(Press-News.org) Newly published research from Colorado State University answers fundamental questions about cellular connectivity in the brain that could be useful in the development of treatments for neurological diseases like autism, epilepsy or schizophrenia.
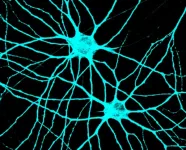
The work, highlighted in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, focuses on how neurons in the brain transmit information between each other through highly specialized subcellular structures called synapses. These delicate structures are key to controlling many processes across the nervous system via electrochemical signaling, and pathogenic mutations in the genes that impair their development can cause severe mental disorders. Despite their important role in linking neurons across different brain regions, the way synapses form and function is still not well understood, said Assistant Professor Soham Chanda.
To answer that fundamental question, Chanda and his team in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology focused on a specific and important type of synapse called GABAergic. He said neuroscience researchers have long hypothesized that these synapses might form because of a release of GABA and the corresponding sensing activity between two neurons in proximity. However, research in the paper now shows that these synapses can begin to develop autonomously and apart from that neuronal communication, mainly due to the scaffolding action of a protein called Gephyrin. These findings clarify the key mechanisms of synaptic formation, which might allow researchers to further focus on synapse dysfunction and health treatment options.
Chanda’s team used human neurons derived from stem cells to develop a model of the brain that could rigorously test these relationships. Using a gene-editing tool called CRISPR-Cas9, they were able to genetically manipulate the system and confirm the role of Gephyrin in the synapse formation process.
“Our study shows that even if a pre-synaptic neuron is not releasing GABA, the post-synaptic neuron can still put together the necessary molecular machineries prepared to sense GABA,” Chanda said. “We used a gene-editing tool to remove the Gephyrin protein from neurons, which largely reduced this autonomous assembly of synapses – confirming its important role irrespective of neuronal communication.”
Using stem cells to advance understanding of neuron and synapse formation
Neuroscientists have traditionally used rodent systems to study these synaptic connections in the brain. While that provides a suitable model, Chanda and his team were interested in testing synapse properties in a human cellular environment that could eventually be more easily translated into treatments.
To achieve this, his team cultivated human stem cells to form brain cells that could mimic the properties of human neurons and synapses. They then conducted extensive high-resolution imaging of these neurons and tracked their electrical activities to understand synaptic mechanisms.
Chanda said that several mutations in the Gephyrin protein have been associated with neurological disorders like epilepsy, which alters neuronal excitability in the human brain. That makes understanding its basic cellular function an important first step towards treatment and prevention.
“Now that we better understand how these synaptic structures interact and organize, the next question will be to elucidate how defects in their relationships can lead to disease and identify the ways one can predict or intervene in that process,” he said.
END
Neuroscience research leverages stem cells to understand how neurons connect and communicate in the brain
Could aid development of treatments for autism, epilepsy or schizophrenia
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NRL CCOR launches on the GOES-U NOAA satellite to monitor space weather
2024-06-26
WASHINGTON – The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory’s (NRL) Compact Coronagraph (CCOR) was launched June 25, on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) from NASA – Kennedy Space Center to detect and characterize coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
The NOAA sponsored NRL to design, integrate, and test CCOR, a small space telescope that will create an artificial eclipse of the sun and ...
Study shows how liver damage from stress and aging might be reversible
2024-06-26
DURHAM, N.C. – While the liver is one of the body’s most resilient organs, it is still vulnerable to the ravages of stress and aging, leading to disease, severe scarring and failure. A Duke Health research team now might have found a way to turn back time and restore the liver.
In experiments using mice and liver tissue from humans, the researchers identified how the aging process prompts certain liver cells to die off. They were then able to reverse the process in the animals with an investigational drug.
The finding, which ...
Bone stem cells with IFITM5 mutation get caught in a loop leading to osteogenesis imperfecta type V
2024-06-26
A study conducted by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions reveals the molecular events leading to osteogenesis imperfecta type V, a form of brittle bone disease caused by a mutation in the gene IFITM5.
The mutation blocks the normal development of bone stem cells into mature cells, which would form healthy bones. Instead, the mutation leads to the formation of bones that are extremely brittle. Children with this disorder have recurrent fractures, bone deformities, chronic pain and other complications. ...
Tai Chi reduces risk of inflammatory disease, treats insomnia among breast cancer survivors
2024-06-26
New research led by UCLA Health confirms that both Tai Chi and cognitive behavioral therapy can reduce insomnia in breast cancer survivors but also may provide additional health benefits by reducing inflammation and bolstering anti-viral defenses.
Chronic insomnia is one of the most prominent symptoms experienced among cancer survivors and poses significant health concerns, including the risk of inflammatory disease that could increase the risk of cancer recurrence.
About 30% of breast cancer survivors are reported to have insomnia, which is twice the rate of the general population. While previous research has shown cognitive behavioral therapy and mind-body ...
Technology presented for measuring carbon in media, advertising and generative AI
2024-06-26
Measuring energy consumption derived from digital activity from a scientific point of view is the challenge faced by Hiili, S.L., a company recently formed and driven by two researchers from the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), Ángel and Rubén Cuevas Rumín, from the Telematics Engineering Department. Specifically, they develop technological solutions that combine Internet measurement techniques and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to make an accurate estimate of the energy consumption of a company's ...
Do people who exercise more have a lower risk of ALS?
2024-06-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 26, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Moderate levels of physical activity and fitness may be linked to a reduced risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) later in life, according to a new study published in the June 26, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study only found an association between physical activity and risk of ALS in male participants, not female participants.
ALS is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. People with ALS lose the ability to initiate ...
Could preventative drug be effective in people with migraine and rebound headache?
2024-06-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 26, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A drug used to prevent migraine may also be effective in people with migraine who experience rebound headaches, according to a new study published in the June 26, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
People with chronic migraine who overused pain medication had fewer monthly migraine and headache days and fewer days using pain medication when taking the migraine prevention drug atogepant.
“There is a high prevalence of pain medication ...
Pathologists awarded grant from American Society of Hematology
2024-06-26
Dr. Zhen Mei, a clinical pathologist, and Dr. Vivian Chang, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist, both at UCLA Health, have been awarded $30,000 from the American Society of Hematology to revise blood cell ranges for people with Duffy-null Associated Neutrophil Count, which is also known as Duffy-negative.
Those who are Duffy-negative, estimated to be two out of three people identifying as Black in the U.S., lack Duffy antigens on the surface of their red blood cells as a mechanism to resist malaria. This helps provide protection but ...
Revolutionizing ovarian cancer treatment with adaptive PARP inhibitor therapy
2024-06-26
TAMPA, Fla. — Ovarian cancer, often diagnosed at an advanced stage, presents significant treatment challenges because patients tend to develop resistance to conventional therapies quickly. Despite aggressive treatment, recurrence rates remain high, and managing this disease effectively requires innovative approaches. Poly-adenosine ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have emerged as a treatment option, targeting specific DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. However, their use is often limited ...
Global consensus for sarcopenia
2024-06-26
“[...] the development of a global conceptual definition of sarcopenia signifies a new dawn for this muscle disease.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 26, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Global consensus for sarcopenia.”
In this new editorial, researchers Ben Kirk, Peggy M. Cawthon, and Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft from the University of Melbourne and Western Health discuss the global societal issue of skeletal muscle loss and weakness, termed Sarcopenia. Low muscle ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
[Press-News.org] Neuroscience research leverages stem cells to understand how neurons connect and communicate in the brainCould aid development of treatments for autism, epilepsy or schizophrenia