(Press-News.org) A Plano high school student conducting research in a University of Texas at Arlington chemistry professor’s lab earned multiple awards at the annual Regeneron International Science and Engineering Fair (ISEF). Regeneron ISEF is the world’s largest pre-college STEM competition for students in grades 9-12.
Chloe Lee, a junior in the International Baccalaureate program at Plano East Senior High School, conducted research in the lab of Junha Jeon, associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry. Her award-winning project, “Chemical Modification of Acetaminophen to Decrease Liver Toxicity,” sought to address the toxicity of the common pain reliever acetaminophen, which is a leading cause of global liver transplantation.
Lee earned the ISEF third-place award of $1,000 in the Chemistry category. The competition also features Special Awards, which are provided by more than 45 professional organizations representing government, industry, and education across a wide variety of scientific disciplines. She received first place from the Patent and Trademark Office Society, second place from the American Chemical Society, and third place from YM American Academy.
Regeneron ISEF is organized by Society for Science, a nonprofit that has been dedicated to expanding scientific literacy, access to STEM education, and scientific research for more than 100 years.
“I chemically modified acetaminophen, the primary active pharmaceutical ingredient in Tylenol, to decrease liver toxicity without sacrificing the drug's effectiveness,” Lee said. “I am very excited and honored to have received multiple awards at ISEF. I felt as if the significance of my research had been recognized, which motivates me to further my work on the subject.”
Lee was introduced to Jeon last year when she participated in a Sustainable Material Workshop sponsored by the National Science Foundation (NSF). Jeon runs the workshop each summer with Ranny So, UTA assistant professor of chemistry and biochemistry, and in collaboration with faculty at Syracuse University, UT Rio Grande Valley, and the State University of New York–College of Environmental Science and Forestry.
The workshop encourages students to pursue careers in STEM fields and features lectures, lab experiences, a tour of university facilities, and workshop certificates. When Lee expressed her interest in organic synthesis research, Jeon offered her the chance to work in his lab.
“I was very fortunate to have this opportunity, and I've honestly enjoyed every moment in the lab,” she said. “Dr. Jeon is an amazing mentor who strengthened my understanding of important underlying chemical mechanisms and apparatuses throughout the research process. He always pushed me to inquire about the research. Furthermore, the resources he provided guided me to the right path. I greatly appreciate his direction.”
Alongside Jeon, Lee was supported by graduate students Suman Das Adhikary and Yao Chung (Jacky) Chang.
“This research is very challenging to a high school student, but Chloe did a wonderful job on design and synthesis of the target molecule and computational docking simulation,” Jeon said. “Her innovative approach to the very well-known yet unsolved Tylenol toxicity issue could pave the way to a solution.”
Lee said she would like to study chemistry in college and hopes to use chemistry research to help address problems facing the global community.
“Fundamentally, I want to help others with my knowledge, so I would like to become a surgeon and researcher who uses concepts in chemistry to positively impact the world.”
END
11th-grade student wins competition with research conducted at UTA
Student honored at largest pre-college STEM competition for her work in Junha Jeon’s lab
2024-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deep learning-assisted lesion segmentation in PET/CT imaging: A feasibility study for salvage radiation therapy in prostate cancer
2024-06-28
“The deployment of DL segmentation methods in 18F-fluciclovine PET/CT imaging represents an intriguing research direction for precision medicine in salvage prostate cancer care.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 28, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on May 20, 2024, entitled, “Deep learning-assisted lesion segmentation in PET/CT imaging: A feasibility study for salvage radiation therapy in prostate cancer.”
In this new editorial, researchers Richard L.J. Qiu, Chih-Wei Chang, ...
Dementia cost calculator will provide precise, annual, national estimates of Alzheimer's financial toll
2024-06-28
An A-list of researchers from across USC is building a dementia cost model that will generate comprehensive national, annual estimates of the cost of dementia that could benefit patients and their families, thanks to a five-year, $8.2 million federal grant from the National Institute on Aging.
A firm grip on the costs of the disease could assist families living with dementia with planning their budgets and support needs, inform treatment and caregiving options, and help shape health care policy.
“We currently have estimates for a particular ...
Moffitt researchers develop synthesis method to enhance access to cancer-fighting withanolides
2024-06-28
TAMPA, Fla. — Withanolides, a class of naturally occurring compounds found in plants, have long been a focus of cancer research due to their ability to inhibit cancer cell growth, induce cell death and prevent metastasis. These compounds are important in developing new cancer treatments. However, the difficulty of obtaining enough of these compounds from plants has hindered research and therapeutic development.
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers have developed a groundbreaking method for the scalable synthesis of withanolides. This innovative approach, published in Science Advances, could revolutionize cancer research by providing ...
Analysis of NASA InSight data suggests Mars hit by meteoroids more often than thought
2024-06-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — NASA’s Mars InSight Lander may be resting on the Red Planet in retirement, but data from the robotic explorer is still leading to seismic discoveries on Earth.
In one of the latest studies using data from the spacecraft, an international team of scientists led by a Brown University researcher found that Mars may be getting bombarded by space rocks at more frequent rates than previously thought. Impact rates could be two to 10 times higher than previously estimated, depending on the size of the meteoroids, according to the study published in Science Advances.
“It’s ...
Serotonin 2C receptor regulates memory in mice and humans – implications for Alzheimer’s disease
2024-06-28
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, the University of Cambridge in the U.K. and collaborating institutions have shown that serotonin 2C receptor in the brain regulates memory in people and animal models. The findings, published in the journal Science Advances, not only provide new insights into the factors involved in healthy memory but also in conditions associated with memory loss, like Alzheimer’s disease, and suggest novel avenues for treatment.
“Serotonin, a compound produced by neurons in the midbrain, acts as a neurotransmitter, passing messages between brain cells,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Yong Xu, professor of pediatrics ...
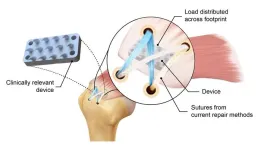
New device inspired by python teeth doubles strength of rotator cuff repairs
2024-06-28
New York, NY—June 24, 2024—Most people, when they think about pythons, visualize the huge snake constricting and swallowing victims whole. But did you know that pythons initially hold onto their prey with their sharp, backward-curving teeth? Medical researchers have long been aware that these teeth are perfect for grasping soft tissue rather than cutting through it, but no one has yet been able to put this concept into surgical practice. Over the years, mimicking these teeth for use in surgery has been a frequent topic ...
The beginnings of fashion
2024-06-28
EMBARGO: 4:00 Sydney AEST June 29 | 14:00 US ET June 28 2024
The beginnings of fashion
Paleolithic eyed needles and the evolution of dress
A team of researchers led by an archaeologist at the University of Sydney are the first to suggest that eyed needles were a new technological innovation used to adorn clothing for social and cultural purposes, marking the major shift from clothes as protection to clothes as an expression of identity.
“Eyed needle tools are an important development in prehistory because they document a transition in the function of clothing from utilitarian to social purposes,” says Dr Ian Gilligan, Honorary Associate ...
Why some tumors are resistant to cell therapies
2024-06-28
FRANKFURT. In congratulating the CARISMa scientists, Goethe University President Prof. Enrico Schleiff said: “The new LOEWE network sets up in Hesse an innovative research program that is currently gathering steam all over the world. It also expands Goethe University’s existing research profile and broadens our network of cooperation partners in the field of CAR cell therapy [editor’s note: CAR is the abbreviation for chimeric antigen receptor]. The network deliberately builds on our university’s ...
Can A.I. tell you if you have osteoporosis? Newly developed deep learning model shows promise
2024-06-28
Osteoporosis is so difficult to detect in early stage it’s called the “silent disease.” What if artificial intelligence could help predict a patient’s chances of having the bone-loss disease before ever stepping into a doctor’s office?
Tulane University researchers made progress toward that vision by developing a new deep learning algorithm that outperformed existing computer-based osteoporosis risk prediction methods, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses and better outcomes for patients with osteoporosis risk.
Their results were recently published in ...
Work-related nerve injuries are common with repetitive motions
2024-06-28
Although you may not always realize it, many of the jobs you do can put strain on, and even cause damage to, your nerves.
Sandra Hearn, M.D., the associate chair of Education and Professional Development in the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, and a team of collaborators, set out to better understand the causes of occupational nerve injuries.
What is an occupational nerve injury?
An occupational nerve injury refers to a problem with your peripheral nerves that's caused by a work-related activity. It's often seen ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
[Press-News.org] 11th-grade student wins competition with research conducted at UTAStudent honored at largest pre-college STEM competition for her work in Junha Jeon’s lab