicists have now built the most precise experiment yet to look for minor deviations from the accepted theory of gravity that could be evidence for such a particle, which theorists have dubbed a chameleon or symmetron.
The experiment, which combines an atom interferometer for precise gravity ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] Multivitamin use and mortality risk in 3 prospective US cohortsJAMA Network Open