(Press-News.org) The incidence of low birth weight rose sharply in India amid the COVID-19 pandemic, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
Globally, 1 in 4 newborns has a low birth weight (less than 5.5 pounds), and the problem disproportionately affects low- and middle-income countries — particularly in South Asia, home to approximately one-fourth of the world’s population.
Santosh Kumar, associate professor of development and global health economics at Notre Dame’s Keough School of Global Affairs, co-authored the study published in Communications Medicine, a Nature series journal.
“This research shows that low birth weight became more common in India during the pandemic,” Kumar said. “We saw the exacerbation of a global health problem that affects educational outcomes and poverty rates.
“Children who have lower birth weight as infants often go on to struggle with school, and this limits their capacity to develop what economists often call ‘human capital’ — the key knowledge and skills that will affect their ability to earn a good living and support themselves and their families.”
The study found that babies born between April 2020 and April 2021 had lower birth weights than previous birth cohorts (those born before the pandemic), Kumar said. Researchers analyzed data from more than 200,000 infants, Kumar said, including a pandemic cohort that included almost 12,000 infants and a pre-pandemic cohort of approximately 192,000.
The prevalence of low birth weight was 20 percent in the pandemic group, up from 17 percent in the pre-pandemic group, Kumar said, and infants in the pandemic group weighed about four-tenths of an ounce less than those in the pre-pandemic group.
Multiple factors related to the pandemic may have affected the health behaviors of pregnant women and contributed to lower birth weights, Kumar said, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus, stress related to social distancing, economic upheaval and the disruption of maternal and neonatal care.
The study’s co-authors were Clare Hill, a Notre Dame undergraduate student majoring in political science and global affairs with a minor in data science, and Timothy J. Halliday, an economist at the University of Hawaii. The study received funding from the Keough School’s Kellogg Institute for International Studies.
Kumar said this latest research, which expands on his work at the intersection of poverty and global health, highlights the need for targeted policies that reduce the incidence of low birth weights — for instance, ensuring that women from low-income populations have adequate nutrients and caloric intake during pregnancy and also have access to quality prenatal care.
“Our research underscores the need for targeted policies to reduce the risk of low birth weight,” Kumar said. “This will help create greater educational and economic opportunity and, ultimately, reduce poverty.”
Contact: Tracy DeStazio, associate director of media relations, 574-631-9958 or tdestazi@nd.edu
END
COVID-19 pandemic tied to low birth weight for infants in India, study shows
2024-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Welch Foundation supports UTA’s drug delivery innovations
2024-07-02
With a $300,000 grant, the Welch Foundation is supporting University of Texas at Arlington research into creating new materials to safely and effectively deliver medications to treat diseases such as cancer.
Since its founding in 1954, the Houston-based Welch Foundation has contributed over $1.1 billion to the advancement of chemistry through research grants, departmental programs, endowed chairs and other special projects in Texas.
“As one of the nation’s largest private funding sources for chemical research, we are committed to supporting the field in a way that advances science while ...
Treatment with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides can impede antibiotic resistance
2024-07-02
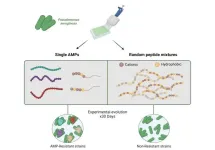
A common infection-causing bacteria was much less likely to evolve antibiotic resistance when treated with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides rather than a single peptide, making these mixtures a viable strategy for developing new antibiotic treatments. Jens Rolff of the Freie Universitat Berlin, Germany, and colleagues report these findings in a new study publishing July 2nd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria have become a major threat to public health. The World Health Organization estimates ...
The Mediterranean Diet is linked to lower risk of mortality in cancer survivors
2024-07-02
The Mediterranean Diet is a powerful ally for health even after a cancer diagnosis. This is the key result of an Italian study carried out as part of the UMBERTO Project, conducted by the Joint Research Platform Umberto Veronesi Foundation - Department of Epidemiology and Prevention of the I.R.C.C.S. Neuromed of Pozzilli, in collaboration with the LUM "Giuseppe Degennaro" University of Casamassima (BA). According to this research, people diagnosed with any type of tumor, who had a high adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in the year preceding their enrollment into the study, live longer and have a reduced risk of cardiovascular mortality, ...
The International Biogeography Society relaunches flagship journal Frontiers of Biogeography on Pensoft’s ARPHA platform
2024-07-02
The International Biogeography Society (TIBS) has relaunched its flagship open-access scientific journal, Frontiers of Biogeography (FoB), on the ARPHA platform, where it will be co-published with Pensoft Publishers.
This collaboration underscores the society’s commitment to maintaining high-quality, high-visibility and low-cost open-access publishing for the biogeographical community.
"This switch of our journal to a cutting-edge platform, and its committed team of editors, should continue to raise the journal's ...
Binghamton University marks official launch of federally funded battery initiative
2024-07-02
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- National Science Foundation (NSF) officials joined Binghamton University, State University of New York to officially launch the Upstate New York Energy Storage Engine. After winning the designation earlier this year, Binghamton University and its New Energy New York and Engine coalition partners gathered to celebrate what this all means to the region.
At a press conference on Thursday, Binghamton University President Harvey Stenger welcomed NSF Assistant Director of the Technology, Innovation and Partnerships (TIP) Directorate Erwin Gianchandani to Binghamton to help launch the Engine program.
Erwin ...
Women of color disproportionately targeted by book bans, study finds
2024-07-02
In 2023, the American Library Association documented hundreds of attempts to remove more than 4,000 books from schools and libraries across nearly all states in the U.S.
In one of the first comprehensive analyses of book bans in the U.S., a University of Colorado Boulder researcher and her collaborators revealed that these bans disproportionally target women authors of color, and a large portion of the banned books feature characters of color.
The findings appeared June 11 in the journal ...
The American Society for Nutrition announces Orlando, Florida as the location for its annual flagship meeting, NUTRITION 2025
2024-07-02
The American Society for Nutrition (ASN) has announced that next year’s meeting is scheduled to be held May 31 – June 3, 2025, in Orlando, Florida. NUTRITION is the premier meeting for the nutrition community, exploring developments in clinical and translational nutrition, food science and systems, diet and disease, basic science, global health and more. In its seventh year, the event has continued to evolve and grow with innovative scientific sessions and networking opportunities for scientists, clinicians and healthcare professionals interested in ...
Serendipity reveals new method to fight cancer with T cells
2024-07-02
MADISON — A promising therapy that treats blood cancers by harnessing the power of the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells could now treat solid tumors more efficiently. Thanks to a recent study published in Molecular Therapy – Methods & Clinical Development from Dan Cappabianca and Krishanu Saha at the Wisconsin Institute for Discovery, Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy can be improved by altering the conditions the T cells are grown in. And it was all discovered by chance.
...
Financial incentives double smoking cessation rate for people with socioeconomic challenges
2024-07-02
OKLAHOMA CITY, OKLA. – A study published today by a University of Oklahoma researcher shows that financial incentives can make a big difference in helping smokers quit. The study found that when people with low socioeconomic staus are offered small financial incentives to stop smoking (in addition to receiving counseling and pharmacotherapy, primarily nicotine replacement therapy), they achieve higher quit rates, with some measures doubling the quit rates, when compared to study participants who received the same treatments without incentives. This finding is particularly important because adults with socioeconomic challanges ...
Biomolecular condensate ‘molecular putty’ properties found encoded in protein sequence
2024-07-02
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – July 2, 2024) Biomolecular condensates are membraneless hubs of condensed proteins and nucleic acids within cells, which researchers are realizing are tied to an increasing number of cellular processes and diseases. Studies of biomolecular condensate formation have uncovered layers of complexity, including their ability to behave like a viscoelastic material. However, the molecular basis for this putty-like property was unknown. Through a multi-institution collaboration, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists examined the interaction networks within condensates ...