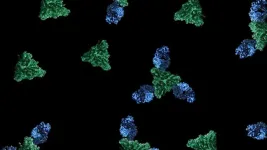
(Press-News.org) In a new study in mice, researchers introduce “CHARM,” a compact and versatile epigenetic editor that can be used to silence prion protein throughout the brain. The tool provides a path towards an effective first-line treatment for patients with deadly prion disease as well as other neurodegenerative diseases caused by the toxic buildup of unwanted proteins. Prion disease – a suite of devastating neurodegenerative disorders that result in rapid-onset dementia and death – is caused by misfolding of the prion protein, PrP, to form toxic aggregates that result in neuronal death. Previous research in mice has shown that removing PrP from neurons can halt prion disease and reverse symptoms, indicating that strategies aimed at reducing PrP expression may represent a viable therapeutic approach even after the onset of symptoms. However, long-term and reversible silencing of PrP-expressing genes using current approaches, such as CRISPRoff, remains a challenge, necessitating the development of a more compact, potent, and safe epigenetic tool. To address this need, Edwin Neumann and colleagues developed a compact and programmable epigenetic silencer called CHARM (Coupled Histone tail for Autoinhibition Release of Methyltransferase), which is capable of silencing targeted genes with high specificity through programmable DNA methylation. The approach, which does not require DNA sequence edits, offers a potentially less cytotoxic alternative to genome-editing techniques that disrupt coding regions or splice sites. Neumann et al. show that CHARM platform can efficiently shut off the prion gene in most neurons throughout the entire mouse brain when delivered systemically by an adeno-associated virus (AAV) without altering the underlying DNA sequence. According to the findings, the approach resulted in more than 80% brain-wide knockdown of PrP expression, greatly exceeding the currently recognized minimal knockdown required for therapeutic effects. Moreover, the authors demonstrate the ability to create self-silencing CHARM editors that turn themselves off after silencing target genes, thereby avoiding potential toxicity and other adverse effects from chronic expression in neurons. “With the development of CHARMs, Neumann et al. have introduced a potent and safe editing technology for gene silencing via AAV delivery into otherwise difficult-to-target organs, such as the brain,” write Madelynn Whittaker and Kiran Musunuru in a related Perspective.
END
Novel epigenic editor, CHARM, enables brain-wide prion protein silencing
2024-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A promising weapon against measles
2024-06-27
LA JOLLA, CA—What happens when measles virus meets a human cell? The viral machinery unfolds in just the right way to reveal key pieces that let it fuse itself into the host cell membrane.
Once the fusion process is complete, the host cell is a goner. It belongs to the virus now.
Scientists in the La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) Center for Vaccine Innovation are working to develop new measles vaccines and therapeutics that stop this fusion process. The researchers recently harnessed an imaging technique called cryo-electron microscopy to show—in ...
The most obese children with dengue are more than twice as likely as others to be hospitalized with dengue, according to study of 4,782 10- to 18-year-olds in Sri Lanka
2024-06-27
The most obese children with dengue are more than twice as likely as others to be hospitalized with dengue, according to study of 4,782 10- to 18-year-olds in Sri Lanka.
####
Article URL: http://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0012248
Article Title: Is the rise in childhood obesity rates leading to an increase in hospitalizations due to dengue?
Author Countries: Sri Lanka, United Kingdom
Funding: This study has been supported by the World Health Organization Unity Studies (GNM and CJ), a global sero-epidemiological standardization initiative, with funding to the World Health Organization and the UK Medical Research Council (GSO). The World Health Organization ...
Prehistoric Pompeii discovered: Most pristine trilobite fossils ever found shake up scientific understanding of the long extinct group
2024-06-27
Researchers have described some of the best-preserved three-dimensional trilobite fossils ever discovered. The fossils, which are more than 500 million years old, were collected in the High Atlas of Morocco and are being referred to by scientists as “Pompeii” trilobites due to their remarkable preservation in ash.
The trilobites, from the Cambrian period, have been the subject of research by an international team of scientists, led by Prof Abderrazak El Albani, a geologist based at University of Poitiers and originally from Morocco. The team included Dr Greg Edgecombe, a palaeontologist ...
Scientists use computational modeling to guide a difficult chemical synthesis
2024-06-27
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Researchers from MIT and the University of Michigan have discovered a new way to drive chemical reactions that could generate a wide variety of compounds with desirable pharmaceutical properties.
These compounds, known as azetidines, are characterized by four-membered rings that include nitrogen. Azetidines have traditionally been much more difficult to synthesize than five-membered nitrogen-containing rings, which are found in many FDA-approved drugs.
The reaction that the researchers used to create azetidines is driven by a photocatalyst that excites the molecules from their ground energy state. Using computational models that they developed, the researchers ...
The worm has turned: DIY lab platform evaluates new molecules in minutes
2024-06-27
Plants are powerhouses of molecular manufacturing. Over the eons, they have evolved to produce a plethora of small molecules — some are beneficial and valuable to humans, others can be deadly. For years, a good way for scientists looking for new medicines to distinguish beneficial plant-derived molecules from harmful ones has been through a scientific sniff test — dab a bit of the molecule at one end of a petri dish and drop tiny nematode worms (C. elegans) at the other, then wait to see if the chemically sensitive worms move toward or away from the compound in question, a process known as chemotaxis.
This “artisanal” ...
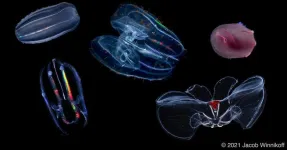
Under pressure: How comb jellies have adapted to life at the bottom of the ocean
2024-06-27
The bottom of the ocean is not hospitable: there is no light; the temperature is freezing cold; and the pressure of all the water above will literally crush you. The animals that live at this depth have developed biophysical adaptations that allow them to survive in these harsh conditions. What are these adaptations and how did they develop?
University of California San Diego Assistant Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry Itay Budin teamed up with researchers from around the country to study the cell membranes of ctenophores (“comb jellies”) and found they had unique lipid structures that allow them to live under intense pressure. Their work appears in Science.
Adapting ...
A CHARMed collaboration created a potent therapy candidate for fatal prion diseases
2024-06-27
EMBARGOED UNTIL 27-Jun-2024 14:00 ET
Drug development is typically slow: the pipeline from basic research discoveries that provide the basis for a new drug to clinical trials to production of a widely available medicine can take decades. But decades can feel impossibly far off to someone who currently has a fatal disease. Broad Institute Senior Group Leader Sonia Vallabh is acutely aware of that race against time, because the topic of her research is a neurodegenerative and ultimately fatal disease–fatal familial insomnia, a type of prion disease–that she will almost certainly develop as she ages. Vallabh and her husband, Eric Minikel, switched careers ...
Researchers find flexible solution for separating gases
2024-06-27
For a broad range of industries, separating gases is an important part of both process and product—from separating nitrogen and oxygen from air for medical purposes to separating carbon dioxide from other gases in the process of carbon capture or removing impurities from natural gas.
Separating gases, however, can be both energy-intensive and expensive. “For example, when separating oxygen and nitrogen, you need to cool the air to very low temperatures until they liquefy. Then, by slowly increasing the temperature, the gases will evaporate at different points, allowing one to become a gas again and separate out,” explains Wei Zhang, a University of Colorado Boulder professor ...
Pacific cod can’t rely on coastal safe havens for protection during marine heat waves, OSU study finds
2024-06-27
During recent periods of unusually warm water in the Gulf of Alaska, young Pacific cod in near shore safe havens where they typically spend their adolescence did not experience the protective effects those areas typically provide, a new Oregon State University study found.
Instead, during marine heat waves in 2014-16 and 2019, young cod in these near shore “nurseries” around Kodiak Island in Alaska experienced significant changes in their abundance, growth rates and diet, with researchers estimating that only the largest 15-25% of the island’s cod population survived the summer. Even after the high temperatures subsided, the ...
Bird flu stays stable on milking equipment for at least one hour
2024-06-27
Bird flu, or H5N1 virus, in unpasteurized milk is stable on metal and rubber components of commercial milking equipment for at least one hour, increasing its potential to infect people and other animals, report researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and Emory University in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
The study underscores the heightened risk of bird flu exposure for dairy farm workers and signals the need for wider adoption of personal protective equipment, including face shields, masks and eye protection.
“Dairy cows have to be milked even if they are sick, and it has not been clear for how long the virus contained in residual milk from the ...