(Press-News.org) Sharing false political information on social media by users may be associated with aspects of personality such as positive schizotypy, a set of traits including paranoia, suspicion and disrupted thinking patterns. It may also be linked to a motivation to increase awareness according to a study published June 26, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Tom Buchanan, University of Westminster, UK, and colleagues.
The spread of false political information on social media can tarnish trust in authentic news and even contribute to social unrest. Knowingly or not, a small portion of social media users actively share false material.
Buchanan and colleagues asked what differentiates those who share false material on social media from those who do not and why they do it. To do this, they tested two categories of factors: individual user differences (like personality) as well as user motivation.
The researchers conducted four individual studies on a total of 1,916 US residents. Participants did not overlap between studies.
Study 1 used a cross-sectional online survey to explore the relationship between individual differences (e.g., positive schizotypy, conscientiousness and decision-making style) and users’ self-reported tendency to share false information.
Study 2 expanded on Study 1 by surveying respondents’ motivations for sharing false information (e.g., activism, manipulation, and entertainment).
In Study 3, participants (whose individual differences and motivations were surveyed) viewed a series of true and false political headlines, and were asked to indicate whether they would consider sharing each and whether each was truthful.
In Study 4, the researchers assessed real Tweets posted by participants to determine if the factors identified in Study 1, 2 and 3 are associated with actual sharing of false material on Twitter.
Across all studies, the researchers found evidence that positive schizotypy is related to sharing false information, both accidentally and deliberately, though they note that the effect sizes are small. This might be because positive schizotypy is associated with decision-making based more on intuition - and sometimes biases - rather than reflective/deliberate thought, though the researchers suspect the mechanism may be complex. As for motivations, participants most commonly reported sharing political information for reasons of ‘raising awareness’.
The researchers noted limitations of their studies: small sample sizes in some cases limited the exploratory analysis that could be performed, and participants may not always have known whether or not the information they shared was false.
A better understanding of who shares false information and why may help in identifying and developing targeted strategies to combat the spread of misinformation, the researchers say. They also suggest further research is needed to understand the links between positive schizotypy and spread of misinformation.
The authors add: “We’ve all seen false political information on social media, but only a few of us choose to share it. This study showed that our specific motivations for sharing, as well as our individual psychological characteristics, are associated with sharing false material both accidentally and on purpose.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304855
Citation: Buchanan T, Perach R, Husbands D, Tout AF, Kostyuk E, Kempley J, et al. (2024) Individual differences in sharing false political information on social media: Deliberate and accidental sharing, motivations and positive schizotypy. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0304855. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304855
Author Countries: UK
Funding: This work was funded by an award to TB from the Leverhulme Trust (RPG-2021-163). https://www.leverhulme.ac.uk. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Sharing false political information on social media may be associated with positive schizotypy
Researchers found evidence that the desire to raise awareness may be an important motivator
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI-generated exam submissions evade detection at reputable UK university
2024-06-26
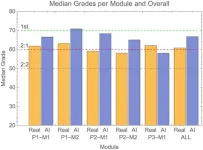
In a test of the examinations system of the University of Reading in the UK, artificial intelligence (AI)-generated submissions went almost entirely undetected, and these fake answers tended to receive higher grades than those achieved by real students. Peter Scarfe of the University of Reading and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 26.
In recent years, AI tools such as ChatGPT have become more advanced and widespread, leading to concerns about students using them to cheat by submitting AI-generated work as their own. Such concerns are heightened ...
The on-and-off affair in DNA
2024-06-26
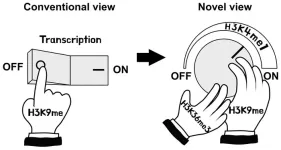
Researchers led by Kannosuke Yabe, Asuka Kamio, and Soichi Inagaki of the University of Tokyo have discovered that in thale cresses histone H3 lysine-9 (H3K9) methylation, conventionally thought to be a mark of turning off gene transcription, can also turn on gene expression via the interactions of two other proteins and histone marks. The molecular mechanisms demonstrate that rather than functioning as a simple “off switch,” H3K9 methylation is more like a “dimmer switch” that fine-tunes DNA transcription. The discovery suggests there might be similar mechanisms in other ...
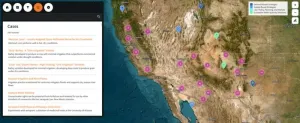
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the US Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought
2024-06-26
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the U.S. Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000246
Article Title: The water adaptation techniques atlas: A new geospatial library of solutions to water scarcity in the U.S. Southwest
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. END ...
AI generated exam answers go undetected in real-world blind test
2024-06-26
Experienced exam markers may struggle to spot answers generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI), researchers have found.
The study was conducted at the University of Reading, UK, where university leaders are working to identify potential risks and opportunities of AI for research, teaching, learning, and assessment, with updated advice already issued to staff and students as a result of their findings.
The researchers are calling for the global education sector to follow the example of Reading, and others who are also forming new ...
How do our memories last a lifetime? New study offers a biological explanation
2024-06-26
Whether it’s a first-time visit to a zoo or when we learned to ride a bicycle, we have memories from our childhoods kept well into adult years. But what explains how these memories last nearly an entire lifetime?
A new study in the journal Science Advances, conducted by a team of international researchers, has uncovered a biological explanation for long-term memories. It centers on the discovery of the role of a molecule, KIBRA, that serves as a “glue” to other molecules, thereby solidifying memory formation.
“Previous efforts to understand ...
Mechanical computer relies on kirigami cubes, not electronics
2024-06-26
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a kirigami-inspired mechanical computer that uses a complex structure of rigid, interconnected polymer cubes to store, retrieve and erase data without relying on electronic components. The system also includes a reversible feature that allows users to control when data editing is permitted and when data should be locked in place.
Mechanical computers are computers that operate using mechanical components rather than electronic ones. Historically, these mechanical components have been things like levers or gears. However, mechanical computers can also be made using structures that are multistable, meaning ...
Acting for a common goal with humanoid robots
2024-06-26
Genova (Italy), 26 June 2024 – Researchers at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) have demonstrated that under specific conditions, humans can treat robots as co-authors of the results of their actions. The condition that enables this phenomenon is that a robot behaves in a human-like, social manner. Engaging in gaze contact and participating in a common emotional experience, such as watching a movie, are the key. The study was published in Science Robotics and paves the way for understanding and designing the optimal circumstances for humans and robots to collaborate in the same environment.
The ...
Time-compression in electron microscopy
2024-06-26
Scientists at the University of Konstanz in Germany have advanced ultrafast electron microscopy to unprecedented time resolution. Reporting in Science Advances, the research team presents a method for the all-optical control, compression, and characterization of electron pulses within a transmission electron microscope using terahertz light. Additionally, the researchers have discovered substantial anti-correlations in the time domain for two-electron and three-electron states, providing deeper insight into the quantum physics of ...
First case of Down syndrome in Neandertals documented in new study
2024-06-26
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- A new study published by an international multidisciplinary team of researchers including faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York, documents the first case of Down syndrome in Neandertals and reveals that they were capable of providing altruistic care and support for a vulnerable member of their social group.
The research, led by anthropologists at the University of Alcalá and the University of Valencia in Spain, studied the skeletal remains of a Neandertal child, whom they affectionately named “Tina”, found at Cova Negra, a cave in Valencia, Spain long known for yielding important Neandertal discoveries.
“The ...
Future risk of coral bleaching set to intensify globally
2024-06-26
An international team of researchers led by the University of Adelaide has projected future marine heatwaves will cause coral reefs to be at severe risk of bleaching for longer periods than previously seen.
Through climate modelling and supercomputing, the researchers discovered that extended bleaching events may significantly disrupt coral spawning.
“We found that coral bleaching will start earlier in the year and last longer than previously thought,” said lead author Dr Camille Mellin, from the University of Adelaide’s Environment Institute.
“Our results show that by 2080, coral bleaching will tend to start in spring, rather than late summer, which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
[Press-News.org] Sharing false political information on social media may be associated with positive schizotypyResearchers found evidence that the desire to raise awareness may be an important motivator