(Press-News.org) Mohammad Moshahid Khan, PhD, principal investigator and associate professor in the Department of Neurology in the College of Medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, was recently awarded a $308,000 grant from the Department of Defense for a study that will investigate the role of the gut microbiome in dystonia, a movement disorder of abnormal postures and involuntary twisting or repetitive movements, to improve neurobehavioral outcomes. Jianfeng Xiao, MD, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Neurology, is the co-investigator of the study.
Although the genetic and environmental causes of dystonia are difficult to determine, dystonia can be developed by factors including traumatic brain injuries, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, use of chronic antipsychotic therapy, and other conditions. The disorder impacts many Americans, and military personnel and veterans often develop dystonia.
Considering gut microbiomes can influence brain behavior and development, and microbiomes can be modified, this study seeks to give a new perspective into the cause of the disease and discover how the gut microbiome may be able to modulate neurobehavioral dysfunction.
“There is no cure for dystonia. Some treatments are available, but they have a lot of side effects. We need to develop disease-modifying therapies that would stop the progression of dystonia symptoms, treat it, or delay the disease’s progression,” Dr. Khan said. “Most of the dystonia research focuses on the genetic and neurological aspects, and we thought there may be another factor that is non-genetic and can be modified, and that’s how we came up with the gut microbiome.”
To conduct this study, the team will examine the gut microbiome in a rodent model of dystonia by identifying specific bacteria or fungi that causes gastrointestinal abnormalities in the model and test the potential use of probiotics in decreasing behavioral deficits. The team aims to find the effectiveness of probiotics in treating neurobehavioral dysfunction in the rodent, in hopes this will lead to developing microbiome-based therapies for humans.
“The major goal is to develop a microbiome-based therapy for the treatment and prevention of dystonia. The mouse model we are using has a mutation that is clinically relevant to a human with dystonia,” Dr. Khan said. “The study opens up an entirely new direction on dystonia research and will provide a significant positive impact by defining the role of gut microbiome in the dystonia pathobiology and testing the impact of the microbiome approach in mitigating the neurobehavioral function in the dystonia.”
END
Researchers awarded Department of Defense grant to study the role of gut microbiomes to improve outcomes in dystonia
2024-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advancing toward a preventative HIV vaccine
2024-07-02
LA JOLLA, CA and NEW YORK, NY—A major challenge in developing a vaccine for HIV is that the virus mutates fast—very fast. Although a person initially becomes infected with one or a few HIV strains, the virus replicates and mutates quickly, resulting in a “swarm” of viral strains existing in a single body. But scientists at Scripps Research; IAVI; the Ragon Institute of Mass General, MIT, and Harvard; La Jolla Institute for Immunology; and additional institutions have conducted a series of preclinical ...
A Global Heat Early Warning system is now essential, and requires planning in four key areas to overcome barriers and enable successful implementation, per new review
2024-07-02
A Global Heat Early Warning system is now essential, and requires planning in four key areas to overcome barriers and enable successful implementation, per new review.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000437
Article Title: Preventing heat-related deaths: The urgent need for a global early warning system for heat
Author Countries: Austria, Denmark, Sweden, Switzerland, US
Funding: CB,IMO, CG and JT are funded by Horizon Europe through the HIGH horizon project funded by the European Union’s Horizon Europe Programme (grant number 101057843). IMO and CG are also ...
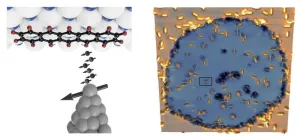
An alternative way to manipulate quantum states
2024-07-02
Electrons have an intrinsic angular momentum, the so-called spin, which means that they can align themselves along a magnetic field, much like a compass needle. In addition to the electric charge of electrons, which determines their behaviour in electronic circuits, their spin is increasingly used for storing and processing data. Already now, one can buy MRAM memory elements (magnetic random access memories), in which information is stored in very small but still classical magnets – that is, ...
Study reveals new factor associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 in people with obesity
2024-07-02
Already at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, a group of Brazilian researchers pioneered in showing why SARS-CoV-2 infection tends to be more severe in diabetic patients. Now, the same team based at the Institute of Biology of the State University of Campinas (IB-UNICAMP) has discovered one of the reasons why obese people who do not have diabetes or even insulin resistance also have an increased risk of developing the severe form of the disease.
“New experiments show that the molecular mechanisms are quite different in the two cases,” Pedro Moraes-Vieira, a professor at IB-UNICAMP, who is coordinating ...
Study finds that influential people can play a valuable role in getting people to act in the best interest of society
2024-07-02
Getting individuals to act in the best interest of society can be a tricky balancing act, one that often walks a fine line between trying to convince people to act of their own volition, versus passing laws and regulations that make these actions compulsory.
In a new paper, published in the journal PNAS Nexus, SFI External Professor Stefani Crabtree (Utah State University) and Science Board Fellow Simon Levin (Princeton University), together with Colin Wren (University of Colorado, Colorado Springs) and Avinash ...
Editorial: Genomics has more to reveal
2024-07-02
“If there was any doubt, this discovery demonstrates that genomics, extensively deployed over the past two decades, still has much to reveal to us.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 2, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “Genomics has more to reveal.”
In this new editorial, researchers Laurène Fenwarth and Nicolas Duployez from the University of Lille and CHU Lille discuss molecular and cytogenetic analyses that are now used to identify mutations and structural variants defining distinct subtypes of acute myeloid leukemias (AML) ...
COVID-19 pandemic tied to low birth weight for infants in India, study shows
2024-07-02
The incidence of low birth weight rose sharply in India amid the COVID-19 pandemic, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
Globally, 1 in 4 newborns has a low birth weight (less than 5.5 pounds), and the problem disproportionately affects low- and middle-income countries — particularly in South Asia, home to approximately one-fourth of the world’s population.
Santosh Kumar, associate professor of development and global health economics at Notre Dame’s Keough School of Global Affairs, co-authored the study published in Communications Medicine, a Nature series journal.
“This research shows that low birth weight became more common in India ...
Welch Foundation supports UTA’s drug delivery innovations
2024-07-02
With a $300,000 grant, the Welch Foundation is supporting University of Texas at Arlington research into creating new materials to safely and effectively deliver medications to treat diseases such as cancer.
Since its founding in 1954, the Houston-based Welch Foundation has contributed over $1.1 billion to the advancement of chemistry through research grants, departmental programs, endowed chairs and other special projects in Texas.
“As one of the nation’s largest private funding sources for chemical research, we are committed to supporting the field in a way that advances science while ...
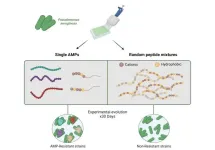
Treatment with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides can impede antibiotic resistance
2024-07-02
A common infection-causing bacteria was much less likely to evolve antibiotic resistance when treated with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides rather than a single peptide, making these mixtures a viable strategy for developing new antibiotic treatments. Jens Rolff of the Freie Universitat Berlin, Germany, and colleagues report these findings in a new study publishing July 2nd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria have become a major threat to public health. The World Health Organization estimates ...
The Mediterranean Diet is linked to lower risk of mortality in cancer survivors
2024-07-02
The Mediterranean Diet is a powerful ally for health even after a cancer diagnosis. This is the key result of an Italian study carried out as part of the UMBERTO Project, conducted by the Joint Research Platform Umberto Veronesi Foundation - Department of Epidemiology and Prevention of the I.R.C.C.S. Neuromed of Pozzilli, in collaboration with the LUM "Giuseppe Degennaro" University of Casamassima (BA). According to this research, people diagnosed with any type of tumor, who had a high adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in the year preceding their enrollment into the study, live longer and have a reduced risk of cardiovascular mortality, ...