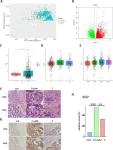
(Press-News.org) Around the time of the untimely death of Freddie Gray, a 25-year-old Black man in police custody, researchers from Johns Hopkins University were collecting data for Communities CARING, a study that examined the relationship of health behaviors among public housing residents in East and West Baltimore communities in Maryland. Led by Kristal Lyn Brown, PhD, an assistant professor in Drexel University’s College of Nursing and Health Professions, a secondary analysis of the data collected for Communities CARING examined the relationship between a high-profile event (Gray’s death) and disordered eating behaviors of Black women both before and after unrest.
Recently published in the Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities, differences in eating behaviors – emotional eating, uncontrolled eating, cognitive restraint – among Black women residing in the neighborhood near where Gray lived were compared to the eating behaviors of women living in a similar neighborhood farther away, on the other side of Baltimore. The original data collection included the cross-sectional in-person interviews of 254 Black women in Baltimore.
“This study was conceptualized through a vicarious racial discrimination lens – or observing racial discrimination or violence toward other members of the Black community,” said Brown, a Drexel FIRST faculty member.
Brown noted that while this study focused on police violence as a form of vicarious racial discrimination, this type of discrimination is not exclusive to police violence. For example, individuals can experience vicarious racial discrimination through social media, at school or in the workplace, shared stories from family, friends, and strangers alike.
“Regardless of how racial discrimination is experienced, it is a stressor and could lead to race-based traumatic stress (RBTS) — a psychological and emotional reaction, as well as several other poor mental and physical health outcomes,” said Brown.
The research team found that Black women living closer to the unrest reported higher levels of emotional eating and smoking and perceived there to be an increase in daytime crime — highlighting that those residing in this neighborhood are dealing with more stressors overall and engage in various forms of coping, including emotional eating.
Additionally, Black women who took the survey after the unrest and lived in closer proximity reported higher cognitive restraint, showing control over food intake.
“This finding was unanticipated, as uncontrolled eating and emotional eating are more commonly linked to stress,” said Brown. “Our study is cross-sectional, so findings do not imply causality; however, findings do underscore the importance of continuing to explore racial discrimination as a stressor and eating behaviors as a potential coping mechanism.”
Brown added that future research should continue to explore unique stressors, such as racial discrimination, and coping behaviors that might be linked to these stressors in minoritized populations — particularly those sitting at the intersection of multiple identities (e.g., race, living in a larger body). There is also a need for longitudinal and mixed methods studies to better understand the lived experiences and eating behaviors of Black women, a high-risk, under studied population — with a focus on environmental perceptions of safety, racial discrimination, race-based trauma and eating behaviors.
In addition to Brown, the study, “Association Between Maladaptive Eating Behaviors Among Black Women and Vicarious Racial Discrimination Following a High-Profile Event,” was co-authored by Amie F. Bettencourt, PhD, Anika L. Hines, PhD, Lisa A. Cooper, MD and Kimberly A. Gudzune, MD of Johns Hopkins University.
END
How do high-profile incidents of racial discrimination affect the eating habits of Black women?
2024-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ETRI revolutionizes 6G core network signal processing
2024-06-27
Korean researchers are strengthening South Korea’s leadership in the global market through the development of 6G, the next-generation mobile communication technology.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that they showcased their latest research results at the “6G Symposium Spring 2024” held in Oulu, Finland, from April 9 to 11, drawing the attention of attendees.
At this symposium, ETRI particularly showcased its “service mesh” technology. This technology is a key 6G technology that addresses complex communication issues among numerous cloud-nativemobile network functions that ...
Potential new target for colorectal cancer treatment
2024-06-27
Researchers have identified a protein called PFDN6 that may play a role in the development and spread of colorectal cancer (CRC). The study, published in [journal name], found that PFDN6 levels are increased in CRC patients and contribute to tumor growth. By reducing PFDN6 in lab studies, scientists were able to slow cancer cell spread and increase cell death. These findings suggest that PFDN6 could be a target for future CRC treatments.
CRC is the third most common cancer worldwide and has a poor prognosis, especially ...
Female heart patients less likely to have additional problems fixed during surgery
2024-06-27
When operating on the heart, surgeons may find another issue in the patient. Depending on what they see, the surgical team may address on the secondary condition during the same operation.
These are sometimes called concomitant procedures.
However, two studies led by Michigan Medicine find that female patients who undergo heart surgery are less likely to have secondary ailments corrected during a procedure — despite guidelines that indicate they should.
“Across the spectrum of cardiovascular care, from medical management to transcatheter and surgical procedures, there is growing evidence that women ...
New technique could lead to more organs being available for transplant
2024-06-27
LONDON, ON – A team at Lawson Health Research Institute is the first in Canada to perform a transplant using a technique called abdominal normothermic regional perfusion (A-NRP), which could lead to more organs being available for transplant. The technique was used to optimize organs from two donors in April 2024 at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC), resulting in the successful transplantation of two kidneys and two livers to four patients.
“Organ donation after circulatory death (when the heart stops beating) has historically been less reliable than organ donation after brain death,” explained Dr. Anton Skaro, Associate Scientist ...
Groundbreaking discovery: Zinc can make crop yields more climate-resilient
2024-06-27
Researchers have discovered that zinc plays a crucial role in the nitrogen fixation process of legumes. This finding, along with the transcriptional regulator Fixation Under Nitrate (FUN), could revolutionize legume-based agriculture by optimizing crop efficiency and reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers. By understanding how zinc and FUN regulate nitrogen fixation, researchers might be able to enhance nitrogen delivery, improve crop yields, and promote more sustainable agricultural practices.
The new knowledge about zinc can change the way we cultivate crops, as plants can ...
Only 4% of teen football academy prospects make top tier
2024-06-27
Just four per cent of talented teen academy prospects make it to the top tier of professional football, a new study has shown.
A sample of nearly 200 players, aged between 13-18, also revealed only six per cent of the budding ballers even go on to play in lower leagues.
The University of Essex researchers discovered the players who succeeded excelled in self-confidence, ball reception skills, dribbling and coaches’ subjective technical assessments.
The study – published in the International Journal ...
Chinese cities outsourced on others’ efforts to cut carbon emissions
2024-06-27
Experts have identified 240 Chinese cities whose emission reduction are mainly benefiting from the carbon mitigation actions of other cities, whilst putting in less effort themselves.
Researchers studied the phenomenon across 309 Chinese cities using data from 2012 to 2017 – a period when China underwent economic reform and industrial transformation.
Constructing a city-level input-output model to assess carbon footprints, the researchers identified 78% of the cities as ‘outsourced beneficiaries’, ...
Phytochemical diversity and herbivory are higher in tropical forests: Study
2024-06-27
It is widely accepted that biological interactions are stronger or more important in generating and maintaining biodiversity in the tropics than in temperate regions. However, this hypothesis has not been fully tested in ecology and evolutionary biology.
In a study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have provided strong support for this central prediction by examining phytochemical diversity and herbivory in 60 tree communities ...
Antarctic ice shelves hold twice as much meltwater as previously thought
2024-06-27
Slush – water-soaked snow – makes up more than half of all meltwater on the Antarctic ice shelves during the height of summer, yet is poorly accounted for in regional climate models.
Researchers led by the University of Cambridge used artificial intelligence techniques to map slush on Antarctic ice shelves, and found that 57% of all meltwater is held in the form of slush, with the remaining amount in surface ponds and lakes.
As the climate warms, more meltwater is formed on the surface of ice shelves, the floating ice surrounding Antarctica which acts as ...
First specific PET scan for TB could enable more effective treatment
2024-06-27
A more accurate way to scan for tuberculosis (TB) has been developed by UK and US researchers, using positron emission tomography (PET).
The team, from the Rosalind Franklin Institute, the Universities of Oxford and Pittsburgh and the National Institutes of Health in the USA, have developed a new radiotracer, which is taken up by live TB bacteria in the body. Radiotracers are radioactive compounds which give off radiation that can be detected by scanners and turned into a 3D image.
The new radiotracer, called FDT, enables PET scans to be used for the first time ...