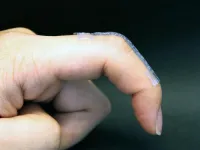
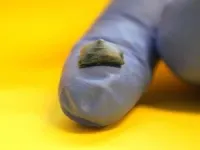
(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — To advance soft robotics, skin-integrated electronics and biomedical devices, researchers at Penn State have developed a 3D-printed material that is soft and stretchable — traits needed for matching the properties of tissues and organs — and that self-assembles. Their approach employs a process that eliminates many drawbacks of previous fabrication methods, such as less conductivity or device failure, the team said.
They published their results in Advanced Materials.
“People have been developing soft and stretchable conductors for almost a decade, but the conductivity is not usually very high,” said corresponding author Tao Zhou, Penn State assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics and of biomedical engineering in the College of Engineering and of materials science and engineering in the College of Earth and Mineral Sciences. “Researchers realized they could reach high conductivity with liquid metal-based conductors, but the significant limitation of that is that it requires a secondary method to activate the material before it can reach a high conductivity.”
Liquid metal-based stretchable conductors suffer from inherent complexity and challenges posed by the post-fabrication activation process, the researchers said. The secondary activation methods include stretching, compressing, shear friction, mechanical sintering and laser activation, all of which can lead to challenges in fabrication and can cause the liquid metal to leak, resulting in device failure.
“Our method does not require any secondary activation to make the material conductive,” said Zhou, who also has affiliations with the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences and the Materials Research Institute. “The material can self-assemble to make its bottom surface be very conductive and its top surface self-insulated.”
In the new method, the researchers combine liquid metal, a conductive polymer mixture called PEDOT:PSS and hydrophilic polyurethane that enables the liquid metal to transform into particles. When the composite soft material is printed and heated, the liquid metal particles on its bottom surface self-assemble into a conductive pathway. The particles in the top layer are exposed to an oxygen-rich environment and oxidize, forming an insulated top layer. The conductive layer is critical for conveying information to the sensor — such as muscle activity recordings and strain sensing on the body — while the insulated layer helps prevent signal leakage that could lead to less accurate data collection.
“Our innovation here is a materials one,” Zhou said. “Normally, when liquid metal mixes with polymers, they are not conductive and require secondary activation to achieve conductivity. But these three components allow for the self-assembly that produces the high conductivity of soft and stretchable material without a secondary activation method.”
The material can also be 3D-printed, Zhou said, making it easier to fabricate wearable devices. The researchers are continuing to explore potential applications, with a focus on assistive technology for people with disabilities.
The papers other authors are Salahuddin Ahmed, Marzia Momin and Jiashu Ren, all doctoral students in the Penn State engineering science and mechanics department, and Hyunjin Lee, a doctoral student in the biomedical engineering department at Penn State. This work was supported by the National Taipei University of Technology-Penn State Collaborative Seed Grant Program and by the Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics, the Materials Research Institute and the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences at Penn State.
END
Self-assembling, highly conductive sensors could improve wearable devices
2024-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lab values predict periprosthetic joint infection in patients with morbid obesity
2024-07-01
Waltham — July 1, 2024 — For patients with severe obesity undergoing knee or hip replacement, commonly obtained laboratory values – including markers of anemia and inflammation – are independent predictors of the risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Hemoglobin level, platelet count, and several markers of systemic inflammation may be relevant to the elevated ...
Study suggests states could cut healthcare costs by delivering patient tailored meals
2024-07-01
Chicago (July 1, 2024) — According to new research looking at every U.S. state, programs that deliver medically tailored meals (MTMs) to people with diet-sensitive conditions such as diabetes and heart disease along with limitations in the ability to perform daily activities could lead to substantial savings in healthcare costs. Using computer models to estimate the benefits of such programs minus the expense of implementing them, researchers found significant variation between U.S. states but an overall net cost savings in almost every state.
“By ...
Novel spectroscopy technique sheds light on NOx reduction
2024-07-01
When power plants burn fossil fuels at high temperatures, nitrogen and oxygen molecules break apart and then recombine to form a class of compounds called nitrogen oxides, or NOx. These gasses are major pollutants and contribute to—among other things—acid rain and global warming.
One way to curb such emissions is with a catalytic converter, similar to what’s used in a vehicle.
“The catalytic converter injects ammonia into the plant’s emissions stream, and the hydrogen in the ammonia reacts with the oxygen in the NOx, and the products ...
Fluorine-18 prostate-specific membrane antigen–1007 PET/CT vs multiparametric MRI for locoregional staging of prostate cancer
2024-07-01
About The Study: In this phase 2 prospective validating paired cohort study, fluorine-18 PSMA-1007 PET/computed tomography was superior to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the locoregional staging of prostate cancer. These findings support PSMA PET in the preoperative workflow of intermediate-risk and high-risk tumors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Adam Kinnaird, M.D., Ph.D., email ask@ualberta.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
Xue to receive funding for project aimed at youth tobacco use prevention
2024-07-01
Hong Xue, Associate Professor, Health Administration and Policy, received funding for the project: “Innovating and Implementing Youth Tobacco Prevention in Virginia.”
Xue will leverage the forefront of technological innovation, utilizing generative artificial intelligence (AI) and state-of-the-art immersive technologies, integrating them with novel just-in-time adaptive intervention strategies, to tackle the pressing public health issue of electronic cigarette/tobacco use among the youth in Virginia.
Xue will receive $450,000 from Virginia ...
Petricoin conducting protein pathway activation based signaling mapping of head and neck cancers
2024-07-01
Emanuel Petricoin, Co-Director, Center for Applied Proteomics and Molecular Medicine (CAPMM), received funding for the project: “Protein Pathway Activation Based Signaling Mapping of Head And Neck Cancers.”
CAPMM researchers will receive laser microdissected tumor samples from banked Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) clinical biopsy samples from patients with HPV‐positive head and neck cancers who were treated for newly diagnosed disease.
The researchers will utilize comprehensive reverse‐phase ...
Marasco studying inclusive design of contactless fingerprints to mitigate skin tone and gender bias
2024-07-01
Emanuela Marasco, Assistant Professor, Center for Secure Information Systems, received funding for the project: “Identity Verification in Smartphones as Social Intersectionality: Inclusive Design of Contactless Fingerprints to Mitigate Skin Tone and Gender Bias.”
She is developing a contactless biometric mobile security application that can mitigate the vulnerabilities of deep artificial intelligence and optical sensors and allow marginalized identities the same access to data security.
As part of their work, members of the project team will identify the impact of physical vulnerabilities; their ...
Physical exercise prevents nerve damage during chemotherapy
2024-07-01
Cancer treatments often cause nerve damage that can lead to long-lasting symptoms. Medication has proven ineffective in these cases. A sports scientist at the University of Basel, together with an interdisciplinary team from Germany, has now shown that simple exercises can prevent nerve damage.
Cancer therapies have improved over the years. It is no longer just about sheer survival: quality of life after recovery is gaining more importance.
Unfortunately, many cancer medications, from chemotherapy to modern immunotherapies, attack the nerves as well as the tumor cells. Some therapies, such as oxaliplatin or vinca alkaloids, leave 70 to 90 percent of patients complaining of pain, balance ...
Scientists turn white fat cells into calorie-burning beige fat
2024-07-01
New UCSF study shows that suppressing a protein turns ordinary fat into a calorie burner and may explain why drug trials attempting the feat haven’t been successful.
Researchers at UC San Francisco have figured out how to turn ordinary white fat cells, which store calories, into beige fat cells that burn calories to maintain body temperature.
The discovery could open the door to developing a new class of weight-loss drugs and may explain why clinical trials of related therapies have ...
How politicizing migration harms health
2024-07-01
Politicians around the world are increasingly mobilizing anti-immigrant sentiment to garner support and votes—a trend that is especially evident as the US presidential election approaches.
While political rhetoric that stereotypes and scapegoats immigrants is well-documented, less attention has been given to the impact of these sentiments on immigrants themselves. In an article published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) and in a recently published book, Migration Stigma (MIT Press), scholars identify “migration ...