(Press-News.org) University of Cincinnati researchers have pioneered an animal model that sheds light on the role an understudied organ in the brain has in repairing damage caused by stroke.
The research, published July 5 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, sought to learn more about how the adult brain generates new neurons to repair damaged tissue.
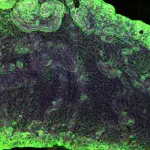
The research team focused on the choroid plexus, a small organ within brain ventricles that produces the brain’s cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF circulates throughout the brain, carrying signaling molecules and other factors thought to be important for maintaining brain function. However, prior to this study, little was known about the roles the choroid plexus and CSF play in brain repair after injury due to a lack of available adult animal models.
“We have discovered a new use of an animal model to be able to allow us to manipulate the adult choroid plexus and CSF for the first time,” said Agnes (Yu) Luo, PhD, corresponding author on the study, and professor and vice chair in the Department of Molecular and Cellular Biosciences in UC’s College of Medicine. “Now that we’ve discovered it, this will be vitally applicable to allow researchers to manipulate the adult choroid plexus and CSF to study different disease models and biological processes.”
UC graduate student and study coauthor Aleksandr Taranov explained that in a process called adult neurogenesis, the adult brain maintains a certain capacity to repair damage by regenerating newly born neurons.
“However, we still don’t know what actually regulates adult neurogenesis and how to redirect the neurons into the lesion site following a stroke,” Taranov said.
Using this new model, the researchers found that removing the choroid plexus — and the resulting loss of CSF in brain ventricles — led to a reduction of newly born immature neurons called neuroblasts. In a model of ischemic stroke, the team found the loss of the choroid plexus and CSF led to fewer neuroblasts migrating to the lesion site and repairing damage caused by a stroke.
“This suggests that the choroid plexus may be needed to retain these neuroblasts in the area where they usually reside,” Taranov said. “And the choroid plexus might actually be required to retain the neuroblasts so they can readily migrate into the stroke site whenever a stroke or other injury occurs.”
Essentially, Luo said, it appears the choroid plexus keeps a garrison of regenerative cells that are ready to be deployed to injured areas in the brain in animal models of stroke. Further research is needed to confirm whether this also occurs in human brains.
Moving forward, Taranov is studying how the loss of the choroid plexus and CSF affects the clearing of toxic proteins in a model of Alzheimer’s disease, and fellow graduate student Elliot Wegman is studying the same effects in a model of Parkinson’s disease.
Other study coauthors include UC’s Alicia Bedolla, and Eri Iwasawa, Farrah Brown, Sarah Baumgartner, Elizabeth Fugate, Joel Levoy, Steven A. Crone and June Goto of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
END
University of Cincinnati study: Overlooked brain organ plays key role in promoting brain repair after stroke
Research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
2024-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Harvard researchers find that gratitude is a useful emotional tool in reducing desire to smoke
2024-07-01
Smoking continues to rank as the foremost preventable cause of premature death. In a paper published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS), Harvard researchers report findings that evoking feelings of gratitude in people who smoke helps reduce their urge to smoke, and increases their likelihood of enrollment in a smoking cessation program. They note that these findings could inform newer approaches to public health messaging campaigns that aim to reduce so-called “appetitive” risk behaviors like smoking, drinking, and drug use.
The research team built on the Appraisal Tendency Framework, a theoretical model of emotiona and decision making, ...
Researchers disclose the effect of social media use on the mental health of college students during the pandemic
2024-07-01
The COVID-19 pandemic had an unprecedented effect on college students’ mental health: symptoms like anxiety and major depression in young adults ages 18-25 increased significantly compared to before the pandemic.
A new study from researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill looks at a possible contributing factor to the worsening trends in mental health: social media.
We know that college students and adolescents are using social media more. Last May, the US Surgeon General issued an advisory on social media and youth mental ...
July Issues of APA Journals cover new research on pharmacogenomics, ADHD medication use, associations between mental health and cardiometabolic complications later in life, and more
2024-07-01
WASHINGTON, D.C., July 1, 2024 — The latest issues of four American Psychiatric Association journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry, Psychiatric Services, American Journal of Psychotherapy and Psychiatric Research and Clinical Practice are now available online.
The July issue of The American Journal of Psychiatry brings together research on affective disorders, pharmacogenomics, and psychiatric illness-related cardiometabolic problems. Highlights include:
• Genome-Wide Association Study of Treatment-Resistant Depression: Shared Biology With Metabolic Traits.
• Pharmacogenomic Clinical ...
Most climate-vulnerable countries with highest hunger rates significantly under-represented in agrifood research
2024-07-01
The most climate-vulnerable countries with the highest hunger rates are significantly under-represented in agrifood research – sparking a need for urgent action and increased investments to redress this imbalance, a major new study has found.
The ‘State of the Field for Research on Agrifood Systems’ report, published by The Juno Evidence Alliance – a partnership of CABI, Havos.Ai and the University of Notre Dame, USA – found that only one out of eight research papers is led by scientists from ...
UMD researchers develop new and improved camera inspired by the human eye
2024-07-01
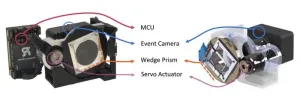
A team led by University of Maryland computer scientists invented a camera mechanism that improves how robots see and react to the world around them. Inspired by how the human eye works, their innovative camera system mimics the tiny involuntary movements used by the eye to maintain clear and stable vision over time. The team’s prototyping and testing of the camera—called the Artificial Microsaccade-Enhanced Event Camera (AMI-EV)—was detailed in a paper published in the journal Science Robotics in May 2024.
“Event cameras are a relatively new technology better at tracking ...
Self-assembling, highly conductive sensors could improve wearable devices
2024-07-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — To advance soft robotics, skin-integrated electronics and biomedical devices, researchers at Penn State have developed a 3D-printed material that is soft and stretchable — traits needed for matching the properties of tissues and organs — and that self-assembles. Their approach employs a process that eliminates many drawbacks of previous fabrication methods, such as less conductivity or device failure, the team said.
They published their results in Advanced Materials.
“People have been developing soft and stretchable conductors for almost a decade, but the conductivity ...
Lab values predict periprosthetic joint infection in patients with morbid obesity
2024-07-01
Waltham — July 1, 2024 — For patients with severe obesity undergoing knee or hip replacement, commonly obtained laboratory values – including markers of anemia and inflammation – are independent predictors of the risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Hemoglobin level, platelet count, and several markers of systemic inflammation may be relevant to the elevated ...
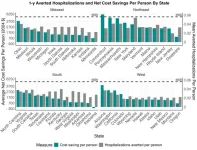
Study suggests states could cut healthcare costs by delivering patient tailored meals
2024-07-01
Chicago (July 1, 2024) — According to new research looking at every U.S. state, programs that deliver medically tailored meals (MTMs) to people with diet-sensitive conditions such as diabetes and heart disease along with limitations in the ability to perform daily activities could lead to substantial savings in healthcare costs. Using computer models to estimate the benefits of such programs minus the expense of implementing them, researchers found significant variation between U.S. states but an overall net cost savings in almost every state.
“By ...
Novel spectroscopy technique sheds light on NOx reduction
2024-07-01
When power plants burn fossil fuels at high temperatures, nitrogen and oxygen molecules break apart and then recombine to form a class of compounds called nitrogen oxides, or NOx. These gasses are major pollutants and contribute to—among other things—acid rain and global warming.
One way to curb such emissions is with a catalytic converter, similar to what’s used in a vehicle.
“The catalytic converter injects ammonia into the plant’s emissions stream, and the hydrogen in the ammonia reacts with the oxygen in the NOx, and the products ...
Fluorine-18 prostate-specific membrane antigen–1007 PET/CT vs multiparametric MRI for locoregional staging of prostate cancer
2024-07-01
About The Study: In this phase 2 prospective validating paired cohort study, fluorine-18 PSMA-1007 PET/computed tomography was superior to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the locoregional staging of prostate cancer. These findings support PSMA PET in the preoperative workflow of intermediate-risk and high-risk tumors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Adam Kinnaird, M.D., Ph.D., email ask@ualberta.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] University of Cincinnati study: Overlooked brain organ plays key role in promoting brain repair after strokeResearch published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences