(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — NASA’s Mars InSight Lander may be resting on the Red Planet in retirement, but data from the robotic explorer is still leading to seismic discoveries on Earth.
In one of the latest studies using data from the spacecraft, an international team of scientists led by a Brown University researcher found that Mars may be getting bombarded by space rocks at more frequent rates than previously thought. Impact rates could be two to 10 times higher than previously estimated, depending on the size of the meteoroids, according to the study published in Science Advances.
“It’s possible Mars is more geologically active than we thought, which holds implications for the age and evolution of the planet’s surface,” said lead researcher Ingrid Daubar, an associate professor of Earth, environmental and planetary sciences at Brown. “Our results are based on a small number of examples available to us, but the estimate of the current impact rate suggests the planet is getting hit much more frequently than we can see using imaging alone.”
As part of the study, the research team used InSight’s highly sensitive onboard seismometer to identify eight new impact craters from meteoroids not previously seen from orbit. The frequency of these cosmic collisions challenges existing notions about how often meteoroids hit the Martian surface and suggests a need to revise current Martian cratering models to incorporate higher impact rates, especially from smaller meteoroids. The findings could ultimately reshape current understandings of the Martian surface — as batterings from small meteoroids continue to sculpt it — and the impact history of not just Mars, but other planets.
“This is going to require us to rethink some of the models the science community uses to estimate the age of planetary surfaces throughout the entire solar system,” Daubar said.
Six of the craters the researchers detected were near the site where the stationary InSight Lander set down. The two distant impacts they identified from the data were the two biggest impacts ever detected by scientists, even after decades of watching from orbit. The larger impacts, each leaving a crater roughly the size of a football field, came just 97 days apart, underscoring the higher frequency of these types of geological events.
“This size impact, we would expect to happen maybe once every couple of decades, maybe even once in a lifetime, but here we have two of them that are just over 90 days apart,” Daubar said. “It could just be a crazy coincidence, but there’s a really, really small likelihood that it’s just coincidence. What’s more likely is that either the two big impacts are related, or the impact rate is a lot higher for Mars than what we thought it was.”
NASA’s InSight’s mission was active from November 2018 to December 2022. One of its main objectives was measuring the planet’s seismological shaking. Previously, new impacts on Mars were spotted with before-and-after images taken from cameras in orbit around the planet. The seismometer provided a new tool to find and detect these impacts, many of which might have otherwise gone unnoticed.
“Planetary impacts are happening all across the solar system all the time,” Daubar said. “We're interested in studying that on Mars because we can then compare and contrast what's happening on Mars to what's happening on the Earth. This is important for understanding our solar system, what's in it and what the population of impacting bodies in our solar system looks like — both as hazards to the Earth and also historically to other planets.”
The rates are also important for assessing potential hazards that impacts pose for future exploration missions as NASA sends rovers or even human missions to space.
To pinpoint when and where the impacts occurred on Mars, Daubar and the research team analyzed seismic signals from InSight and then compared that seismic data with images taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
The team visually confirmed eight of the events as new craters by examining before-and-after images. This dual approach of using seismic data and orbital imagery allowed them to confirm the seismic signals were caused by impacts and cross-check their findings to ensure accuracy.
The InSight lander collected seismic data from its landing until its solar panels, as expected, were covered in dust to the extent that the lander could no longer generate power.
The current study by Daubar and the research team ties into a companion paper in Nature Communications that uses even more data from InSight to look at all the very high frequency seismic events the lander detected. The companion paper, also published on June 28, 2024, assumes all these events were caused by impacts and finds the resulting estimated rate falls in line with what the researchers from Daubar’s team calculated independently, further strengthening each team’s findings.
“It’s possible that more events that InSight picked up during its mission were actually impacts,” Daubar said. “Next steps are to do more detailed orbital searches to try to confirm this using machine learning techniques. If we can confirm even more impacts, we might be able to find other seismic signals that were caused by impacts, too.”
Along with Brown, the study also involved researchers from the Institut Supérieur de l'Aéronautique et de l'Espace, University of Oxford, Imperial College London, U.S. Geological Survey, ETH Zürich, University of Arizona, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and Université Paris Cité.
The work was supported by NASA, CNES, the French Space Agency, and the United Kingdom Space Agency.
END
Analysis of NASA InSight data suggests Mars hit by meteoroids more often than thought
A new study led by a Brown researcher reveals the frequency of space rocks pummeling Mars is higher than previously estimated and detects two of the largest impacts ever seen by scientists on the Red Planet
2024-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Serotonin 2C receptor regulates memory in mice and humans – implications for Alzheimer’s disease
2024-06-28
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, the University of Cambridge in the U.K. and collaborating institutions have shown that serotonin 2C receptor in the brain regulates memory in people and animal models. The findings, published in the journal Science Advances, not only provide new insights into the factors involved in healthy memory but also in conditions associated with memory loss, like Alzheimer’s disease, and suggest novel avenues for treatment.
“Serotonin, a compound produced by neurons in the midbrain, acts as a neurotransmitter, passing messages between brain cells,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Yong Xu, professor of pediatrics ...
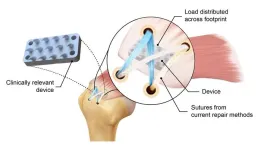
New device inspired by python teeth doubles strength of rotator cuff repairs
2024-06-28
New York, NY—June 24, 2024—Most people, when they think about pythons, visualize the huge snake constricting and swallowing victims whole. But did you know that pythons initially hold onto their prey with their sharp, backward-curving teeth? Medical researchers have long been aware that these teeth are perfect for grasping soft tissue rather than cutting through it, but no one has yet been able to put this concept into surgical practice. Over the years, mimicking these teeth for use in surgery has been a frequent topic ...
The beginnings of fashion
2024-06-28
EMBARGO: 4:00 Sydney AEST June 29 | 14:00 US ET June 28 2024
The beginnings of fashion
Paleolithic eyed needles and the evolution of dress
A team of researchers led by an archaeologist at the University of Sydney are the first to suggest that eyed needles were a new technological innovation used to adorn clothing for social and cultural purposes, marking the major shift from clothes as protection to clothes as an expression of identity.
“Eyed needle tools are an important development in prehistory because they document a transition in the function of clothing from utilitarian to social purposes,” says Dr Ian Gilligan, Honorary Associate ...
Why some tumors are resistant to cell therapies
2024-06-28
FRANKFURT. In congratulating the CARISMa scientists, Goethe University President Prof. Enrico Schleiff said: “The new LOEWE network sets up in Hesse an innovative research program that is currently gathering steam all over the world. It also expands Goethe University’s existing research profile and broadens our network of cooperation partners in the field of CAR cell therapy [editor’s note: CAR is the abbreviation for chimeric antigen receptor]. The network deliberately builds on our university’s ...
Can A.I. tell you if you have osteoporosis? Newly developed deep learning model shows promise
2024-06-28
Osteoporosis is so difficult to detect in early stage it’s called the “silent disease.” What if artificial intelligence could help predict a patient’s chances of having the bone-loss disease before ever stepping into a doctor’s office?
Tulane University researchers made progress toward that vision by developing a new deep learning algorithm that outperformed existing computer-based osteoporosis risk prediction methods, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses and better outcomes for patients with osteoporosis risk.
Their results were recently published in ...
Work-related nerve injuries are common with repetitive motions
2024-06-28
Although you may not always realize it, many of the jobs you do can put strain on, and even cause damage to, your nerves.
Sandra Hearn, M.D., the associate chair of Education and Professional Development in the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, and a team of collaborators, set out to better understand the causes of occupational nerve injuries.
What is an occupational nerve injury?
An occupational nerve injury refers to a problem with your peripheral nerves that's caused by a work-related activity. It's often seen ...
Mount Sinai study reveals significant differences in RNA editing between postmortem and living human brain
2024-06-28
Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have shed valuable light on the nuanced functions and intricate regulatory methods of RNA editing, a critical mechanism underlying brain development and disease.
In a study published June 26 in Nature Communications, the team reported finding major differences between postmortem and living prefrontal cortex brain tissues as they relate to one of the most abundant RNA modifications in the brain, known as adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) editing. This discovery will play a significant role ...
Penn researchers will investigate link between TBI and dementia with $10M NIH grant
2024-06-28
PHILADELPHIA— A team of researchers led by Penn Medicine will investigate the link between traumatic brain injuries (TBI) and Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) over the next five years with a $10 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Using an extensive tissue bank including over 1,000 samples, the researchers aim to uncover the underlying biological mechanisms of TBI-related neurodegeneration (TReND) from a variety of brain injury types. ...
Aston University researchers break ‘world record’ again for data transmission speed
2024-06-28
Aston Institute of Photonic Research academics are part of a team that sent data at a rate of 402 terabits per second
This beats their previous record of 301 terabits per second
They constructed the first optical transmission system covering six wavelength bands.
Aston University researchers are part of a team that has sent data at a record rate of 402 terabits per second using commercially available optical fibre.
This beats their previous record, announced in March 2024, of 301 terabits or 301,000,000 megabits per second using a single, standard optical fibre.
"If compared to the internet connection speed recommendations of Netflix, of 3 Mbit/s ...
A few surgical procedures account for high number of opioid prescriptions
2024-06-28
A handful of common surgical procedures account for large shares of all opioids dispensed after surgery in children and adults, according to two studies recently published by researchers at the University of Michigan.
The studies, published this week in Pediatrics and JAMA Network Open, report that the top three procedures for children ages 0-11 account for 59% of opioids dispensed after surgery (tonsillectomies and adenoidectomies 50%, upper extremity fractures 5% and removal of deep implants 4%). Among those ages 12-21, the top three procedures account for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
[Press-News.org] Analysis of NASA InSight data suggests Mars hit by meteoroids more often than thoughtA new study led by a Brown researcher reveals the frequency of space rocks pummeling Mars is higher than previously estimated and detects two of the largest impacts ever seen by scientists on the Red Planet